Central–Eastern Oceanic languages
| Central–Eastern Oceanic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: | The Pacific |
| Linguistic classification: |
|
| Subdivisions: | |
| Glottolog: | None |
|
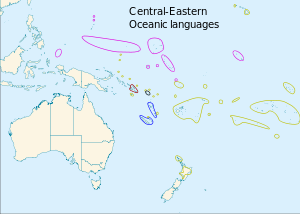
The branches of CE Oceanic Dark red = Southeast Solomons Blue = Southern Oceanic Pink = Micronesian Ocher = Fijian-Polynesian (not shown: Rapa Nui) The black oval between red and blue is the Temotu languages. | |
The over 200 Central–Eastern Oceanic languages form a branch of the Oceanic language family within the Austronesian languages.
Components
Traditional classifications have posited a Remote Oceanic branch within this family, but this was abandoned in Lynch et al. (2002), as no defining features could be found for such a group of languages.
- Southeast Solomons
- Southern Oceanic linkage (languages of New Caledonia and Vanuatu, such as Paicî)
- Central Pacific (Polynesian and the indigenous Austronesian languages of Fiji)
- Micronesian
In 2007 Ross & Næss moved the Utupua-Vanikoro languages from Central-Eastern to the newly established Temotu branch of Oceanic.
References
- Lynch, John, Malcolm Ross & Terry Crowley. (2002). The Oceanic languages. Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.