Four-tensor
Four-tensor is a frequent abbreviation for a tensor in a four-dimensional spacetime.[1]
Syntax
General four-tensors are usually written as 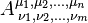 , with the indices taking integral values from 0 to 3. Such a tensor is said to have contravariant rank n and covariant rank m.[1]
, with the indices taking integral values from 0 to 3. Such a tensor is said to have contravariant rank n and covariant rank m.[1]
Examples
One of the simplest non-trivial examples of a four-tensor is the four-displacement 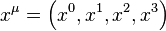 , a four-tensor with contravariant rank 1 and covariant rank 0. Four-tensors of this kind are usually known as four-vectors. Here the component
, a four-tensor with contravariant rank 1 and covariant rank 0. Four-tensors of this kind are usually known as four-vectors. Here the component 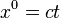 gives the displacement of a body in time (time is multiplied by the speed of light
gives the displacement of a body in time (time is multiplied by the speed of light  so that
so that 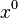 has dimensions of length). The remaining components of the four-displacement form the spatial displacement vector
has dimensions of length). The remaining components of the four-displacement form the spatial displacement vector 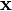 .[1]
.[1]
Similarly, the four-momentum 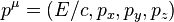 of a body is equivalent to the energy-momentum tensor of said body. The element
of a body is equivalent to the energy-momentum tensor of said body. The element 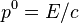 represents the momentum of the body as a result of it travelling through time (directly comparable to the internal energy of the body). The elements
represents the momentum of the body as a result of it travelling through time (directly comparable to the internal energy of the body). The elements 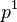 ,
, 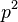 and
and 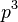 correspond to the momentum of the body as a result of it travelling through space, written in vector notation as
correspond to the momentum of the body as a result of it travelling through space, written in vector notation as 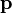 .[1]
.[1]
The electromagnetic field tensor is an example of a rank two contravariant tensor:[1]
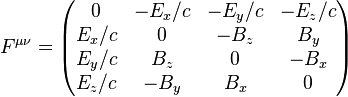
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lambourne, Robert J A. Relativity, Gravitation and Cosmology. Cambridge University Press. 2010.