Barium oxide
 | |
| | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Barium monoxide Barium protoxide Calcined baryta Baria | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1304-28-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 56180 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.753 |
| PubChem | 62392 |
| RTECS number | CQ9800000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BaO | |
| Molar mass | 153.326 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 5.72 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 1,923 °C (3,493 °F; 2,196 K) |
| Boiling point | ~ 2,000 °C (3,630 °F; 2,270 K) |
| 3.48 g/100 mL (20 °C) 90.8 g/100 mL (100 °C) Reacts to form Ba(OH)2 | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, dilute mineral acids and alkalies; insoluble in acetone and liquid ammonia |
| Structure | |
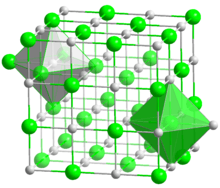
| cubic, cF8 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Octahedral | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S |
70 J·mol−1·K−1[1] |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−582 kJ·mol−1[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | See: data page |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R20/22 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S28 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
Barium hydroxide Barium peroxide |
| Other cations |
Calcium oxide Strontium oxide |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Barium oxide, BaO, is a white hygroscopic non-flammable compound. It has a cubic structure and is used in cathode ray tubes, crown glass, and catalysts. It is harmful to human skin and if swallowed in large quantity causes irritation. Excessive quantities of barium oxide may lead to death.
It is prepared by heating barium carbonate with coke, carbon black or tar or by thermal decomposition of Barium nitrate.
Uses
Barium oxide is used as a coating for hot cathodes, for example, those in cathode ray tubes. It replaced lead(II) oxide in the production of certain kinds of glass such as optical crown glass. While lead oxide raised the refractive index, it also raised the dispersive power, which barium oxide does not alter.[3] Barium oxide also has use as an ethoxylation catalyst in the reaction of ethylene oxide and alcohols, which takes place between 150 and 200 °C.[4]
It is also a source of pure oxygen through heat fluctuation. It readily oxidises to BaO1+x by formation of a peroxide ion. The complete peroxidation of BaO to BaO2 occurs at moderate temperatures but the increased entropy of the O2 molecule at high temperatures means that BaO2 decomposes to O2 and BaO at 1175K.[5]
The reaction was used as a large scale method to produce oxygen before the air separation became the dominant method in the beginning of the 20th century. The method was named after its inventors the Brin process.[6]
Preparation
Barium oxide is made by heating barium carbonate with coke, carbon black or tar. It may also be prepared by thermal decomposition of barium nitrate.[7] Likewise, it is often formed through the decomposition of other barium salts.[8]
- 2Ba + O2 → 2BaO
- BaCO3 → BaO + CO2
Safety issues
Barium oxide is an irritant. If it contacts the skin or the eyes or is inhaled it causes pain and redness. However, it is more dangerous when ingested. It can cause nausea and diarrhea, muscle paralysis, cardiac arrhythmia, and can cause death. If ingested, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Barium oxide should not be released environmentally; it is harmful to aquatic organisms.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.
- ↑ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.
- ↑ "Barium Oxide (chemical compound)". Encyclopædia Britanica. Encyclopædia Britanica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ↑ Nield, Gerald; Washecheck, Paul; Yang, Kang (05-04). "United States Patent 4210764". Retrieved 2007-02-20. Check date values in:
|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ S.C. Middleburgh, K.P.D. Lagerlof, R.W. Grimes - Accommodation of Excess Oxygen in Group II Oxides http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05452.x/pdf
- ↑ Jensen, William B. (2009). "The Origin of the Brin Process for the Manufacture of Oxygen". Journal of Chemical Education. 86 (11): 1266. Bibcode:2009JChEd..86.1266J. doi:10.1021/ed086p1266.
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ↑ "Compounds of barium: barium (II) oxide". Web Elements. The University of Sheffield. 2007-01-26. Retrieved 2007-02-22.
- ↑ "Barium Oxide (ICSC)". IPCS. October 1999. Archived from the original on 26 February 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
