Genista tinctoria
| Genista tinctoria | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Genista |
| Species: | G. tinctoria |
| Binomial name | |
| Genista tinctoria L. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Genista tinctoria. |
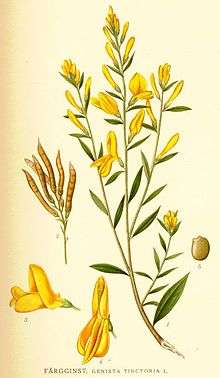
Genista tinctoria (dyer’s greenweed[1] or dyer's broom) is a species of flowering plant of the family Fabaceae, native to meadows and pastures in Europe and Turkey. Its other common names include dyer's whin, waxen woad and waxen wood.[2]
Description

It is a variable deciduous shrub growing to 60–90 centimetres (24–35 in) tall by 100 cm (39 in) wide, the stems woody, slightly hairy, and branched. The alternate, nearly sessile leaves are glabrous and lanceolate. Golden yellow pea-like flowers are borne in erect narrow racemes from spring to early summer. The fruit is a long, shiny pod shaped like a green bean pod.[3]
Properties and uses
Numerous cultivars have been selected for garden use, of which 'Royal Gold' has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.[4]
The plant, as its Latin and common names suggest, has been used from ancient times for producing a yellow dye, which combined with woad also provides a green colour.[2]
It was from this plant that the isoflavone genistein was first isolated in 1899; hence the name of the chemical compound. The medicinal parts are the flowering twigs.
The plant has been used in popular medicine and herbalism for various complaints, including skin diseases, even in modern times.[5][6][7]
References
- ↑ "BSBI List 2007" (xls). Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- 1 2 "Broom, Dyer's". Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ↑ RHS A-Z encyclopedia of garden plants. United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley. 2008. p. 1136. ISBN 1405332964.
- ↑ "Genista tinctoria 'Royal Gold'". Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ↑ Walter ED (1941). "Genistin (an isoflavone glucoside) and its aglucone, genistein, from soybeans". J Am Chem Soc. 62 (12): 3273–3276. doi:10.1021/ja01857a013.
- ↑ John Lust. The Herb Book. p. 176.
- ↑ N. Yoirish (2001). Curative Properties of Honey and Bee Venom. p. 111.