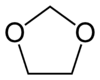
Dioxolane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dioxolane | |||
| Other names
1,3-dioxolane, formal glycol[2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 646-06-0 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:87597 | ||
| ChemSpider | 12066 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.422 | ||
| PubChem | 12586 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 74.08 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.06 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −95 °C (−139 °F; 178 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-Dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.
Dioxolanes as a class of compounds
Dioxolanes are a group of organic compounds containing the dioxolane ring. Dioxolanes can be prepared by acetalization of aldehydes and ketalization of ketones with ethylene glycol.[3]

(+)-cis-Dioxolane is the trivial name for L-(+)-cis-2-methyl-4-trimethylammoniummethyl-1,3-dioxolane iodide which is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist.
See also
References
- ↑ 1,3-Dioxolane at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ formal glycol - PubChem Public Chemical Database
- ↑ R. A. Daignault, E. L. Eliel (1973). "2-Cyclohexyloxyethanol (involves acetalisation of cyclohexanone)". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 5, p. 303
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.