United States presidential election, 1876
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
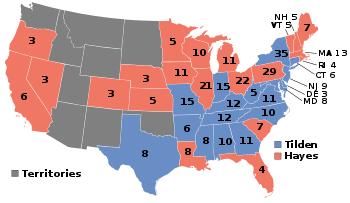
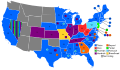
| Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Hayes/Wheeler, blue denotes those won by Tilden/Hendricks. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The United States presidential election of 1876 was the 23rd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 1876. It was one of the most contentious and controversial presidential elections in American history. The results of the election remain among the most disputed ever, although it isn't disputed that Samuel J. Tilden of New York outpolled Ohio's Rutherford B. Hayes in the popular vote. After a first count of votes, Tilden won 184 electoral votes to Hayes's 165, with 20 votes unresolved. These 20 electoral votes were in dispute in four states. In the case of Florida, Louisiana, and South Carolina, each party reported its candidate had won the state, while in Oregon one elector was replaced after being declared illegal for being an "elected or appointed official". The question of who should have been awarded these electoral votes is the source of the continued controversy concerning the results of this election.
An informal deal was struck to resolve the dispute: the Compromise of 1877, which awarded all 20 electoral votes to Hayes. In return for the Democrats' acquiescence to Hayes's election, the Republicans agreed to withdraw federal troops from the South to end the Reconstruction Era of the United States. The Compromise effectively ceded power in the Southern states to the Democratic Redeemers, who went on to pursue their agenda of returning the South to a political economy resembling that of its pre-war condition, including the disenfranchisement of black voters.
This was the first presidential election since 1852 in which the Democratic candidate won a majority of the popular vote. This is also the only election in which a candidate for president received more than 50 percent of the popular vote, but was not elected president by the Electoral College, and one of five elections (in addition to 1824, 1888, 2000 and 2016) in which the person who won the most popular votes did not win the election. To date, it remains the election that recorded the smallest electoral vote victory and the election that yielded the highest voter turnout of the eligible voting age population[1][2] in American history, at 81.8%.
Nominations
Republican Party nomination
Republican candidates:
-

Senator James G. Blaine from Maine
-

Senator Oliver P. Morton from Indiana
-

Senator Roscoe Conkling from New York
-

Representative
William A. Wheeler from New York -

President Ulysses S. Grant[1][2]
(declined in 1875)

It was widely assumed during the year 1875 that incumbent President Ulysses S. Grant would run for a third term as president in spite of the poor economic conditions, the numerous political scandals that had developed since he assumed office in 1869, and a long-standing tradition set by the first president, George Washington, not to stay in office longer than two terms. Grant's inner circle advised him to go for a third term and he almost did, but the House, by a sweeping 233 to 18 vote, passed a resolution declaring that the two-term tradition was to prevent a dictatorship. Late in the year, the president withdrew from the running for 1876.
When the Sixth Republican National Convention assembled on June 14, 1876, it appeared that James G. Blaine would be the nominee. On the first ballot, Blaine was just 100 votes short of a majority. His vote began to slide after the second ballot, however, as many Republicans feared that Blaine could not win the general election. Anti-Blaine delegates could not agree on a candidate until Blaine's total rose to 41% on the sixth ballot. Leaders of the reform Republicans met privately and considered alternatives. Their choice was Ohio's reform governor, Rutherford B. Hayes. On the seventh ballot, Hayes was nominated with 384 votes to 351 for Blaine and 21 for Benjamin Bristow. William A. Wheeler was nominated for vice-president by a much larger margin (366–89) over his chief rival, Frederick Theodore Frelinghuysen, who later served as a member of the electoral commission that awarded the election to Hayes.
| Presidential Ballot | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ballot | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| James G. Blaine | 285 | 296 | 293 | 292 | 286 | 308 | 351 | ||||||||||||||||
| Oliver P. Morton | 124 | 120 | 113 | 108 | 95 | 85 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| Benjamin Bristow | 113 | 114 | 121 | 126 | 114 | 111 | 21 | ||||||||||||||||
| Roscoe Conkling | 99 | 93 | 90 | 84 | 82 | 81 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| Rutherford B. Hayes | 61 | 64 | 67 | 68 | 104 | 113 | 384 | ||||||||||||||||
| John F. Hartranft | 58 | 63 | 68 | 71 | 69 | 50 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| Marshall Jewell | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| William A. Wheeler | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| Elihu B. Washburne | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
-

1st Presidential Ballot
-
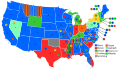
2nd Presidential Ballot
-
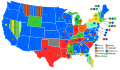
3rd Presidential Ballot
-
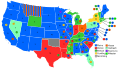
4th Presidential Ballot
-
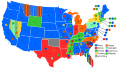
5th Presidential Ballot
-
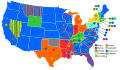
6th Presidential Ballot
-
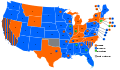
7th Presidential Ballot
| Vice Presidential Ballot | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ballot | 1st Partial | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| William A. Wheeler | 366 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frederick T. Frelinghuysen | 89 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stewart L. Woodford | 70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marshall Jewell | 38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Joseph R. Hawley | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
-
Recorded Vice Presidential Ballot
Democratic Party nomination
Democratic candidates:
- Samuel J. Tilden, governor of New York
- Thomas A. Hendricks, governor of Indiana
- Winfield Scott Hancock, United States Army major general from Pennsylvania
- William Allen, former governor of Ohio
- Thomas F. Bayard, U.S. senator from Delaware
- Joel Parker, former governor of New Jersey
-

William Allen from Ohio
-

Joel Parker from New Jersey

The 12th Democratic National Convention assembled in St. Louis, Missouri, in June 1876, the first political convention held by one of the major American parties west of the Mississippi River. Five thousand people jammed the auditorium in St. Louis with hopes for the first presidential victory for the Democratic Party in 20 years. The platform called for immediate and sweeping reforms in response to the scandals that had plagued the Grant administration. Tilden won more than 400 votes on the first ballot and the nomination by a landslide on the second.
Tilden defeated Thomas A. Hendricks, Winfield Scott Hancock, William Allen, Thomas F. Bayard, and Joel Parker for the presidential nomination. Although Tilden was strongly opposed by "Honest John" Kelly, the leader of New York's Tammany Hall, he was still able to obtain the nomination. Thomas Hendricks was nominated for vice-president, since he was the only person put forward for the position.
The Democratic platform pledged to replace the corruption of the Grant administration with honest, efficient government and to end "the rapacity of carpetbag tyrannies" in the South. It also called for treaty protection for naturalized United States citizens visiting their homelands, restrictions on Asian immigration, tariff reform, and opposition to land grants for railroads.[3]
It has been claimed that Tilden's nomination was received by the voting Democrats with more enthusiasm than any leader since Andrew Jackson.[4]
| Presidential Ballot | ||||||
| 1st Before Shifts | 1st After Shifts | 2nd Before Shifts | 2nd After Shifts | Unanimous | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samuel J. Tilden | 401.5 | 417.5 | 535 | 534 | 738 | |
| Thomas A. Hendricks | 140.5 | 140.5 | 85 | 60 | ||
| Winfield Scott Hancock | 75 | 75 | 58 | 59 | ||
| William Allen | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | ||
| Thomas F. Bayard | 33 | 33 | 4 | 11 | ||
| Joel Parker | 18 | 18 | 0 | 18 | ||
| James Broadhead | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Allen G. Thurman | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||
-
1st Presidential Ballot
Before Shifts -

1st Presidential Ballot
After Shifts -

Estimated 2nd Presidential Ballot
Source: Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876. (September 3, 2012).
| Vice Presidential Ballot | |
| 1st | |
|---|---|
| Thomas A. Hendricks | 730 |
| Blank | 8 |
Source: Official proceedings of the National Democratic convention, held in St. Louis, Mo., June 27th, 28th and 29th, 1876. (September 3, 2012).
Greenback Party nomination
Greenback candidates:
- Peter Cooper, U.S. philanthropist from New York
- Andrew Curtin, former governor of Pennsylvania
- William Allen, former governor of Ohio
- Alexander Campbell, U.S. representative from Illinois
Candidates gallery
-

William Allen from Ohio
The Greenback Party had been organized by agricultural interests in Indianapolis in 1874 to urge the federal government to inflate the economy through the mass issuance of paper money called greenbacks. Its first national nominating convention was held in Indianapolis in the spring of 1876. Peter Cooper was nominated for president with 352 votes to 119 for three other contenders. The convention nominated anti-monopolist Senator Newton Booth of California for vice-president; after Booth declined to run, the national committee chose Samuel Fenton Cary as his replacement on the ticket.
| Presidential Ballot | |
| Ballot | 1st |
|---|---|
| Peter Cooper | 352 |
| Andrew Curtin | 58 |
| William Allen | 31 |
| Alexander Campbell | 30 |
Source: US President - G Convention. Our Campaigns. (February 10, 2012).
Prohibition Party nomination
The Prohibition Party, in its second national convention, nominated Green Clay Smith as its presidential candidate and Gideon T. Stewart as its vice-presidential candidate.
American National Party nomination
This small political party used several different names, often with different names in different states. It was a continuation of the Anti-Masonic Party that met in 1872 and nominated Charles Francis Adams for president. When Adams declined to run, the party did not contest the 1872 election.
The convention was held from June 8 to 10, 1875, in Liberty Hall, Pittsburgh. B.T. Roberts of New York served as chairman, and Jonathan Blanchard was the keynote speaker.
The platform supported the Reconstruction Amendments to the Constitution, international arbitration, the reading of the scriptures in public schools, specie payments, justice for Native Americans, abolition of the Electoral College, and prohibition of the sale of alcoholic beverages. It declared the first day of the week to be a day of rest for the United States. The platform opposed secret societies and monopolies.
The convention considered three potential presidential nominees: Charles F. Adams, Jonathan Blanchard, and James B. Walker. When Blanchard declined to run, Walker was unanimously nominated. The convention then nominated Donald Kirkpatrick of New York unanimously for vice-president.[5]
General election
Campaign



Tilden, who had prosecuted machine politicians in New York and sent legendary political boss William M. Tweed to jail, ran as a reform candidate against the background of the corruption of the Grant administration. Both parties backed civil service reform and an end to Reconstruction. Both sides mounted mud-slinging campaigns, with Democratic attacks on Republican corruption being countered by Republicans raising the Civil War issue, a tactic ridiculed by Democrats who called it "waving the bloody shirt". Republicans chanted, "Not every Democrat was a rebel, but every rebel was a Democrat."
Hayes was a virtual unknown outside his home state of Ohio, where he had served two terms as a Congressman and then two terms as governor. Henry Adams wrote "[Hayes] is a third-rate nonentity whose only recommendations are that he is obnoxious to no one." He had served in the Civil War with distinction as colonel of the 23rd Ohio Regiment and was wounded several times, which made him marketable to veterans. Hayes's most important asset was the help he provided the Republican ticket in carrying the crucial swing state of Ohio.
The Democratic strategy for victory in the South was highly reliant on paramilitary groups such as the Red Shirts and the White League. Using the strategy of the Mississippi Plan, these groups actively suppressed black and white Republican voter turnouts by disrupting meetings and rallies and even using violence and intimidation. They saw themselves as the military wing of the Democratic Party.
The South Carolina Democratic Party, however, made genuine efforts to recruit black voters. Its gubernatorial candidate, former Confederate General Wade Hampton, said at his first campaign speech on 16 September: "If there is a white man in this assembly who believes when I am elected governor that I will stand between him and the law, or grant to him any immunities or privileges that shall not be granted to the colored man, he is mistaken and I tell him so now."[6] South Carolina Democrats were so successful in peacefully recruiting black voters that hundreds of blacks put on red shirts and marched along side their counterparts.[7] This led to violence in Charleston.[8]
Because it was considered improper for a candidate to pursue the presidency actively, neither Tilden nor Hayes actively stumped as part of the campaign, leaving that job to surrogates.
Colorado
Colorado was admitted to the Union as the 38th state on August 1, 1876. With insufficient time or money to organize a presidential election in the new state, Colorado's state legislature selected the state's electors. These electors in turn gave their three votes to Hayes and the Republican Party. This was the last election in which any state chose electors through its state legislature.
Electoral disputes
In Florida (with 4 electoral votes), Louisiana (with 8), and South Carolina (with 7), reported returns favored Tilden, but election results in each state were marked by fraud and threats of violence against Republican voters. One of the points of contention revolved around the design of ballots. At the time, parties would print ballots or "tickets" to enable voters to support them in the open ballots. To aid illiterate voters the parties would print symbols on the tickets. In this election, many Democratic ballots were printed with the Republican symbol, Abraham Lincoln, on them.[9] The Republican-dominated state electoral commissions subsequently disallowed a sufficient number of Democratic votes to award their electoral votes to Hayes.
Republicans, however, were also guilty of voter fraud and intimidation and simply used their control of the election returning boards to cast out enough Democratic votes to fabricate Republican popular vote majorities in each state. According to historian Roy Morris, “The actions of the returning boards…would not bear close scrutiny; any reasonably impartial board was likely to reverse the findings, particularly for Louisiana…”[10]
In two southern states, the governor recognized by the United States had signed the Republican certificates. The Democratic certificates from Florida were signed by the state attorney-general and the new Democratic governor. Those from Louisiana were signed by the Democratic gubernatorial candidate, and those from South Carolina by no state official. In the latter state, the Tilden electors simply claimed that they were chosen by the popular vote, and they were rejected by the state election board.[11]
Meanwhile, in Oregon, the vote of a single elector was disputed. The statewide result clearly favored Hayes, but the state's Democratic governor, La Fayette Grover, claimed that one elector, former postmaster John Watts, was ineligible under Article II, Section 1, of the United States Constitution, since he was a "person holding an office of trust or profit under the United States." Grover then substituted a Democratic elector in his place. The two Republican electors dismissed Grover's action and each reported three votes for Hayes, while the Democratic elector, C.A. Cronin, reported one vote for Tilden and two votes for Hayes. The two Republican electors presented a certificate signed by the secretary of state of Oregon. Cronin and the two electors he appointed (Cronin voted for Tilden while his associates voted for Hayes) used a certificate signed by the governor and attested by the secretary of state.[11] Ultimately, all three of Oregon's votes were awarded to Hayes.
Hayes thus had a majority of one in the Electoral College. The Democrats cried fraud. Suppressed excitement pervaded the country. Threats were even muttered that Hayes would never be inaugurated. In Columbus, Ohio, a shot was fired at Governor Hayes's residence as he sat down to dinner. Supporters marched to his home, calling for the "president". Hayes urged the crowd that, "it is impossible, at so early a time, to obtain the result."[12] President Grant quietly strengthened the military force in and around Washington.[11]
The Constitution provides that "the President of the Senate shall, in presence of the Senate and House of Representatives, open all the [electoral] certificates, and the votes shall then be counted." Certain Republicans held that the power to count the votes lay with the President of the Senate, the House and Senate being mere spectators. The Democrats objected to this construction, since Mr. Ferry, the Republican President of the Senate, could then count the votes of the disputed states for Hayes. The Democrats insisted that Congress should continue the practice followed since 1865, which was that no vote objected to should be counted except by the concurrence of both houses. The House had a solid Democratic majority; by throwing out the vote of one state, it could elect Tilden.[11]
Facing an unprecedented constitutional crisis, the Congress of the United States passed a law on January 29, 1877 that formed a 15-member Electoral Commission to settle the result. Five members were selected from each house of Congress, and they were joined by five members of the Supreme Court. William M. Evarts served as counsel for the Republican Party. The Compromise of 1877 might have helped the Democrats accept this electoral commission as well.
The majority party in each house named three members and the minority party two. As the Republicans controlled the Senate and the Democrats the House of Representatives, this yielded five Democratic and five Republican members of the Commission. Of the Supreme Court justices, two Republicans and two Democrats were chosen, with the fifth to be selected by these four.
The justices first selected a political independent, Justice David Davis. According to one historian, "[n]o one, perhaps not even Davis himself, knew which presidential candidate he preferred."[12] Just as the Electoral Commission Bill was passing Congress, the legislature of Illinois elected Davis to the Senate. Democrats in the Illinois legislature believed that they had purchased Davis's support by voting for him. However, they had made a miscalculation; instead of staying on the Supreme Court so that he could serve on the Commission, he promptly resigned as a Justice in order to take his Senate seat.[13] All the remaining available justices were Republicans, so the four justices already selected chose Justice Joseph P. Bradley, who was considered the most impartial remaining member of the court. This selection proved decisive.

It was drawing perilously near to Inauguration Day. The commission met on the last day of January. The cases of Florida, Louisiana, Oregon, and South Carolina were in succession submitted to it by Congress. Eminent counsel appeared for each side. There were double sets of returns from every one of the states named.[11]
The commission first decided not to question any returns that were prima facie lawful.[11] Bradley joined the other seven Republican committee members in a series of 8–7 votes that gave all 20 disputed electoral votes to Hayes, giving Hayes a 185–184 electoral vote victory. The commission adjourned on March 2; two days later Hayes was inaugurated without disturbance.[11]
During intense closed-door meetings, Democratic leaders agreed with reluctance to accept Hayes as president in return for the withdrawal of Federal troops from the last two still-occupied Southern states, South Carolina and Louisiana. Republican leaders in return agreed on a number of handouts and entitlements, including Federal subsidies for a transcontinental railroad line through the South. Although some of these promises were not kept, in particular the railroad proposal, it was enough for the time being to avert a dangerous standoff.
The returns accepted by the Commission put Hayes' margin of victory in South Carolina at 889 votes, the second-closest popular vote margin in a decisive state in U.S. history, after the election of 2000, which was decided by 537 votes in Florida (though in 2000, the declared margin of victory in the Electoral College for George W. Bush was five votes, as opposed to Hayes' one vote).
It is not possible to conclude definitively what the result would have been if a fair election had been held without the violence and intimidation throughout the South that disenfranchised many African Americans made eligible to vote under the 15th Amendment.[14] Nevertheless, in the likeliest fair scenario, Hayes would have won the election with 189 electoral votes to Tilden's 180 by winning all of the states that he did ultimately carry, plus Mississippi, but minus Florida.[14] In a truly fair election, it seems probable that South Carolina, Mississippi, and Louisiana, which all had majority black populations, would have gone Republican.[14] Regardless, Hayes would be the last Republican until Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1956 to win the electoral votes of Louisiana and the last Republican until Barry M. Goldwater in 1964 to carry South Carolina. Florida, with a majority white population, would have likely gone to Tilden in a fair election.[14] It is therefore likely that Hayes would have won appreciably more of the popular vote in a fair election, perhaps even a plurality or majority.[14]
Upon his defeat, Tilden said, "I can retire to public life with the consciousness that I shall receive from posterity the credit of having been elected to the highest position in the gift of the people, without any of the cares and responsibilities of the office."
Hayes, however, chose to pay-off those who helped him win the electoral college with government sinecures. Democratic governors soon replaced Carpetbag Republicans in the three disputed Southern states but Hayes arranged appointments of the former GOP governors and other state officials who helped him win the election. Louisiana’s 1876 gubernatorial candidate became the U. S. Counsel to Liverpool and the outgoing governor who signed the returns sent to Washington moved up to the U. S. Senate in a deal arranged by Ohio Senator John Sherman, who was the younger brother of General-of-the-Army William T. Sherman.[15]
The four—two white and two black—members of Louisiana’s election board were given federal posts. One of the white men was appointed the chief customs collector in New Orleans and the other became his assistant. (Customs posts were notoriously corrupt during that era.) One of the blacks became a deputy naval officer at the port and the other got a customs house post for his brother. In total, sixty-nine men involved in the Republican-winning Louisiana count were rewarded with federal appointments. In all, some fifty relatives and friends of the Louisiana returning board got positions at the New Orleans custom’s house.[16]
Results
According to the Commission's rulings, of the 2,249 counties and independent cities making returns, Tilden won in 1,301 (57.85%) while Hayes carried only 947 (42.11%). One county (0.04%) in Nevada split evenly between Tilden and Hayes.
The election of 1876 was the last one held before the end of the Reconstruction era, which sought to protect the rights of African Americans in the South who usually voted for Republican presidential candidates. It was not until the election of 1920 that one of the states of the Confederacy was ever again carried by a Republican presidential candidate. In that case, it was Tennessee, a state that never experienced a long period of occupation by Federal troops and was completely "reconstructed" well before the first presidential election of the Reconstruction period (1868). None of the Southern states that experienced long periods of occupation by Federal troops was carried by a Republican again until the election of 1928 (Texas, Florida, North Carolina, and Virginia).
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote[17] | Electoral vote[18] |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Pct | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Elect. vote[19] | ||||
| Rutherford B. Hayes | Republican | Ohio | 4,034,142 | 47.92% | 185 | William A. Wheeler | New York | 185 |
| Samuel J. Tilden | Democratic | New York | 4,286,808 | 50.92% | 184 | Thomas A. Hendricks | Indiana | 184 |
| Peter Cooper | Greenback | New York | 83,726 | 0.99% | 0 | Samuel Fenton Cary | Ohio | 0 |
| Green Clay Smith | Prohibition | Kentucky | 6,945 | 0.08% | 0 | Gideon T. Stewart | Ohio | 0 |
| James Walker | American National Party | Illinois | 463 | 0.01% | 0 | Donald Kirkpatrick | New York | 0 |
| Other | 6,575 | 0.08% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 8,418,659 | 100% | 369 | 369 | ||||
| Needed to win | 185 | 185 | ||||||
Geography of results

-
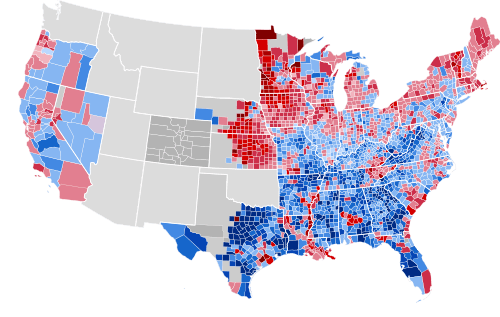
Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Cartographic gallery
-
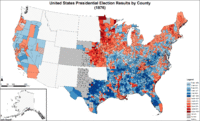
Map of presidential election results by county.
-
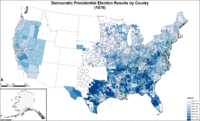
Map of Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
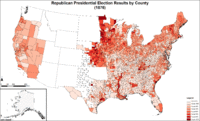
Map of Republican presidential election results by county.
-

Map of "other" presidential election results by county.
-
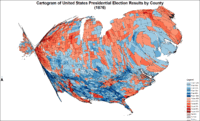
Cartogram of presidential election results by county.
-
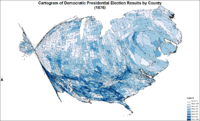
Cartogram of Democratic presidential election results by county.
-
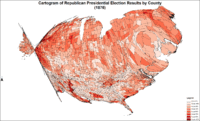
Cartogram of Republican presidential election results by county.
-
Cartogram of "other" presidential election results by county.
Results by state
Source: Data from Walter Dean Burnham, Presidential ballots, 1836-1892 (Johns Hopkins University Press, 1955) pp 247–57.[20]
| States won by Tilden/Hendricks |
| States won by Hayes/Wheeler |
| Samuel J. Tilden Democratic |
Rutherford B. Hayes Republican |
Peter Cooper Greenback |
Green Smith Prohibition |
Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | # | |
| Alabama | 10 | 102,989 | 59.98 | 10 | 68,708 | 40.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 34,281 | 19.97 | 171,699 | AL |
| Arkansas | 6 | 58,086 | 59.92 | 6 | 38,649 | 39.87 | - | 211 | 0.22 | - | - | - | - | 19,437 | 20.05 | 96,946 | AR |
| California | 6 | 76,460 | 49.08 | - | 79,258 | 50.88 | 6 | 47 | 0.03 | - | - | - | - | -2,798 | -1.80 | 155,784 | CA |
| Colorado* | 3 | 3 | CO | ||||||||||||||
| Connecticut | 6 | 61,927 | 50.70 | 6 | 59,033 | 48.33 | - | 774 | 0.63 | - | 374 | 0.31 | - | 2,894 | 2.37 | 122,134 | CT |
| Delaware | 3 | 13,381 | 55.45 | 3 | 10,752 | 44.55 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2,629 | 10.89 | 24,133 | DE |
| Florida | 4 | 22,927 | 49.01 | - | 23,849 | 50.99 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -922 | -1.97 | 46,776 | FL |
| Georgia | 11 | 130,157 | 72.03 | 11 | 50,533 | 27.97 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 79,624 | 44.07 | 180,690 | GA |
| Illinois | 21 | 258,611 | 46.66 | - | 278,232 | 50.20 | 21 | 17,207 | 3.10 | - | - | - | - | -19,621 | -3.54 | 554,227 | IL |
| Indiana | 15 | 213,526 | 48.65 | 15 | 208,011 | 47.39 | - | 17,233 | 3.93 | - | 141 | 0.03 | - | 5,515 | 1.26 | 438,911 | IN |
| Iowa | 11 | 112,121 | 38.28 | - | 171,326 | 58.50 | 11 | 9,431 | 3.22 | - | - | - | - | -59,205 | -20.21 | 292,878 | IA |
| Kansas | 5 | 37,902 | 30.53 | - | 78,324 | 63.10 | 5 | 7,770 | 6.26 | - | 110 | 0.09 | - | -40,422 | -32.56 | 124,134 | KS |
| Kentucky | 12 | 160,060 | 61.41 | 12 | 97,568 | 37.44 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 62,492 | 23.98 | 260,626 | KY |
| Louisiana | 8 | 70,508 | 48.35 | - | 75,315 | 51.65 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -4,807 | -3.30 | 145,823 | LA |
| Maine | 7 | 49,917 | 42.65 | - | 66,300 | 56.64 | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -16,383 | -14.00 | 117,045 | ME |
| Maryland | 8 | 91,779 | 56.05 | 8 | 71,980 | 43.95 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 19,799 | 12.09 | 163,759 | MD |
| Massachusetts | 13 | 108,777 | 41.90 | - | 150,064 | 57.80 | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -41,287 | -15.90 | 259,620 | MA |
| Michigan | 11 | 141,685 | 44.49 | - | 166,901 | 52.41 | 11 | 9,023 | 2.83 | - | 766 | 0.24 | - | -25,216 | -7.92 | 318,450 | MI |
| Minnesota | 5 | 48,587 | 39.16 | - | 72,955 | 58.80 | 5 | 2,389 | 1.93 | - | 144 | 0.12 | - | -24,368 | -19.64 | 124,075 | MN |
| Mississippi | 8 | 112,173 | 68.08 | 8 | 52,603 | 31.92 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 59,570 | 36.15 | 164,776 | MS |
| Missouri | 15 | 202,086 | 57.64 | 15 | 145,027 | 41.36 | - | 3,497 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | 57,059 | 16.27 | 350,610 | MO |
| Nebraska | 3 | 17,413 | 35.30 | - | 31,915 | 64.70 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -14,502 | -29.40 | 49,328 | NE |
| Nevada | 3 | 9,308 | 47.27 | - | 10,383 | 52.73 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -1,075 | -5.46 | 19,691 | NV |
| New Hampshire | 5 | 38,510 | 48.05 | - | 41,540 | 51.83 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -3,030 | -3.78 | 80,141 | NH |
| New Jersey | 9 | 115,962 | 52.66 | 9 | 103,517 | 47.01 | - | 714 | 0.32 | - | - | - | - | 12,445 | 5.65 | 220,193 | NJ |
| New York | 35 | 521,949 | 51.40 | 35 | 489,207 | 48.17 | - | 1,978 | 0.19 | - | 2,369 | 0.23 | - | 32,742 | 3.22 | 1,015,503 | NY |
| North Carolina | 10 | 125,427 | 53.62 | 10 | 108,484 | 46.38 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 16,943 | 7.24 | 233,911 | NC |
| Ohio | 22 | 323,182 | 49.07 | - | 330,698 | 50.21 | 22 | 3,057 | 0.46 | - | 1,636 | 0.25 | - | -7,516 | -1.14 | 658,649 | OH |
| Oregon | 3 | 14,157 | 47.38 | - | 15,214 | 50.92 | 3 | 510 | 1.71 | - | - | - | - | -1,057 | -3.54 | 29,881 | OR |
| Pennsylvania | 29 | 366,204 | 48.25 | - | 384,184 | 50.62 | 29 | 7,204 | 0.95 | - | 1,318 | 0.17 | - | -17,980 | -2.37 | 758,993 | PA |
| Rhode Island | 4 | 10,712 | 40.23 | - | 15,787 | 59.29 | 4 | 68 | 0.26 | - | 60 | 0.23 | - | -5,075 | -19.06 | 26,627 | RI |
| South Carolina | 7 | 90,897 | 49.76 | - | 91,786 | 50.24 | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -889 | -0.49 | 182,683 | SC |
| Tennessee | 12 | 133,177 | 59.79 | 12 | 89,566 | 40.21 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 43,611 | 19.58 | 222,743 | TN |
| Texas | 8 | 104,755 | 70.04 | 8 | 44,800 | 29.96 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 59,955 | 40.09 | 149,555 | TX |
| Vermont | 5 | 20,254 | 31.38 | - | 44,091 | 68.30 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | -23,837 | -36.93 | 64,553 | VT |
| Virginia | 11 | 140,770 | 59.58 | 11 | 95,518 | 40.42 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 45,252 | 19.15 | 236,288 | VA |
| West Virginia | 5 | 56,546 | 56.75 | 5 | 41,997 | 42.15 | - | 1,104 | 1.11 | - | - | - | - | 14,549 | 14.60 | 99,647 | WV |
| Wisconsin | 10 | 123,926 | 48.19 | - | 130,067 | 50.57 | 10 | 1,509 | 0.59 | - | 27 | 0.01 | - | -6,141 | -2.39 | 257,177 | WI |
| TOTALS: | 369 | 4,286,808 | 50.92 | 184 | 4,034,142 | 47.92 | 185 | 83,726 | 0.99 | - | 6,945 | 0.08 | - | 252,666 | 3.00 | 8,418,659 | US |
Close states
Margin of victory less than 5% (171 electoral votes):
- South Carolina, 0.49%
- Ohio, 1.14%
- Indiana, 1.26%
- California, 1.80%
- Florida, 1.97%
- Pennsylvania, 2.37%
- Connecticut, 2.37%
- Wisconsin, 2.39%
- New York, 3.22%
- Louisiana, 3.30%
- Oregon, 3.54%
- Illinois, 3.54%
- New Hampshire, 3.78%
Margin of victory between 5% and 10% (33 electoral votes):
- Nevada, 5.46%
- New Jersey, 5.65%
- North Carolina, 7.24%
- Michigan, 7.92%
Popular culture
The Presidential Election of 1876 is a major theme of Gore Vidal's novel 1876.
See also
- American election campaigns in the 19th century
- History of the United States (1865–1918)
- Third Party System
References
- 1 2 Between 1828-1928: "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections: 1828 - 2008". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara. Retrieved 2012-11-09.
- ↑ Between 1932 and 2008: "Table 397. Participation in Elections for President and U.S. Representatives: 1932 to 2010" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau, Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2012. U.S. Census Bureau.
- ↑ DeGregorio, William (1997). The Complete Book of U.S. Presidents. New York: Gramercy. ISBN 0-517-18353-6.
- ↑ They Also Ran
- ↑ "US President - American National Convention Race - Jun 08, 1875". Our Campaigns. 2010-06-21. Retrieved 2014-02-17.
- ↑ Roy Morris, Fraud of the Century (New York: Simon & Schuster, 2003), 152
- ↑ Roy Morris, Fraud of the Century, 152
- ↑ Roy Morris Fraud of the Century,154
- ↑ "Flashback to 1876: History repeats itself". BBC News. London. December 12, 2000. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ↑ Roy Morris, Fraud of the Century, 221
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Andrews, E. Benjamin (1912). History of the United States. Charles Scribner's Sons.
- 1 2 Morris, Roy, Jr. (2003). Fraud Of The Century: Rutherford B. Hayes, Samuel Tilden And The Stolen Election Of 1876. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 168, 239. ISBN 978-0-7432-5552-3
- ↑ "Hayes v. Tilden: The Electoral College Controversy of 1876–1877." Archived February 20, 2006, at the Wayback Machine. HarpWeek
- 1 2 3 4 5 Who Won the 1876 Election? Issue 9 of Buttons and Ballots, in Spring 1997.
- ↑ Eric Foner, Reconstruction, 543, 604-05; Roy Morris, Fraud of the Century, 245-46
- ↑ Eric Foner, Reconstruction, 543, 604-05; Roy Morris, Fraud of the Century, 245-46
- ↑ Leip, David. "1876 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved July 27, 2005.
- ↑ "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
- ↑ "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
- ↑ "1876 Presidential General Election Data - National". Retrieved May 7, 2013.
Reference and further reading
- Appleton's Annual Cyclopedia ...for 1876 (1885), comprehensive world coverage
- John Bigelow, Author, Edited by, Nikki Oldaker, The Life of Samuel J. Tilden. (2009 Revised edition-retype-set-new photos). 444 pages, Full Color. ISBN 978-0-9786698-1-2
- Holt, Michael F. By One Vote: The Disputed Presidential Election of 1876. (2008). 304 pages, ISBN 978-0-7006-1608-4
- Flick, Alexander C. (1939). Samuel J. Tilden — A Study In Political Sagacity.
- Haworth, Paul Leland (1906). The Hayes-Tilden Disputed Presidential Election of 1876.
- Hoogenboom, Ari (1995). Rutherford B. Hayes: Warrior and President. ISBN 0-7006-0641-6.
- Morris, Roy, Jr. (2004). Fraud Of The Century: Rutherford B. Hayes, Samuel Tilden And The Stolen Election Of 1876.
- Authors Nikki Oldaker with John Bigelow, 2006, "Samuel Tilden the Real 19th President" 288 pages ISBN 978-0-9786698-0-5
- Polakoff, Keith Ian (1973). The Politics of Inertia: The Election of 1876 and the End of Reconstruction.
- Rehnquist, William H. (2004). The Centennial Crisis: The Disputed Election of 1876. Knopf Publishing Group. ISBN 0-375-41387-1., popular account
- Summers, Mark Wahlgren.The Press Gang: Newspapers and Politics, 1865-1878 (1994)
- Summers, Mark Wahlgren. The Era of Good Stealings (1993), covers corruption 1868-1877
- Richard White, "Corporations, Corruption, and the Modern Lobby: A Gilded Age Story of the West and the South in Washington, D.C." Southern Spaces, April 16, 2009
- Woodward, C. Vann (1951). Reunion and Reaction: The Compromise of 1877 and the End of Reconstruction.
Primary sources
- Democratic National Committee (1876). The Campaign Text Book: Why the People Want a Change. The Republican Party Reviewed….
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States presidential election, 1876. |
- Presidential Election of 1876: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Rutherford B. Hayes On The Election of 1876: Original Letter Shapell Manuscript Foundation
- 1876 popular vote by counties
- Hayes Presidential Library with essays by historians
- Hayes vs. Tilden: The Electoral College Controversy of 1876-1877
- Samuel Tilden
- How close was the 1876 election? at the Wayback Machine (archived August 25, 2012) — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Booknotes interview with Roy Morris, Jr. on Fraud of the Century: Rutherford B. Hayes, Samuel Tilden, and the Stolen Election of 1876, April 6, 2003.
- Election of 1876 in Counting the Votes