Caudate lobe of liver
| Caudate lobe of liver | |
|---|---|
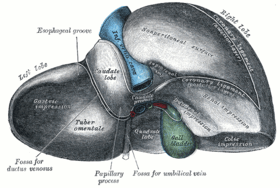 Posterior and inferior surfaces of the liver (caudate lobe visible at center top). | |
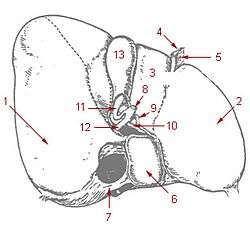 1: Right lobe of liver 2: Left lobe of liver 3: Quadrate lobe of liver 4: Round ligament of liver 5: Falciform ligament 6: Caudate lobe of liver 7: Inferior vena cava 8: Common bile duct 9: Hepatic artery 10: Portal vein 11: Cystic duct 12: Hepatic duct 13: Gallbladder | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin |
Lobus caudatus, segmentum hepatis posterius I |
| TA | A05.8.01.030 |
| FMA | 13365 |
The caudate lobe (posterior hepatic segment I, Spigelian lobe) is situated upon the postero-superior surface of the liver on the right lobe of the liver, opposite the tenth and eleventh thoracic vertebrae.
Description
The caudate lobe of the liver is bounded below, by the porta hepatis; on the right, by the fossa for the inferior vena cava; and, on the left, by the fossa for the ductus venosus and the physiological division of the liver called the ligamentum venosum.
It looks backward, being nearly vertical in position; it is longer from above downward than from side to side, and is somewhat concave in the transverse direction.
It is situated behind the porta, and separates the fossa for the gall-bladder from the commencement of the fossa for the inferior vena cava.
Clinical significance
Budd–Chiari syndrome, caused by occlusion of hepatic venous outflow, can lead to hypertrophy of the caudate lobe due to its own caval anastomosis that allows for continued function of this lobe of the liver.
Etymology
The caudate lobe is named after the tail-shaped hepatic tissue (cauda; Latin, "tail") caudate process of the liver, which provides surface continuity between the caudate lobe and the visceral surface of the right lobe of the liver. The caudate process is a small elevation of the hepatic substance extending obliquely and laterally, from the lower extremity of the caudate lobe to the under surface of the right lobe.
Additional images
-

The celiac artery and its branches; the liver has been raised, and the lesser omentum and anterior layer of the greater omentum removed.
-
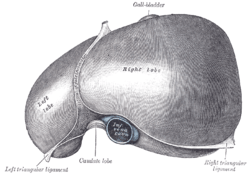
The superior surface of the liver.
-
Inferior surface of the liver.
-
Caudate lobe of liver.Inferior surface of liver.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy diagram: 12581.000-1 at Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, Elsevier
- Anatomy photo:38:12-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Visceral Surface of the Liver"
- Cross section image: pembody/body8a - Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
- MedicalMnemonics.com: 270