Chemistry of photolithography
Photolithography is a process in removing select portions of thin films used in microfabrication. Microfabrication is the production of parts on the micro- and nano- scale, typically on the surface of silicon wafers for the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Photolithography makes this process possible through the combined used of hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS), photoresist (positive or negative), a spin coater, photomask, an exposure system and other various chemicals. By carefully manipulating these factors it is possible to create nearly any geometry microstructure on the surface of a silicon wafer.[1] The chemical interaction between all the different components and the surface of the silicon wafer makes photolithography an interesting chemistry problem. Current science has been able to create features on the surface of silicon wafers between 1 and 100 µm.[2]

Silicon wafer
Silicon wafers are cut from a solid ingot of nearly-pure (99.9999999%) silicon. This is done through the process of Czochralski growth, which is diagramed in the image on the right, and produces a single intact diamond cubic silicon crystal. Due to its structure, monocrystalline silicon is anisotropic, which gives it different structural and electrical properties in different plane directions. Using miller indexes to denote the different plane orientations, the (1,0,0) and the (1,1,1) faces are typically used in silicon wafers (see image). The silicon ingot is oriented and cut along one these planes to expose that surface for processing through photolithography. The reason to use either of these planar faces depends on the application for which the silicon wafer will be used, or how it will be processed. At any rate, this depends of the use of etchants, photoresist, and acids to treat the surface, and the chemical interactions of these chemicals with the crystal surface depends on the surface properties of that crystalline face. A table on the right depicts the surface energies, atomic densities, and interatomic spacing of the three planes for a silicon crystal.[3]

| Miller Index (plane surface) | |||
| (1,0,0) | (1,1,0) | (1,1,1) | |
| Atomic density (1014/cm2)[4] | 6.78 | 9.59 | 15.66 |
| Spacing (Å)[5] | 5.43 | 3.84 | 3.13 |
| Surface Energy (ergs/cm2)[6][7] | 2130 | 1510 | 1230 |
Photoresist
In photolithography, photoresist compounds are used create a mask on the surface of a silicon wafer. The mask allows for precise control over the doping and etching processes used to form devices on silicon wafers. It is important for the mask to hold up to chemical attack during the etching process. Photoresists have three major components, a solvent, resin, and sensitizer (or photoactive compound). The compound is applied to the silicon wafer in liquid form and polymerization is controlled through exposure to light. Because Photoresists are non polar compounds, and silicon dioxide has a polar character, adhesion problems can manifest between the two materials. When photoresist does not adhere properly, features lose resolution. Photoresist Adhesion becomes very important as feature sizes get smaller. In order to reliably create small features, the surface of the silicon wafer must be made hydrophobic to promote photoresist adhesion.
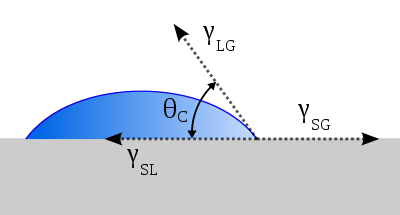
The adhesion characteristics can be observed and tested with a goniometer test. The surface energy characteristics of the silicon wafer can be measured by placing a drop of deionized water or ethylene glycol and measuring the contact angle of the droplet. Using the Young's relation and tabulated values for interfacial energy, we can estimate the surface energy of the solid.[8]
•Young's Relation:
- Interfacial energy between solid and vapor - Interfacial energy between solid and liquid - Interfacial energy between liquid and vapor θ - Contact Angle
Positive resist
Positive photoresists are composed of a novolac resin, ethyl lactate solvent, and Diazonaphthaquinone (DQ) as the photoactive compound.[9] Positive photoresist reacts with light to cause the polymer to break down and become soluble in a developer solution. Positive resist has better resistance to etchant than negative photoresist. Positive resists are better for producing small feature size, but does not adhere to silicon wafers as well as negative resist. When making small features it is critical to have good adhesion.
Negative resist
Negative photoresists are composed of a poly(cis-isoprene) matrix, xylene solvent, and bis-arylazide as the photoactive compound. Negative photoresists react to light by polymerizing. The unexposed portions can be removed by using a developer solution. negative resist has better adhesion and is great for features greater than 2 µm in size.
HMDS

A common method to increase adhesion of photoresist on the silicon wafer surface is to treat the wafer with Hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS). A new silicon wafer has a polar surface and has some adsorbed water on the surface.[10] The wafer can undergo a dehydration bake to remove adsorbed water, and followed by the HMDS treatment also known as the priming stage. HMDS can be dispensed in liquid form onto the wafer using a syringe while the wafer is attached to a vacuum chuck in a spin coater. HMDS can also be applied in gas form in the process known as the vapor prime. The HMDS promotes good photoresist-to-wafer adhesion because it ensures the wafer surface is hydrophobic. After HMDS treatment the silicon surface oxide becomes silated, leaving a non-polar surface.[11] The pristine silicon (100) face has a surface energy value of 56.9 mN/m, which is reduced to a value of 44.1 mN/m after HMDS treatment[12] The molecular formula for hexamethyldisilazane is C6H19NSi2.

Spin coating
There are four basic parameters that are involved in spin coating: solution viscosity, solid content (density), angular speed, and spin time.[13] A range of thicknesses can be achieved by spin coating. Most commonly the thicknesses range from 1-200 µm. The main properties that affect the thickness of the film are viscosity and spin speed. The more viscous the solvent the thicker the film will be and the faster the wafer is spun the thinner the film will be. By manipulating these two factors the different range of thicknesses is possible.
• thickness:
ρ - density μ - viscosity ω - angular velocity t - time
The density and viscosity both relate to the actual properties of the photoresist. This parameter can be manipulated by diluting the photoresist and adding different components to it to change its properties. The angular velocity and time relate to the spin coater and how fast it is spinning and for how long.
A common issue in spin coating is a "beading" up of solvent at the edge of the silicon wafer. A process known as backside washing is most commonly used to spin this bead off of the wafer. By programming multiple different spin speeds into the spin coating apparatus the thickness of the solvent can be made uniform without the "beading" up at the edges.

Spin coating has its limitations, though. Currently engineers and scientist are working on figuring out a better way to apply photoresist to the substrate of a silicon wafer. Spin coating can result in issues with wafer topography such as non-round substrates, oversized substrates, fragile substrates and material consumption. One potential solution to this issue is spraying the photoresist onto the surface.[14] By spraying the photoresist onto the surface of the wafer as opposed to spin coating the photoresist you save a lot of photoresist, and are able to make smaller and more precise parts. Spray coating is still in its development phase and much more research needs to be done to make it cost effective and applicable.
See also
References
- ↑ Fourkas, John T. (15 April 2010). "Nanoscale Photolithography with Visible Light". The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 1 (8): 1221–1227. doi:10.1021/jz1002082. Retrieved June 3, 2012.
- ↑ Microelectromechanical systems
- ↑ Xiaoge, Gregory Zhang. Silicon/Electrolyte Interface.
- ↑ Xiaoge, Gregory Zhang. Silicon/Electrolyte Interface.
- ↑ Xiaoge, Gregory Zhang. Silicon/Electrolyte Interface.
- ↑ Jaccodine, R J (1963). "Surface Energy of Germanium and Silicon". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 110 (6): 524. doi:10.1149/1.2425806. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ↑ Zdyb, A; Olchowik, Mucha (2006). "Dependence of GaAs and Si surface energy on the misorientation angle of crystal planes". Materials Science - Poland. 24 (4): 1110.
- ↑ Chow, T S (13 July 1998). "Wetting of rough surfaces". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 10 (27): L445–L451. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/10/27/001.
- ↑ Darling, R. B. "Positive Photoresists" (PDF). University of Washington. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ↑ "Substrate Cleaning Adhesion Promotion" (PDF). Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ Chen, Jem-Kun; Hsieh, Huang; Kuo, Chang (29 October 2008). "Poly (methyl methacralate) Brushes" (PDF). Macromolecules. 41 (22). doi:10.1021/ma801127m.
- ↑ Chen, Hsieh, Huang, Li, Kuo, Chang, Jem-Kun, Chih-Yi, Chih-Feng, P.M., Shiao-Wei, Feng-Chih. "Using Solvent Immersion to Fabricate Variably Patterned Poly(methyl methacrylate) Brushes on Silicon Surfaces" (PDF). Macromolecules, 2008, 41 (22).
- ↑ Shie, Jie-Ren; Yang, Yung-Kuand (26 April 2008). "Optimization of a photoresist coating process for photolithography in wafer manufacture via a radial basis neural network: A case study". Microelectronic Engineering. 85: 1664–1670. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.04.019.
- ↑ Pabo, E.F. (7–9 December 2011). "Advances in spray coating technologies for MEMS, 3DICs and additional applications". Electronics Packaging Technology Conference. 13: 349–353. Retrieved June 3, 2012.