Control system security
Control system security is the prevention of intentional or unintentional interference with the proper operation of industrial automation and control systems. These control systems manage essential services including electricity, petroleum production, water, transportation, manufacturing, and communications. They rely on computers, networks, operating systems, applications, and programmable controllers, each of which could contain security vulnerabilities. The 2010 discovery of the Stuxnet worm demonstrated the vulnerability of these systems to cyber incidents.[1] The United States and other governments have passed cyber-security regulations requiring enhanced protection for control systems operating critical infrastructure.
Control system security is known by several other names such as SCADA security, PCN security, industrial network security, and control system cyber security.
Risks
Insecurity of industrial automation and control systems can lead consequences in categories such as:
- Safety
- Environmental impact
- Lost production
- Equipment damage
- Information theft
- Company image
Vulnerability of control systems
Industrial automation and control systems have become far more vulnerable to security incidents due to the following trends that have occurred over the last 10 to 15 years.
- Heavy use of Commercial Off-the Shelf Technology (COTS) and protocols. Integration of technology such as MS Windows, SQL, and Ethernet means that process control systems are now vulnerable to the same viruses, worms and trojans that affect IT systems
- Enterprise integration (using plant, corporate and even public networks) means that process control systems (legacy) are now being subjected to stresses they were not designed for
- Demand for Remote Access - 24/7 access for engineering, operations or technical support means more insecure or rogue connections to control system
- Public Information - Manuals on how to use control system are publicly available to would be attackers as well as to legitimate users
Regulation of control system security is rare. The United States, for example, only does so for the nuclear power and the chemical industries.[2]
Government efforts
The U.S. Government Computer Emergency Readiness team (US-CERT) has instituted a Control Systems Security Program (CSSP) which has made available a large set of free National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards documents regarding control system security.
Control system security standards
ISA/IEC-62443 (Formerly ISA-99)
ISA/IEC-62443 is a series of standards, technical reports, and related information that define procedures for implementing electronically secure Industrial Automation and Control Systems (IACS). This guidance applies to end-users (i.e. asset owner), system integrators, security practitioners, and control systems manufacturers responsible for manufacturing, designing, implementing, or managing industrial automation and control systems.
These documents were originally referred to as ANSI/ISA-99 or ISA99 standards, as they were created by the International Society for Automation (ISA) and publicly released as American National Standards Institute (ANSI) documents. In 2010, they were renumbered to be the ANSI/ISA-62443 series. This change was intended to align the ISA and ANSI document numbering with the corresponding International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards.
All ISA work products are now numbered using the convention “ISA-62443-x-y” and previous ISA99 nomenclature is maintained for continuity purposes only. Corresponding IEC documents are referenced as “IEC 62443-x-y”. The approved IEC and ISA versions are generally identical for all functional purposes.
ISA99 remains the name of the Industrial Automation and Control System Security Committee of the ISA. Since 2002, the committee has been developing a multi-part series of standards and technical reports on the subject of IACS security. These work products are then submitted to the ISA approval and then publishing under ANSI. They are also submitted to IEC for review and approval as standards and specifications in the IEC 62443 series.
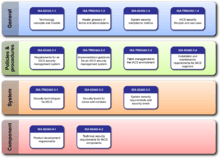
All ISA-62443 standards and technical reports are organized into four general categories called General, Policies and Procedures, System and Component.
- The first (top) category includes common or foundational information such as concepts, models and terminology. Also included are work products that describe security metrics and security life cycles for IACS.
- The second category of work products targets the Asset Owner. These address various aspects of creating and maintaining an effective IACS security program.
- The third category includes work products that describe system design guidance and requirements for the secure integration of control systems. Core in this is the zone and conduit design model.
- The fourth category includes work products that describe the specific product development and technical requirements of control system products. This is primarily intended for control product vendors, but can be used by integrator and asset owners for to assist in the procurement of secure products.
More information about the activities and plans of the ISA99 committee is available on the committee Wiki site ()
American Petroleum Institute
API 1164 Pipeline SCADA Security
North American Electric Reliability Committee (NERC)
NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Standards
Guidance documents
American Chemistry Council
UK Government Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure
CPNI Security for Industrial Control Systems Guidance
Control system security certification
IEC 62443 Conformity Assessment Program
The ISA Security Compliance Institute (ISCI) www.isasecure.org operates the first conformity assessment scheme for IEC 62443 IACS cybersecurity standards. This program certifies Commercial Off-the-shelf (COTS) IACS products and systems, addressing securing the IACS supply chain.
Certification Offerings Two COTS product certifications are available under the ISASecure® brand: ISASecure-EDSA (Embedded Device Security Assurance) certifying IACS products to the IEC 62443-4-2 IACS cybersecurity standard and ISASecure-SSA (System Security Assurance), certifying IACS systems to the IEC 62443-3-3 IACS cybersecurity standard.
A third certification, SDLA (Secure Development Lifecycle Assurance) is available which certifies IACS development organizations to the IEC 62443-4-1 cybersecurity standard, providing assurances that a supplier organization has institutionalized cybersecurity into their product development practices.
ISO 17065 and Global Accreditation The ISASecure 62443 conformity assessment scheme is an ISO 17065 program whose labs (certification bodies or CB) are independently accredited by ANSI/ANAB, JAB and other global ISO 17011 accreditation bodies (AB). The certification labs must also meet ISO 17025 lab accreditation requirements to ensure consistent application of certification requirements and recognized tools.
Through Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MRA) with IAF, ILAC and others, the accreditation of the ISASecure labs by the ISA 17011 accreditation bodies ensures that certificates issued by any of the ISASecure labs are globally recognized.
Test Tool Recognition The ISASecure scheme includes a process for recognizing test tools to ensure the tools meet functional requirements necessary and sufficient to execute all required product tests and that test results will be consistent among the recognized tools.
Chemicals, Oil and Gas Industries ISCI development processes include maintenance policies to ensure that the ISASecure certifications remain in alignment with the IEC 62443 standards as they evolve. While the IEC 62443 standards are designed to horizontally address technical cybersecurity requirements of a cross-section of process industries, the ISASecure scheme’s certification requirements working groups include subject matter experts from the chemical and oil and gas industries and are reflective of their cybersecurity needs.
References
- ↑ Byres, Eric; Cusimano, John (2012-02). "The 7 Steps to ICS Security". Tofino Security and exida Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 3, 2011. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Gross, Michael Joseph (2011-04). "A Declaration of Cyber-War". Vanity Fair. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on July 13, 2014. Retrieved March 3, 2011. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
External links
- ISA 99 Standards
- ISA Security Compliance Institute
- NERC Standards (see CIP 002-009)
- NIST webpage NIST