2005 WY55
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovery date | November 26, 2005 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 2005 WY55 |
Apollo 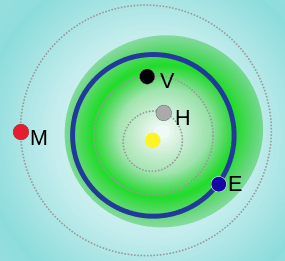 NEO, PHA | |
| Orbital characteristics[2][3] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 1451 days (3.97 yr) |
| Aphelion | 4.2823 AU (640.62 Gm) (Q) |
| Perihelion | 0.69532 AU (104.018 Gm) (q) |
| 2.4888 AU (372.32 Gm) (a) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.72062 (e) |
| 3.93 yr (1434.1 d) | |
| 188.701° (M) | |
| 0° 15m 3.708s /day (n) | |
| Inclination | 7.27198° (i) |
| 248.22° (Ω) | |
| 286.15° (ω) | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00387045 AU (579,011 km) |
| Jupiter MOID | 0.953735 AU (142.6767 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 190-250 meters[1][3] |
| 20.7[2] | |
|
| |
2005 WY55 is a near-Earth Asteroid belonging to the Apollo family.[3] It was first discovered on November 26, 2005.[1] The asteroid will pass within 330,000 km (0.9 lunar distances) from the Earth on May 28, 2065.[4][5] It has an absolute magnitude (H) of 20.68.[2] It is estimated to be 190 to 250 meters in diameter.[1][3] It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on July 1, 2006.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "CRT 2005 Object Archive". Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- 1 2 3 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 30 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "Asteroid General Data - 2005 WY55". Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ↑ "Sormano Astronomical Observatory: Table of Asteroids Next Closest Approaches to the Earth". Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ↑ "Near Earth Asteroids (NEAs)". 2011-11-10. Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ↑ "Date/Time Removed". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. Retrieved 2012-03-19.
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java) / Horizons Ephemeris
- 2005 WY55 at the JPL Small-Body Database
| Preceded by 2012 UE34 |
Large NEO Earth close approach (inside the orbit of the Moon) 28 May 2065 |
Succeeded by 2011 WL2 |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.