Federal Board of Revenue (Pakistan)
|
Federal Board of Revenue (Revenue Division) | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Type | Revenue Collection |
| Jurisdiction |
Pakistan |
| Headquarters | Islamabad, ICT, Pakistan |
| Employees | 23000 approx |
| Ministers responsible |
|
| Agency executive |
|
| Parent department | Ministry of Finance, Revenue & Statistics |
| Website |
www |
The Federal Board of Revenue (more commonly known by its initials as FBR) is a semi-autonomous federal agency of Pakistan that is responsible for enforcing fiscal laws and collecting revenue for the government of Pakistan.[1] FBR has the responsibility for (i) formulation and administration of fiscal policies, (ii) levy and collection of federal duties, taxes and other levies, and (iii) quasi-judicial function of deciding Customs & taxation cases and appeals. FBR is perhaps the largest federal department in Pakistan. FBR primarily operates through its main collection arms comprising Customs collectorates, Regional Tax Offices (RTOs) and Large Taxpayer Units (LTUs) across the country. FBR has two major wings: the Inland Revenue & Customs. The Inland Revenue Service (formerly known as Income Tax Department) administers domestic taxation including Sales Tax, Income Tax and Federal Excise Duties. The Pakistan Customs Service administers import duties and other taxes collected at import stage, as well regulates international trade with regard to prohibitions & restrictions imposed by the government. For the purpose of collection of revenue and pursuing tax evaders, FBR's powers & functions also include but are not limited to: carrying out inquiries and audits/investigations into the tax affairs, commanding arrests, attachment as well as public auction of movable and immovable assets of a non-compliant. Nisar Muhammad is the current chairman of FBR, since October 2015. He took over from Tariq Bajwa, who served as Chairman for a little over two years. Nisar had earlier served under Bajwa in the capacity of Member Customs, where he rose in esteem by consistently exceeding his targets.
History and description
The Central Board of Revenue (CBR) was created on April 1, 1924 through enactment of the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1924. In 1944, a full-fledged Revenue Division was created under the Ministry of Finance. After independence, this arrangement continued up to 31 August 1960 when on the recommendations of the Administrative Re-organization Committee, CBR was made an attached department of the Ministry of Finance. In 1974, further changes were made to streamline the organization and its functions. Consequently, the post of Chairman CBR was created with the status of ex officio Additional Secretary and Secretary Finance was relieved of his duties as ex officio Chairman of the CBR.
In order to remove impediments in the exercise of administrative powers of a Secretary to the Government and effective formulation and implementation of fiscal policy measures, the status of CBR as a Revenue Division was restored under the Ministry of Finance on October 22, 1991. However, the Revenue Division was abolished in January 1995, and CBR reverted to the pre-1991 position. The Revenue Division continued to exist since from December 1, 1998; however, owing to the recent controversy which arose when the federal government appointed the new CBR Chairman of the seventh common, bypassing several senior-most officials in the Customs & Federal Excise department, Prime Minister of Pakistan gave an additional charge of Revenue Division, Government of Pakistan to the then Secretary Finance and now the chairman of the agency Salman Siddiq, Government of Pakistan, thereby violating Federal Board of Revenue Act, 2007 as the senior officials in the then Customs & Excise Group now Pakistan Customs Service (PCS) refused reporting to a junior officer.
By the enactment of FBR Act 2007 in July 2007 the Central Board of Revenue has now become Federal Board of Revenue. The status of FBR as Revenue Division has again been restored.

Members of the Board
- Member Inland Revenue (Operations)
- Member Inland Revenue (Policy)
- Member Customs
- Member Administration
- Member Taxpayers Audit
- Member Legal
- Member Accounting
- Member FATE
- Member Information Technology
- Member Research, Planning and Reforms
Directorates Under FBR's Jurisdiction
- Directorate General of Transit Trade
- Directorate General of Intelligence & Investigation -Inland Revenue
- Directorate General of Intelligence & Investigation -Customs
- Directorate General of Internal Audit (Inland Revenue)
- Directorate General of Internal Audit (Customs )
- Directorate General of Training & Research (Inland Revenue)
- Directorate general of Training and Research (Customs)
- Directorate of Withholding Tax
- Directorate General of Valuation
- Directorate General of Input Output Coefficient Organization
- Directorate General of Reform & Automation
- Directorate of Post Clearance Audit
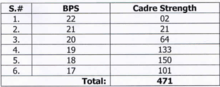
Cadre Strength of Inland Revenue Service
One of the largest cadres in Pakistan Civil Services. The cadre strength mentioned here doesn't include provincial revenue authorities i.e. Punjab Revenue Authority and Sindh Revenue Authority. The officers are posted at various Regional Tax Offices (RTO) and Large Tax Payer Units (LTU) and Tax Facilitation Centers.

Cadre Strength of Pakistan Customs Service
Comprises the smaller yet more spread out component of FBR. The field offices are named Model Customs Collectorates.
Notable former chairmen
First Ex Officio Chairman of CBR was Sir Victor Turner from August 14, 1947 to February 1, 1950. Ghulam Ishaq Khan also who later became the president of Pakistan served as the board chairman from May 31, 1966 to September 8, 1970. The then Finance Secretary A G N Kazi also served as Chairman CBR from 1970-71 until his Additional Secretary M Zulfiqar took over as the first full-time Chairman of the Board.
Tax collection trend
This is a chart of trend of taxes collected by the Central Board of Revenue of Pakistan with figures in millions of Pakistani Rupees.
| Year | Total | Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 129,282,087 | 658,485,060 | 211,597,027 |
| 2000 | 982,392,277 | 251,124,585 | 124,5267,692 |
| 2005 | 429,282,087 | 129,282,087 | 611,597,027 |
Since the mid-1990s, Sales Tax has grown dramatically in significance to the exchequer while Excise collection has stagnated.
See also
- Taxation in Pakistan
- PRAL
References
- ↑ Welcome to Federal Board of Revenue! Revenue Division Pakistan
- ↑ "FBR Members". http://www.fbr.gov.pk/ShowArticle.aspx?view=Article&ActionID=61&ArticleID=. External link in
|website=(help); - ↑ "Members". www.fbr.gov.pk.
- ↑ "IRS Training". http://dgtrdt.gov.pk/html/Publications.html. External link in
|website=(help); - ↑ "IRS cadre". http://hrms.fbr.gov.pk/Uploads/2015/Mar/0718-IR-I-20153162015_115633_AM.pdf. External link in
|website=(help); - ↑ "Customs". http://hrms.fbr.gov.pk/Uploads/2015/Apr/0995-C-I-20154302015_73308_PM.pdf. External link in
|website=(help);
