Antonov An-225 Mriya
| An-225 Mriya | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The An-225 in current livery, 2012 | |
| Role | Strategic airlifter |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Design group | Antonov |
| Built by | Antonov Serial Production Plant |
| First flight | 21 December 1988 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Antonov Airlines |
| Produced | 1988 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Antonov An-124 |
The Antonov An-225 Mriya (Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-225 Мрія (dream or inspiration), NATO reporting name: "Cossack") is a strategic airlift cargo aircraft that was designed by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union in the 1980s. It is powered by six turbofan engines and is the longest and heaviest airplane ever built, with a maximum takeoff weight of 640 tonnes (710 short tons). It also has the largest wingspan of any aircraft in operational service. The single example built has the Ukrainian civil registration UR-82060. A second airframe was partially built; its completion was halted because of lack of funding and interest.
The Antonov An-225, initially developed for the task of transporting the Buran spaceplane, was an enlargement of the successful Antonov An-124. The first and only An-225 was completed in 1988. After successfully fulfilling its Soviet military missions, it was mothballed for eight years. It was then refurbished and re-introduced, and is in commercial operation with Antonov Airlines carrying oversized payloads.[1] The airlifter holds the absolute world records for an airlifted single-item payload of 189,980 kilograms (418,830 pounds),[2][3] and an airlifted total payload of 253,820 kg (559,580 lb).[4][5] It has also transported a payload of 247,000 kg (545,000 lb) on a commercial flight.[6]
Development
The Antonov An-225 was designed to airlift the Energia rocket's boosters and the Buran space shuttle for the Soviet space program. It was developed as a replacement for the Myasishchev VM-T. The An-225's original mission and objectives are almost identical to that of the United States' Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.[7][8]
.jpg)
The An-225 first flew on 21 December 1988 with a 74-minute flight from Kiev. The aircraft was on static display at the Paris Air Show in 1989 and it flew during the public days at the Farnborough air show in 1990. Two aircraft were ordered, but only one An-225 (registration CCCP-82060 later UR-82060[9]) was finished. It can carry ultra-heavy and oversize freight, up to 250,000 kg (550,000 lb) internally,[7] or 200,000 kg (440,000 lb) on the upper fuselage. Cargo on the upper fuselage can be 70 m (230 ft) long.[10]
A second An-225 was partially built during the late 1980s for the Soviet space program. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and the cancellation of the Buran space program, the lone operational An-225 was placed in storage in 1994.[11] The six Ivchenko-Progress engines were removed for use on An-124s, and the second uncompleted An-225 airframe was also stored. The first An-225 was later re-engined and put into service.[5][12]
By 2000, the need for additional An-225 capacity had become apparent, so the decision was made in September 2006 to complete the second An-225. The second airframe was scheduled for completion around 2008,[13] then delayed. By August 2009, the aircraft had not been completed and work had been abandoned.[1][14] In May 2011, the Antonov CEO is reported to have said that the completion of a second An-225 Mriya transport aircraft with a carrying capacity of 250 tons requires at least $300 million, but if the financing is provided, its completion could be achieved in three years.[15] According to different sources, the second jet is 60–70% complete.[16]
In April 2013, the Russian government announced plans to revive Soviet-era air launch projects that would use a purpose-built modification to the An-225 as a midair launchpad.[17]
In August 2016, representatives from Ukraine's Antonov and Aerospace Industry Corporation of China, an import-export company operating out of Hong Kong,[18] signed an agreement to recommence production of the An-225, with China now planning to procure and fly the first model by 2019.[19][20] The aviation media cast doubt on the production restart, indicating that due to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict needed parts from Russia are unavailable, although they may be made in China instead.[21]
Design

Based on Antonov's earlier An-124, the An-225 has fuselage barrel extensions added fore and aft of the wings. The wings also received root extensions to increase span. Two more Progress D-18T turbofan engines were added to the new wing roots, bringing the total to six. An increased-capacity landing gear system with 32 wheels was designed, some of which are steerable, enabling the aircraft to turn within a 60 m-wide (200 ft) runway. Like its An-124 predecessor, the An-225 has nose gear designed to kneel so cargo can be more easily loaded and unloaded.[5] Unlike the An-124, which has a rear cargo door and ramp, the An-225 design left these off to save weight, and the empennage design was changed from a single vertical stabilizer to a twin tail with an oversized horizontal stabilizer. The twin tail was essential to enable the plane to carry large, heavy external loads that would disturb the airflow around a conventional tail. Unlike the An-124, the An-225 was not intended for tactical airlifting and is not designed for short-field operation.[7]

Initially the An-225 had a maximum gross weight of 600 t (660 short tons), but from 2000 to 2001 the aircraft underwent modifications at a cost of US$20M such as the addition of a reinforced floor, which increased the maximum gross weight to 640 t (710 short tons).[22][23][24]
Both the earlier and later takeoff weights establish the An-225 as the world's heaviest aircraft, being heavier than the double-deck Airbus A380. It is surpassed in other size-related categories, however: Airbus claims to have improved upon the An-225's maximum landing weight by landing an A380 at 591.7 tonnes (1,304,000 lb) during tests,[25] and the Hughes H-4 Hercules, known as the "Spruce Goose", has a greater wingspan and a greater overall height. But the Spruce Goose is 20% shorter and overall lighter, due to the materials used in its construction. It only flew once, making the An-225 the largest aircraft in the world to fly multiple times.[5][26]
The An-225's pressurized cargo hold is 1,300 m3 (46,000 cu ft) in volume; 6.4 m (21 ft 0 in) wide, 4.4 m (14 ft) high, and 43.35 m (142 ft 3 in) long[5][27][28] — longer than the first flight of the Wright Flyer.[29][30][31]
Operational history

During the last years of the Soviet space program, the An-225 was employed as the prime method of transporting the Buran space shuttle.[26]
Antonov commercialization

In the late 1980s, the Soviet government was looking to generate revenue from its military assets. In 1989, the Antonov Design Bureau set up a holding company as a heavy airlift shipping corporation under the name "Antonov Airlines", based in Kiev, Ukraine and operating from London Luton Airport in partnership with the Air Foyle HeavyLift.[10][32]
The company began operations with a fleet of four An-124-100s and three Antonov An-12s, but a need for aircraft larger than the An-124 became apparent in the late 1990s. In response, the original An-225 was re-engined, modified for heavy cargo transport, and placed back in service under the management of Antonov Airlines.

On 23 May 2001, the An-225 received its type certificate from the Interstate Aviation Committee Aviation Register (IAC AR).[33] On 11 September 2001, carrying four main battle tanks[5] at a record load of 253.82 tonnes (279.79 short tons) of cargo,[4] the An-225 flew at an altitude of up to 10,750 m (35,270 ft)[34] over a closed circuit of 1,000 km (620 mi) at a speed of 763.2 km/h (474.2 mph).[35][36]
Regular commercial flights
The type's first flight in commercial service departed from Stuttgart, Germany on 3 January 2002, and flew to Thumrait, Oman with 216,000 prepared meals for American military personnel based in the region. This vast number of ready meals was transported on some 375 pallets and weighed 187.5 tons.[37]
The An-225 has since become the workhorse of the Antonov Airlines fleet, transporting objects once thought impossible to move by air, such as 150-tonne generators. It has become an asset to international relief organizations for its ability to quickly transport huge quantities of emergency supplies during disaster relief operations.[38]
The An-225 has been contracted by the Canadian and U.S. governments to transport military supplies to the Middle East in support of coalition forces.[38] An example of the cost of shipping cargo by An-225 was over 2 million DKK (approx. €266,000) for flying a chimney duct from Billund, Denmark to Kazakhstan in 2004.[39]

On 11 August 2009, the heaviest single cargo item ever sent via air freight was loaded onto the An-225. At 16.23 m (53.2 ft) long and 4.27 m (14.0 ft) wide, its consignment, a generator for a gas power plant in Armenia along with its loading frame, weighed in at a record 189 tonnes (417,000 lb).[2][3]
During 2009, the An-225 was painted in a new blue and yellow paint scheme,[40] after Antonov ceased cooperation with AirFoyle and partnered with Volga-Dnepr in 2006.[41]
On 11 June 2010, the An-225 carried the world's longest piece of air cargo, two 42.1 m (138 ft) test wind turbine blades from Tianjin, China to Skrydstrup, Denmark.[42][43]
Operators
- Antonov Airlines for Soviet Buran program; the company (and aircraft) passed to Ukraine after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Specifications (An-225 Mriya)
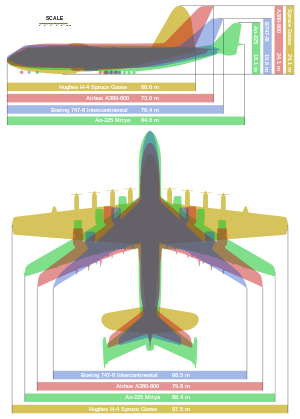

Data from Vectorsite,[7] Antonov's Heavy Transports,[44] and others[5][12][27][28]
General characteristics
- Crew: 6
- Length: 84 m (275 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 88.4 m (290 ft 0 in)
- Height: 18.1 m (59 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 905 m2 (9,740 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 8.6
- Empty weight: 285,000 kg (628,317 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 640,000 kg (1,410,958 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 300,000 kg
- Cargo hold – volume 1,300 m3 (46,000 cu ft), 43.35 m (142.2 ft) long × 6.4 m (21 ft) wide × 4.4 m (14 ft) tall
- Powerplant: 6 × ZMKB Progress D-18 turbofans, 229.5 kN (51,600 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 850 km/h (528 mph; 459 kn)
- Cruising speed: 800 km/h (497 mph; 432 kn)
- Range: 15,400 km (9,569 mi; 8,315 nmi) with maximum fuel; range with 200 tonnes payload: 4,000 km (2,500 mi)
- Service ceiling: 11,000 m (36,089 ft)
- Wing loading: 662.9 kg/m2 (135.8 lb/sq ft)
- Thrust/weight: 0.234
Notable appearances in media
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Airbus Beluga
- Boeing 747-8F
- Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft
- Boeing Dreamlifter (747 Large Cargo Freighter)
- Lockheed C-5 Galaxy
- Myasishchev VM-T
- Related lists
References
- 1 2 "World's largest aircraft, An-225, emerges to set new lift record". Flightglobal. Flight International. 17 August 2009. Archived from the original on 20 August 2009. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- 1 2 Cargo manifest picture Air Cargo News 13 November 2009. Retrieved: 30 May 2012.
- 1 2 Ukraine's An-225 aircraft sets new record for heaviest single cargo item transported by air Archived 30 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine., Eye for Transport, 18 August 2009.
- 1 2 "Payload record in the official FAI database". Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 An-225 (An-225-100) "Мрiя". Russian Aviation Museum, 20 October 2001. Retrieved: 31 October 2010.
- ↑ "An-225 sets new record for payload". Flightglobal. 29 June 2004. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Greg Goebel. "Antonov An-225 Mriya ("Cossack")". The Antonov Giants: An-22, An-124, & An-225. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- ↑ Greg Goebel. "The Soviet Buran shuttle program". Postscript: The Other Shuttles. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- ↑ "Aviation Photo #1154941: Antonov An-225 Mriya - Antonov Design Bureau". airliners.net. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- 1 2 "AN-225 Mriya / Super Heavy Transport". Antonov ASTC. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ↑ Antonov An-225 Mriya. Airliners.net.
- 1 2 "Antonov An-225 Mriya (Cossack) Heavy Lift Strategic Long-Range Transport" Military Factory, 23 August 2012. Retrieved: 6 September 2012.
- ↑ Antonov An-225 Mriya Aircraft History, Facts and Pictures. Aviationexplorer
- ↑ The Mriya 2: Pictures. Buran-energia.com
- ↑ webstudio, TAC. "Ukrainian Journal". ukrainianjournal.com. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ↑ "Ukraine may finish the construction of second An-225 Mriya transport aircraft – News – Russian Aviation". Ruaviation.Com. Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- ↑ Правительство задумалось о "Воздушном старте". Interfax (in Russian). April 23, 2013. Retrieved April 29, 2013.
- ↑ "A private company to run the world's largest transport aircraft production in China? The truth is...". Toutiao (in Chinese). 1 September 2016. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- ↑ Jennings, Gareth (31 August 2016). "China and Ukraine agree to restart An-225 production". IHS Jane's. London. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
- ↑ "ANTONOV Company signed Cooperation agreement on the AN−225 programme with AICC". ANTONOV Company. Kiev. 31 August 2016. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- ↑ Grady, Mary (14 September 2016). "World's Largest Airplane Back In Play". AVweb. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ↑ Forward, David C: "Antonov's Dream Machine", p. 23. Airways magazine, June 2004
- ↑ Spaeth, Andreas: "When size matters", p. 29. Air International magazine, December 2009
- ↑ Gordon, Yefim; Dmitriy and Sergey Komissarov: "The Six-Engined Dream", page 76. Antonov's Heavy Transports: The An-22, An-124/225 and An-70. Midland, 2004. ISBN 1-85780-182-2.
- ↑ Learmount, David (3 June 2009). "Airbus reveals A380-linked pilot systems secrets". London: Flightglobal. Retrieved 9 July 2009.
- 1 2 "Antonov An-225 Mryia (Cossack)". The Aviation Zone. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- 1 2 "AN-225 Mriya" GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved: 6 September 2012.
- 1 2 "Antonov An 225" Air Charter Service. Retrieved: 6 September 2012.
- ↑ "Exhibitions". si.edu. 28 April 2016. Retrieved 16 September 2016.
- ↑ "100 Years Ago, the Dream of Icarus Became Reality." Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine. FAI NEWS, December 17, 2003. Retrieved: January 5, 2007.
- ↑ Lindberg, Mark. "Century of Flight." Wings of History Museum, 2003. Retrieved: August 27, 2011.
- ↑ "An-225 Mriya, NATO: Cossack". Goleta Air & Space Museum. Retrieved 31 March 2004.
- ↑ "Type Certificates for Aircraft". Archived from the original on 30 April 2008. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ↑ "Height record with 250t payload in the FAI database".
- ↑ "Speed record with 250t payload over 1000km closed circuit in the official FAI database". Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- ↑ "Special planes: The Antonov-225 "Mriya"". European Tribune. 8 April 2006.
- ↑ "Antonov Airlines:An-225 Mriya". AirFoyle.
- 1 2 "Antonov An-225". Aircraft-Info.net. Archived from the original on 1 April 2004. Retrieved 15 February 2004.
- ↑ Steelcon News Archived 16 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.. steelcon.com. Retrieved: 13 June 2010.
- ↑ "Photo of the AN-225 in new paint scheme". Spotters.net. 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2009.
- ↑ Ingram, Frederick C. Volga-Dnepr Group answers.com. Retrieved: 24 July 2010.
- ↑ "Ukraine's Mriya An-225 aircraft sets new record". Kyiv Post. Interfax-Ukraine. 11 June 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ↑ "Geodis Wilson managed record-breaking airfreight move" (Press release). SNCF Geodis. 11 June 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ↑ Gordon, Yefim (2004). Antonov's Heavy Transports: Big Lifters for War & Peace. Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-182-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Images | |
|---|---|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| Video | |
|
| |
|
|