Italian Air Force
| Italian Air Force Aeronautica Militare | |
|---|---|
|
Coat of Arms of the Italian Air Force | |
| Founded | 28 March 1923 as Regia Aeronautica |
| Country |
|
| Size |
43,000 personnel 545 aircraft |
| Part of |
|
| Motto(s) |
Latin: Virtute Siderum Tenus (English: With valor to the stars) |
| March | Marcia di Ordinanza dell'Aeronautica Militare (Ordinance March of the Air Force) by Alberto Di Miniello |
| Anniversaries | 28 March (Air Force Day) |
| Decorations |
1 Cavalier Cross of the Military Order of Savoy 3 Cavalier Crosses of the Military Order of Italy 2 Gold Medals of Military Valor 1 Gold Medal of Aviation Valor 5 Silver Medals of Military Valor 2 Silver Medals of Civil Valor 1 War Cross of Military Valor 1 Silver Medal of Merit of the Italian Red Cross 1 Gold Medal of Benemerited Public Honor 1 Gold Medal of Merit for Public Health |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of Staff of Military Aviation | Lieutenant General Enzo Vecciarelli |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel |
 |
The Italian Air Force (Italian: Aeronautica Militare; AM) is the aerial defence force of the Italian Republic. The Air Force was founded as an independent service arm on March 28, 1923, by King Victor Emmanuel III as the Regia Aeronautica (which equates to "Royal Air Force"). After World War II, when Italy was made a republic by referendum, the Regia Aeronautica was given its current name. Since its formation the service has held a prominent role in modern Italian military history. The aerobatic display team is the Frecce Tricolori.
History
Early history and World War I
Among the earlier adopters of military aviation, Italy's air arm dates back to 1884, when the Italian Royal Army (Regio Esercito) was authorised to acquire its own air component. The Air Service (Corpo Aeronautico Militare) operated balloons based near Rome.

In 1911, reconnaissance and bombing sorties during the Italo-Turkish War by the Servizio Aeronautico represented the first ever use of heavier than air aircraft in armed conflict.
The Regia Aeronautica and World War II
On 28 March 1923, the Italian air force was founded as an independent service by King Vittorio Emanuele III of the Kingdom of Italy (Regno d'Italia). This air force was known as the Regia Aeronautica (Royal Air Force). During the 1930s, the fledgeling Regia Aeronautica was involved in its first military operations, first in Ethiopia in 1935, and later in the Spanish Civil War between 1936 and 1939. After a period of neutrality, Italy entered World War II on 10 June 1940 alongside Germany. The Regia Aeronautica could deploy more than 3,000 aircraft, although less than 60% were serviceable. The Regia Aeronautica fought from the icy steppes of Russia to the sand of the North African desert losing men and machines.
After the armistice of 8 September 1943, Italy was divided into two sides, and the same fate befell the Regia Aeronautica. The Air Force was split into the Italian Co-Belligerent Air Force in the south aligned with the Allies, and the pro-Axis Aeronautica Nazionale Repubblicana in the north until the end of the war. The end of the hostilities, on 8 May 1945, opened the gates to the rebirth of military aviation in Italy.
The birth of the Aeronautica Militare and the Cold War

A popular vote by the people resulted in the end of the Kingdom of Italy and the establishment of the Italian Republic on 18 June 1946. Hence the Regia Aeronautica lost its "Royal" designation, and it became the Aeronautica Militare, a name that it has continued to hold ever since.
The Peace Treaty of Paris of 1947 placed severe restrictions on all of the Italian armed forces, but then the establishment of NATO in 1949 with Italy as a founding member brought about the necessity for the modernization of all of the Italian armed forces, including the Italian Air Force. American military aid sent by the Mutual Defense Assistance Program brought about the introduction of American-made P-47 Thunderbolt and P-51 Mustang propeller-driven fighter planes. Then in 1952, the Italian Air Force was granted jet fighters for the first time, American F-84G Thunderjets and F-86D Sabre jets. Next F-84F jet fighters and C-119 Flying Boxcar transport planes were sent from the United States to the Italian Air Force. The reborn Italian aviation industry also began to develop and produce a few ingenious aircraft designs of its own, such as the Fiat G91, the Aermacchi MB-326, the Piaggio Aero P.166, and the line of Agusta-Bell helicopters.
The first supersonic fighters to serve in the Italian Air Force were American-designed F-104 Starfighters that were produced by a group of several European aircraft companies that included Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, Dornier, Fiat, Fokker, and SABCA. During the 1970s, the Air Force acquired the Italian Aeritalia G222 and the modern American C-130 Hercules tactical transport planes, capable of carrying cargo or paratroopers. It also received the new Lockheed-Aeritalia F-104S Starfighter fighters for ground attack and air-defense purposes.


A push to expand the Italian aircraft industry led Italy into the trilateral project that developed the Panavia Tornado fighter-bomber and air-defense fighters along with West Germany and the United Kingdom. This was a huge development and production project. Tornado fighters are still in service with all three countries, plus a few more, as of 2012. Also, Italian companies worked together with the Embraer Company of Brazil in the smaller project of developing and producing the AMX International AMX aircraft.
From the end of the Cold War to 2013
In 1990, after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, Italy joined the coalition forces, and for the first time in 45 years Italian pilots and aircraft were assigned to combat operations. With the need to replace the obsolescent F-104 Starfighters, Italy joined with Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom in the development of the Eurofighter Typhoon. With the Eurofighter Typhoon still some years from introduction to service, in 1994, 24 Air Defence Versions of the Panavia Tornado were leased from the United Kingdom for a period of 10 years. The ADV Tornados served as fighter-interceptors to supplement and then to replace the old F-104 Starfighters. The last of the Italian F-104s was removed from service in 2004.
Armed conflicts in Somalia and Mozambique, and on the nearby Balkan Peninsula, led to the Italian Air Force becoming a participant in multinational air forces, such as the NATO force over the former Yugoslavia. This latter one occurred just a few minutes flying time east of the Italian peninsula, and the commanders-in-chief of the Italian Air Force soon saw the need to improve the Italian air defenses.
The Eurofighter Typhoons were originally expected to enter service beginning in the year 2000, but this did not happen on time. Hence the Italian Air Force needed to search for a supplement, and then a replacement for the Panavia Tornado Air Defence Version fighters that the Italian government had leased from the United Kingdom. This lease was expiring in 2004, and the Italian government did not want to take on the high expense of extending the lease. Hence the Italian government turned to the United States, and it leased from the Americans 34 F-16 Fighting Falcon multirole fighter planes for the Italian Air Force on multi-year leases. The last of these fighters was returned to the United States in May 2012, following the Air Force's acquisition of a sufficient number of Eurofighter Typhoons over a period of several years. These Typhoons will serve at first in the mission of air-defense fighters after finally having replaced all of the F-104s, all of the Tornado ADVs, and all of the F-16s.
The capability of the Italian Air Force in air transportation has been improved with the acquisition of 22 American C-130J tactical transports, and 12 Alenia C-27J Spartans, which have replaced all of the G222s. In 2003, the Italian Air Force extended its capabilities to small-scale land warfare by small special forces units. This was done by forming the 17º Stormo Incursori ("17th Special Operations Wing"), also known as RIAM, Reparto Incursori Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Raiders Group). This is a unit that is aimed primarily towards missions such as raids on land-based aeronautical compounds, on Forward Air Control units, and in Combat Search and Rescue operations.[1]
Equipment
As of 2014, the Italian Air Force[2] operates a total active fleet of 557 aerial vehicles,[3] of which 209 are manned combat aircraft and 12 Unmanned combat aerial vehicle. In addition there are 14 more Eurofighter Typhoon on order and 75 F-35 planned for the Italian Air force. These figures have been taken from Flightglobal.com[4][5] and the International Institute for Strategic Studies.[6][7][8]
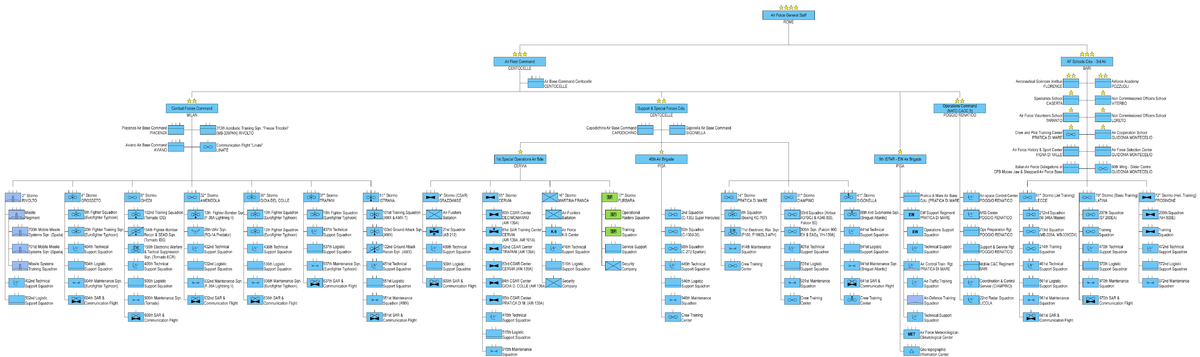
Organisation and formations
Major Commands
- Stato Maggiore Aeronautica Militare (Air Force General Staff) in Rome[9]
- Comando della Squadra Aerea (Air Fleet Command) in Rome
- Comando logistico dell'Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Logistic Command) in Rome
- Comando 1 Regione Aerea (1st (North Italy) Air Region Command) in Milan
- Comando delle Scuole Aeronautica Militare - 3ª Regione Aerea (Air Force Schools Command - 3rd (South Italy) Air Region) in Bari
Air Fleet Command
The Air Fleet Command (Comando della Squadra Aerea or CSA) controls all operative units, the intelligence and electronic warfare capabilities, and the operational headquarter of the air force. The CSA ensures that unit is equipped, trained and prepared for combat duty and controls them during combat operations.
- Air Fleet Command in Rome
- Comando Operazioni Aeree (Air Operations Command) in Poggio Renatico
- Comando delle Forze da Combattimento (Combat Forces Command) in Milan
- Comando delle Forze di Supporto e Speciali (Support and Special Forces Command) in Rome
- 9th Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance - Electronic Warfare (I.S.T.A.R.-E.W.) Air Brigade at Pratica di Mare Air Base
Air Operations Command
The Comando Operativo delle Forze Aeree (Air Operations Command or COFA) conducts all operations of the Aeronautica Militare. The COFA controls all military radar installations in Italy and its Gruppo Riporto e Controllo Difesa Aerea coordinates the control of and if necessary the defence of the Italian Air-space. If needed the COFA can directly employ and command all units of the Air Fleet Command.
- Comando Operativo Delle Forze Aeree (Air Operations Command) in Poggio Renatico
- Italian Air Operations Center (ITA-AOC) in Poggio Renatico
- Reparto Preparazione alle Operazioni (Operations Preparation Regiment - RPO) in Poggio Renatico
- Air Control Centre, Recognised Air Picture Production Centre and Sensor Fusion Post (ARS) in Poggio Renatico
- Reparto Supporto e Servizi Generali (Main Support and Service Regiment) in Poggio Renatico
- Reparto Mobile di Comando e Controllo (Mobile Command and Control Regiment) at Bari Air Base (Air-transpotable command and control post)
- Servizio di Coordinamento e Controllo dell'AM (Air Force Coordination and Control Service - S.C.C.AM) at Ciampino (Air traffic management)
- S.C.C.AM Abano Terme
- S.C.C.AM Linate Air Base
- S.C.C.AM Brindisi
- 22º Gruppo Radar (22nd Radar Squadron) in Licola
- 112ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Mortara
- 113ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Lame di Concordia
- 114ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Potenza Picena
- 115ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Capomele
- 121ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Poggio Ballone
- 123ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Capofrasca
- 131ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Jacotenente
- 132ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Crotone
- 133ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in San Giovanni Teatino
- 134ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Lampedusa
- 135ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Marsala
- 136ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Otranto
- 137ª Squadriglia Radar Remota (Radar Station) in Mezzogregorio
- Italian Delegation at NATO's Analysis and Simulation Centre for Air Operations (CASPOA) in Limonest, France
- Italian Delegation at NATO's European Air Transport Command (EATC) in Eindhoven, Netherlands
Combat Forces Command
- Combat Forces Command (Comando delle Forze da Combattimento) in Milan
- Comando Aeroporto Piacenza (Piacenza Air Base Command)
- Comando Aeroporto Aviano (Aviano Air Base Command)
-
 313º Gruppo Addestramento Acrobatico (313th Acrobatic Training Squadron – Frecce Tricolori) operating 20 × MB-339PAN at Rivolto Air Base
313º Gruppo Addestramento Acrobatico (313th Acrobatic Training Squadron – Frecce Tricolori) operating 20 × MB-339PAN at Rivolto Air Base - Squadriglia Collegamenti Linate (Communication Flight Linate) at Linate Air Base
-
 2º Stormo Mario d'Agostini (2nd Wing) at Rivolto Air Base
2º Stormo Mario d'Agostini (2nd Wing) at Rivolto Air Base
- Missile Regiment (Reparto Missili)
- 700º Gruppo Mobile Sistemi Missilistici (700th Mobile Missile Systems Squadron) operating Spada Air-defence system
- 701º Gruppo Mobile Sistemi Missilistici (701st Mobile Missile Systems Squadron) operating Spada Air-defence system
- Gruppo Addestramento Sistemi Missilistici (Missile Systems Training Squadron)
- 402º Gruppo STO (402nd Technical Support Squadron)
- 502º Gruppo SLO (502nd Logistic Support Squadron)
- Missile Regiment (Reparto Missili)
-
 4º Stormo Amedeo d'Aosta (4th Wing) at Grosseto Air Base
4º Stormo Amedeo d'Aosta (4th Wing) at Grosseto Air Base
- 9º Gruppo ADX (9th Fighter Squadron) operating Eurofighter Typhoon
- 20º Gruppo OCU ADX (20th Fighter Training Squadron) operating Eurofighter Typhoon (Twin-seat variant)
- 404º Gruppo STO (404th Technical Support Squadron)
- 504º Gruppo SLO (504th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 904º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (904th Eurofighter Typhoon Maintenance Squadron)
- 604ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (604th SAR and Communication Flight)
-
 6º Stormo Alfredo Fusco (6th Wing) at Ghedi Air Base
6º Stormo Alfredo Fusco (6th Wing) at Ghedi Air Base
- 102º Gruppo OCU (102nd Training Squadron) operating Tornado IDS
- 154º Gruppo FBX-STRIKE-RECCE (154th Fighter-Bomber Reconnaissance & SEAD Squadron) operating Tornado IDS
- 155º Gruppo ETS (155th Electronic Warfare and Tactical Suppression Squadron) operating 16 × Tornado ECR
- 406º Gruppo STO (406th Technical Support Squadron)
- 506º Gruppo SLO (506th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 906º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (904th Tornado Maintenance Squadron)
- 606ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (606th|SAR and Communication Flight)
-
 32º Stormo Armando Boetto (32nd Wing) at Amendola Air Base
32º Stormo Armando Boetto (32nd Wing) at Amendola Air Base
- 13º Gruppo FBA (13th Fighter-Bomber Squadron) operating F-35A Lightning II
- 28º Gruppo UAV (28th Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Squadron) operating 5 × RQ-1A Predator
- 432º Gruppo STO (432nd Technical Support Squadron)
- 532º Gruppo SLO (532nd Logistic Support Squadron)
- 932º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (932nd (F-35A Lightning II) Maintenance Squadron)
- 632ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (632nd SAR and Communication Flight)
-
 36º Stormo Riccardo Helmut Seidl (36th Wing) at Gioia del Colle Air Base
36º Stormo Riccardo Helmut Seidl (36th Wing) at Gioia del Colle Air Base
- 10º Gruppo ADX (10th Fighter Squadron) operating Eurofighter Typhoon
- 12º Gruppo ADX (12th Fighter Squadron) operating Eurofighter Typhoon
- 436º Gruppo STO (436th Technical Support Squadron)
- 536º Gruppo SLO (536th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 936º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (936th Maintenance Squadron)
- 636ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (636th SAR and Communication Flight)
-
 37º Stormo Cesare Toschi (37th Wing) at Trapani Air Base
37º Stormo Cesare Toschi (37th Wing) at Trapani Air Base
- 18º Gruppo ADX (18th Fighter Squadron) Eurofighter Typhoon
- 437º Gruppo STO (437th Technical Support Squadron)
- 537º Gruppo SLO (537th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 937º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (937th Maintenance Squadron)
- 637ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (637th SAR and Communication Flight)
-
 51º Stormo Ferruccio Serafini (51st Wing) at Istrana Air Base
51º Stormo Ferruccio Serafini (51st Wing) at Istrana Air Base
- 101º Gruppo OCU (101st Training Squadron - were disbanded) operating 11× AMX-T
- 132º Gruppo FBA/RECCE (132nd Ground Attack Reconnaissance Squadron) operating 35 x AMX
- 451º Gruppo STO (451st Technical Support Squadron)
- 551º Gruppo SLO (551st Logistic Support Squadron)
- 951º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (951st Maintenance Squadron)
- 651ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (651st SAR and Communication Flight)
Support and Special Forces Command
- Support and Special Forces Command (Comando delle Forze di Supporto e Speciali) in Centocelle
- Comando Aeroporto Sigonella (Sigonella Air Base Command)
- Comando Aeroporto Capodichino (Capodichino Air Base Command), supporting Naval Support Activity Naples home of the United States Sixth Fleet
- 5° Gruppo Manutenzione Velivoli (5th Aircraft Maintenance Squadron)
- Rappresentanza dell’Aeronautica Militare (Aeronautica Delegation) at the NATO Air Base Geilenkirchen in Germany at NATO's airborne early warning and control wing
-
 1ª Brigata Aerea Operazioni Speciali Vezio Mezzetti (1st Special Operations Air Brigade) at Cervia Air Base
1ª Brigata Aerea Operazioni Speciali Vezio Mezzetti (1st Special Operations Air Brigade) at Cervia Air Base
-
 9º Stormo Francesco Baracca (9th CSAR Wing) at Grazzanise Air Base
9º Stormo Francesco Baracca (9th CSAR Wing) at Grazzanise Air Base
-
 15º Stormo Stefano Cagna (15th Wing) at Cervia Air Base[10]
15º Stormo Stefano Cagna (15th Wing) at Cervia Air Base[10]
- 80º Centro C/SAR (82nd Combat/Search and Rescue Center) at Decimomannu Air Base operating AgustaWestland 139A helicopters
- 81º Centro Addestramento SAR (81st Search and Rescue Training Center) at Cervia Air Base operating AgustaWestland 139A and AgustaWestland AW101A helicopters
- 82º Centro C/SAR (82nd Combat/Search and Rescue Center) at Trapani Air Base operating AgustaWestland 139A helicopters
- 83º Gruppo C/SAR (83rd Combat/Search and Rescue Center) at Cervia Air Base operating AgustaWesland 139A helicopters
- 84º Centro C/SAR (84th Combat/Search and Rescue Center) at Gioia del Colle Air Base operating AgustaWestland 139A helicopters
- 85º Centro C/SAR (85th Combat/Search and Rescue Center) at Pratica di Mare Air Base operating AW 139A helicopters
- 387ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (387th Communication Flight), at Grazzanise Air Base, operating AgustaWesland 101 helicopters
- 615ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (615th Communication Flight), at Cervia Air Base, operating NH 500 NE helicopters
- 672ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (672nd Communication Flight), in Salto di Quirra, operating AB-212 helicopters
- 415º Gruppo STO (415th Technical Support Squadron)
- 515º Gruppo SLO (515th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 915º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (915th Maintenance Squadron)
-
 16º Stormo (16th Force Protection Wing) at Martina Franca Air Base
16º Stormo (16th Force Protection Wing) at Martina Franca Air Base
- Battaglione Fucilieri dell'Aria (Air-Fusiliers Battalion)
- Air Force Canine Center
- 416º Gruppo STO (416th Technical Support Squadron)
- 516º Gruppo SLO (516th Logistic Support Squadron)
- Security Company (Compagnia Difesa)
- 17º Stormo (17th Special Forces Wing) in Cerveteri
- Operational Special Forces Squadron (Gruppo Operativo Incursori)
- Training Squadron (Gruppo Addestramento)
- Service Support Squadron (Gruppo Servizi di Supporto)
- Security Company (Compagnia Difesa)
-
-
 46ª Brigata Aerea Silvio Angelucci (46th Air Brigade) at Pisa Air Base
46ª Brigata Aerea Silvio Angelucci (46th Air Brigade) at Pisa Air Base
- 2º Gruppo (2nd Squadron) 11 × C-130J Super Hercules
- 50º Gruppo (50th Squadron) 10 × C-130J-30
- 98º Gruppo (98th Squadron) 12 × C-27J Spartan
- 446º Gruppo STO (446th Technical Support Squadron)
- 546º Gruppo SLO (546th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 946º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (946th Maintenance Squadron)
- Crew Training Center (Centro Addestramento Equipaggi)
-
 14º Stormo Sergio Sartoff (14th Wing) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
14º Stormo Sergio Sartoff (14th Wing) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- 8º Gruppo I Cavalieri (8th Squadron) operating 4 × Boeing KC-767
- 71º Gruppo I Persei (71st Electronic Warfare Squadron) operating P180 Avanti, P.166DL3 APH
- 914° Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (914th Maintenance Squadron )
- Centro Addestramento Equipaggi (Crew Training Center)
-
 31º Stormo Carmelo Raiti (31st Wing) at Rome Ciampino Airport
31º Stormo Carmelo Raiti (31st Wing) at Rome Ciampino Airport
- 93º Gruppo (93rd Squadron) operating 3 × Airbus A319CJ, 1 x Airbus A340-500, 2 × Falcon 50
- 306º Gruppo (306th Squadron) operating 2 × Falcon 900EX, 3 × Falcon 900EASy, 2 × AgustaWestland VH-139A
- 431º Gruppo STO (431st Technical Support Squadron)
- 531º Gruppo SLO (531st Logistic Support Squadron)
- 931º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (931st Maintenance Squadron)
- Centro Addestramento Equipaggi (Crew Training Center)
-
 41º Stormo Athos Ammannato (41st Wing) at Sigonella Air Base
41º Stormo Athos Ammannato (41st Wing) at Sigonella Air Base
- 88º Gruppo A/S (88th Anti Submarine Squadron) operating 12 × Breguet Atlantic, being replaced by ATR 72 ASW
- 441º Gruppo STO (441st Technical Support Squadron)
- 541º Gruppo SLO (541st Logistic Support Squadron)
- 941º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (941st (Breguet Atlantic) Maintenance Squadron)
- 641ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (641st SAR and Communication Flight)
- Centro Addestramento Equipaggi (Crew Training Center)
9th (I.S.T.A.R.-E.W.) Air Brigade
- 9th Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance - Electronic Warfare (I.S.T.A.R.-E.W.) Air Brigade at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Comando Aeroporto di Pratica di Mare (Pratica di Mare Air Base Command)
- Reparto Supporto Tecnico Operativo Guerra Elettronica (Electronic Warfare Technical-operational Support Regiment) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Gruppo Supporto Operativo (Operational Support Squadron)
- Gruppo Supporto Tecnico (Technical Support Squadron)
- Reparto Addestramento Controllo Spazio Aereo (Air-space Control Training Regiment) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Gruppo Addestramento Operativo Traffico Aereo (Air-traffic Training Squadron)
- Gruppo Addestramento Operativo Difesa Aerea (Air-defence Training Squadron)
- Gruppo Supporto Tecnico (Technical Support Squadron)
- Centro Informazioni Geotopografiche Aeronautiche (Air Force Geo-topographic Information Center) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Centro Nazionale Meteorologia e Climatologia Aeronautica (Air Force National Meteorological-Climatological Center) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Centro Operativo per la Meteorologia (Meteorological Center) in Rome
Air Force Logistic Command
The Air Force Logistic Command provides operational units with all the required necessary logistics, combat support and service support functions.
- Comando Logistico dell'Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Logistic Command) in Rome
- 1ª Divisione – Centro Sperimentale di Volo (1st Division – Test Flight Center) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- 2ª Divisione – Supporto Tecnico Operativo Aeromobili Armamento ed Avionica (2nd Division – Avionic and Armaments Support) in Rome
- 3ª Divisione – Supporto Tecnico Operativo Sistemi Comando e Controllo Telecomunicazioni e Telematica (3rd Division – IT Support) in Rome
- Servizio dei Supporti (Support Service) in Rome
- Servizio Infrastrutture (Infrastructure Service) in Rome
- Servizio di Commissariato e Amministrazione (Commissariat and Administration Service) in Rome
- Servizio Sanitario Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Medical Service) in Rome
- Poligono Sperimentale e di Addestramento Interforze di Salto di Quirra (Joint Test and Training Range Salto di Quirra)
1st Division – Test Flight Center
- 1ª Divisione – Centro Sperimentale di Volo (1st Division – Test Flight Center)
-
 Reparto Sperimentale Volo (Test Flight Department)
Reparto Sperimentale Volo (Test Flight Department)
- 311º Gruppo Volo (311th Flight Squadron)
- Gruppo Sistemi Spaziali (Space Systems Squadron)
- Gruppo Tecnico (Technical Squadron)
- Gruppo Gestione Software (Software Squadron)
- Reparto Chimico (Chemical Research Department)
- Gruppo Materiali Strutturali (Structural Materials Squadron)
- Gruppo Materiali di Consumo (Fuel Materials Squadron)
- Gruppo Controlli non Distruttivi (Control Squadron)
- Gruppo Analisi e prove Chimiche e Fisiche (Chemical and Physical Analysis and Experimentation Squadron)
- Reparto Armamento (Weapons Research Department)
- Gruppo Armamento Convenzionale (Conventional Weapons Squadron)
- Gruppo Indagini Balistiche (Ballistic Research Squadron)
- Gruppo Indagini Tecniche (Technical Research Squadron)
- Reparto Medicina Aeronautica e Spaziale (Air and Space Medicine Department)
- Gruppo Alta Quota ed Ambienti Estremi (High Altitude and Extreme Environments Squadron)
- Gruppo Biodinamica (Biodynamic Squadron)
- Gruppo Fattori umani (Human Factor Squadron)
-
2nd Division – Avionic and Armaments Support
- 2ª Divisione – Supporto Tecnico Operativo Aeromobili Armamento ed Avionica (2nd Division – Avionic and Armaments Support)
- 1º Reparto Supporto Aeromobili (1st Aircraft Support Unit) with 13 detachments at air bases
- 2º Reparto Supporto Sistemi Avionica Armamento (2nd Weapons Avionics Systems Support Unit)
- Centro Polifunzionale Velivoli Aerotattici di Cameri (Cameri Air-tactical Aircraft Center) in Novara
- Comando Aeroporto di Cameri (Cameri Air Base Command)
- Nucleo Iniziale di Formazione (NIF) JSF (Initial JSF/F-35 Formation Unit)
- 1º Reparto Manutenzione Velivoli (1st Aircraft Maintenance Unit) responsible for Tornado and Eurofighter Typhoon
- 1º Deposito Centrale
- 2º Deposito Centrale
- 3º Reparto Manutenzione Velivoli (3rd Aircraft Maintenance Unit) at Istrana Air Base responsible for AMX
- 6º Reparto Manutenzione Elicotteri (6th Helicopter Maintenance Unit) at Pratica di Mare Air Base responsible for helicopters
- 10º Reparto Manutenzione Velivoli (10th Aircraft Maintenance Unit) at Galatina Air Base responsible for Aermacchi MB-339
- 11º Reparto Manutenzione Velivoli (11th Aircraft Maintenance Unit) at Sigonella Air Base responsible for Breguet Atlantic
- 2º Reparto Manutenzione Missili (2nd Missile Maintenance Unit) at Padua Air Base responsible for air-launched and ground-launched missiles used by the air force
- Deposito centrale sistemi missilistici (Central Missile Depot)
- 5° Gruppo Manutenzione Velivoli (5th Aircraft Maintenance Squadron) at Capodichino Air Base
- Centro Logistico Polivalente (Multi-use Logistic Center) at Guidonia Air Base
- Centro Logistico Munizionamento e Armamento Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Ammunition and Weapons Logistic Center) in Orte
- Gruppo Rifornimento Area Nord (Supply Group Nord) in Sanguinetto
- Gruppo Rifornimento Area Sud (Supply Group South) in Francavilla Fontana
- 1° Servizio Tecnico Distaccato (1st Technical Service Detachment) at Caselle Air Base
- Aeronautica Delegation at the C-130J Program in Dayton, US
- Aeronautica Delegation at the International Eurofighter Support Team in Madrid, Spain
- Aeronautica Delegation at the International Weapon System Support Centre in Hallbergmoos, Germany
- Aeronautica Delegation at the IAFFT in Warton, UK
3rd Division – IT Support
- 3ª Divisione – Supporto Tecnico Operativo Sistemi Comando e Controllo Telecomunicazioni e Telematica (3rd Division – IT Support) provides operational support and maintenance for Command and Control, Signals and Radar systems
- 1º Reparto - Sistemi Difesa Aerea, Assistenza al Volo, Telecomunicazioni (1st Department - Air-defense, Flight Control, and Signal Systems)
- 2º Reparto - Sistemi Automatizzati (2nd Department - Automatic Systems) providing hardware and software support
- 4^ Brigata Telecomunicazioni e Sistemi per la Difesa Aerea e l’Assistenza al Volo (4th Signals and Air Defense Systems and Flight Support Brigade) at Latina Air Base
- 1° Reparto Tecnico Comunicazioni (1st Technical Communications Department) in Milan
- 2° Reparto Tecnico Comunicazioni (2nd Technical Communications Department) at Bari Air Base
- Reparto Gestione ed Innovazione Sistemi Comando e Controllo (Command and Control Systems Maintenance and Development Department) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Reparto Sistemi Informativi Automatizzati (Automatic Information Systems Department) in Acquasanta
Services
- Servizio dei Supporti (Support Service) in Rome
- 1° Reparto – Supporto Operativo (1st Department - Operational Support)
- 2° Reparto – Servizio Chimico-Fisico (2nd Department - Chemical-Physical Service)
- Servizio Infrastrutture (Infrastructure Service) in Rome
- 1° Reparto – Programmi (1st Department - Planning)
- 2° Reparto – Lavori (2nd Department - Construction)
- Servizio di Commissariato e Amministrazione (Commissariat and Administration Service) in Rome
- 1° Reparto – Commissariato (1st Department - Commissariat), provisioning, clothing, personal equipment department
- 2° Reparto – Amministrazione (2nd Department - Administration), human resources department
- Ufficio Gestione Risorse e Coordinamento Operativo (Ressources Management and Operational Coordination Office)
- Servizio Sanitario Aeronautica Militare (Aeronautica Militare Medical Service) in Rome
- Commissione Sanitaria di Appello (Medical Examination Commission) in Rome
- Istituto Perfezionamento Addestramento Medicina Aeronautica e Spaziale (Aeronautic and Spacial Medical Perfectioning Training Institut) in Rome
- Infermeria Principale (Main Pharmacy) at Pratica di Mare Air Base
- Istituto di Medicina Aerospaziale dell'A.M. di Milano (Air Force Medical Center Milan)
- Istituto di Medicina Aerospaziale dell'A.M. di Roma (Air Force Medical Center Rome)
1st Air Region
The 1st Air Region provides territorial functions and liaisons with communal, provincial and regional administrations in the North of Italy.
- 1ª Regione Aerea (1st Air Region) in Milan
- Airport Command / Headquarters- 1st Air Region at Linate Air Base
- Area Logistic Support Center / "Umberto Maddalena" High School in Cadimare
- Aeronautic Detachment in Capo Mele
- Airport Detachment in Toblach
Air Force Schools Command - 3rd Air Region
The Comando Scuole dell'Aeronautica Militare is responsible for the formation and training of all members of the Aeronautica Militare. It controls all schools and three training wings:
- Comando Scuole dell'Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Schools Command) in Bari
- Istituto di Scienze Militari Aeronautiche (Aeronautical Sciences Institute) in Florence
- Scuola Militare Aeronautica Giulio Douhet (Air Force High School) in Florence
- Accademia Aeronautica (Air Force Academy) in Pozzuoli
- Scuola Marescialli Aeronautica Militare (Non Commissioned Officers School) in Viterbo
- Scuola Specialisti Aeronautica Militare (Specialists School) in Caserta
- Scuola di Perfezionamento Sottufficiali Aeronautica Militare (Non Commissioned Officers School) in Loreto
- Scuola Lingue Estere (Foreign Languages School) in Loreto
- Scuola volontari di truppa Aeronautica militare (Air Force Volunteers School) in Taranto
- Scuola di Aerocooperazione (Air Cooperation School – an inter-service coordination & training center) in Guidonia Montecelio
- Centro di Selezione Aeronautica Militare (Air Force Selection Center) in Guidonia Montecelio
-
 60º Stormo - Centro di Volo a Vela (60th Wing - Glider Centre) in Guidonia Montecelio
60º Stormo - Centro di Volo a Vela (60th Wing - Glider Centre) in Guidonia Montecelio - Centro Storiografico e Sportivo Aeronautica Militare (Air Force History & Sport Center) in Vigna di Valle
- Centro Addestramento Equipaggi - Multi Crew (Crew and Pilot Training Center for other armed services, police forces, and other government agencies) at Pratica di Mare Air Base operating P.180 Avanti
- Rappresentanza Aeronautica Militare Italiana Moose Jaw (Italian Air Force Delegation Moose Jaw) at CFB Moose Jaw, Canada
- Rappresentanza Aeronautica Militare Italiana Sheppard (Italian Air Force Delegation Sheppard) at Sheppard Air Force Base, USA
-
 61º Stormo (61st (Jet Training) Wing) at Galatina Air Base
61º Stormo (61st (Jet Training) Wing) at Galatina Air Base
- 212º Gruppo Volo (212nd Squadron) operating M-346A Master
- 213º Gruppo Volo (213rd Squadron) operating MB-339A/MLU and MB-339CDII
- 214º Gruppo Volo (214th Squadron) training navigators and weapon officers on MB-339A/MLU and MB-339CDII
- 461º Gruppo STO (461st Technical Support Squadron)
- 561º Gruppo SLO (561st Logistic Support Squadron)
- 961º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (961st Maintenance Squadron)
- 661ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (661st Communication Flight)
-
 70º Stormo Giulio Cesare Graziani (70th (Basic Training) Wing) at Latina Air Base
70º Stormo Giulio Cesare Graziani (70th (Basic Training) Wing) at Latina Air Base
- 207º Gruppo (207th Squadron) operating SF.260EA
- Gruppo Istruzione Professionale (Training Squadron)
- 470º Gruppo STO (470th Technical Support Squadron)
- 570º Gruppo SLO (570th Logistic Support Squadron)
- 970º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (970th Maintenance Squadron)
- 670ª Squadriglia Collegamenti (674th Communication Flight)
-
 72º Stormo (72nd (Helicopter Training) Wing) at Frosinone Air Base
72º Stormo (72nd (Helicopter Training) Wing) at Frosinone Air Base
- 208º Gruppo (208th Squadron) operating NH-500E helicopters
- Gruppo Istruzione Professionale (Training Squadron)
- 472º Gruppo STO (472nd Technical Support Squadron)
- 572º Gruppo SLO (572nd Logistic Support Squadron)
- 972º Gruppo Efficienza Aeromobili (972nd Maintenance Squadron)
- Istituto di Scienze Militari Aeronautiche (Aeronautical Sciences Institute) in Florence
Air Force Structure Graphic
Chiefs of the Air force, rank structure
| Ufficiali generali – General officers | |||||
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| generale | |||||
| General | |||||
 |
 |
 | |||
| generale di squadra aerea | generale di divisione aerea | generale di brigata aerea | |||
| Lieutenant general | Major general, Divisional General | Brigadier general | |||
| Ufficiali superiori – Senior officers | |||||
 |
 |
 | |||
| colonnello | tenente colonnello | maggiore | |||
| Colonel | Lieutenant colonel | Major | |||
| Ufficiali inferiori – Junior officers | |||||
 |
|||||
| capitano | tenente | sottotenente | |||
| Captain | First Lieutenant, Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | |||
| Sottufficiali – Non-commissioned officers | |||||
 | |||||
| primo maresciallo luogotenente | |||||
| 1st Lieutenant marshall | |||||
| primo maresciallo | maresciallo di prima classe | maresciallo di seconda classe | maresciallo di terza classe | ||
| 1st marshall | 1st class marshall | 2nd class marshall | 3rd class marshall | ||
 |
 |
 | |||
| sergente maggiore capo | sergente maggiore | sergente | |||
| Chief sergeant major | Sergeant Major | Staff Sergeant | |||
| Truppa – Enlisted personnel | |||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No insignia |
| primo aviere capo | primo aviere scelto | aviere capo | primo aviere | aviere scelto | aviere |
| First chief Airman | First Senior airman | Chief Airman | Airman First Class | Senior Airman | Airman Basic |
| Name | Term start | Term end |
|---|---|---|
| Pier Ruggero Piccio | 1 January 1926 | 6 February 1927 |
| Armando Armani | 10 February 1927 | 13 October 1928 |
| Giuseppe Valle | 22 February 1930 | 23 November 1933 |
| Antonio Bosio | 23 November 1933 | 22 March 1934 |
| Giuseppe Valle | 22 March 1934 | 10 November 1939 |
| Francesco Pricolo | 10 November 1939 | 15 November 1941 |
| Rino Corso Fougier | 15 November 1941 | 27 July 1943 |
| Renato Sandalli | 27 July 1943 | 18 June 1944 |
| Pietro Piacentini | 19 June 1944 | 13 December 1944 |
| Mario Ajmone Cat | 13 December 1944 | 5 February 1951 |
| Aldo Urbani | 5 February 1951 | 10 November 1955 |
| Ferdinando Raffaelli | 10 November 1955 | 1 February 1958 |
| Silvio Napoli | 1 February 1958 | 1 September 1961 |
| Aldo Remondino | 1 September 1961 | 28 February 1968 |
| Duilio S. Fanali | 28 February 1968 | 1 November 1971 |
| Vincenzo Lucertini | 1 November 1971 | 27 February 1974 |
| Dino Ciarlo | 27 February 1974 | 20 June 1977 |
| Alessandro Mettimano | 20 June 1977 | 1 April 1980 |
| Lamberto Bartolucci | 2 April 1980 | 12 October 1983 |
| Basilio Cottone | 19 October 1983 | 17 September 1986 |
| Franco Pisano | 18 September 1986 | 15 April 1990 |
| Stelio Nardini | 16 April 1990 | 24 March 1993 |
| Adelchi Pillinini | 25 March 1993 | 3 June 1995 |
| Mario Arpino | 4 June 1995 | 5 February 1999 |
| Andrea Fornasiero | 5 February 1999 | 5 August 2001 |
| Sandro Ferracuti | 5 August 2001 | 4 August 2004 |
| Leonardo Tricarico | 5 August 2004 | 19 September 2006 |
| Vincenzo Camporini | 19 September 2006 | 30 January 2008 |
| Daniele Tei | 30 January 2008 | 25 February 2010 |
| Giuseppe Bernardis | 25 February 2010 | 25 February 2013 |
| Pasquale Preziosa | 25 February 2013 | 30 March 2016 |
| Enzo Vecciarelli | 30 March 2016 | ... |
See also
References
- ↑ Italy opens F-35 assembly line, as political opposition grows. Flightglobal.com (2013-07-18). Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ↑ Italian Air Force. The Aviationist. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ↑ .Schede Aeromobili Aeronautica Militare.
- ↑ World Air Forces 2014 December 10, 2013
- ↑ "World Air Forces 2013". Flightglobal.com, 11 December 2012.
- ↑ "The Military Balance 2013"., 14 March 2013.
- ↑ " Italy's ruling party divided over order for F-35 combat jets", 30 May 2013
- ↑ "Defence Statistics 2014" May 15, 2014
- ↑ "Air Force Organisation". Aeronautica Militare. Italian Air Force. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- ↑ "Il portale dell'Aeronautica Militare - Chiuso 5° Stormo, giunti HH-3F 15° Stormo". Retrieved 23 December 2014.
Sources
- International Institute for Strategic Studies; Hackett, James (ed.) (2010-02-03). The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge. ISBN 1-85743-557-5.
- Malizia, Nicola. F-47D "Thunderbolt" (Aviolibri Records n.6) (Bilingual Italian/English). Rome, Italy: IBN Editore, 2005. ISBN 88-7565-021-7.
- Mattioli, Marco. Lockheed P-38 Lightning in Italian Service, 1943–1955 (Aviolibri Records n.4) (Bilingual Italian/English). Rome, Italia: IBN Editore, 2004. ISBN 88-7565-010-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Air force of Italy. |
