Anisocytosis
| Anisocytosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | R71 |
| ICD-9-CM | 790.09 |
| DiseasesDB | 725 |
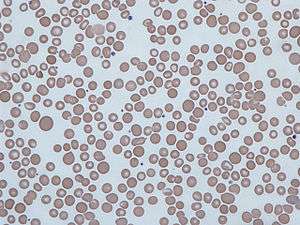
Anisocytosis is a medical term meaning that a patient's red blood cells are of unequal size. This is commonly found in anemia and other blood conditions. False diagnostic flagging may be triggered by an elevated WBC count, agglutinated RBCs, RBC fragments, giant platelets or platelet clumps. In addition, it is a characteristic feature of bovine blood.
The red cell distribution width (RDW) is a measurement of anisocytosis[1] and is calculated as a coefficient of variation of the distribution of RBC volumes divided by the mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Types
Anisocytosis is identified by RDW and is classified according to the size of RBC measured by MCV. According to this, it can be divided into
- Anisocytosis with microcytosis – Iron deficiency, sickle cell anemia
- Anisocytosis with macrocytosis – Folate or vitamin B12 deficiency, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, cytotoxic chemotherapy, chronic liver disease, myelodysplastic syndrome
Increased RDW is seen in iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia major (Cooley's anemia), thalassemia intermedia and myelodysplastic syndromes
- Anisocytosis with normal RBC size – Early iron, vit B12 or folate deficiency, dimorphic anemia, Sickle cell disease, chronic liver disease, Myelodysplastic syndrome[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Barbara J. Bain (2006). Blood cells: a practical guide. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 66–. ISBN 978-1-4051-4265-6. Retrieved 10 November 2010.
- ↑ Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) at eMedicine