Friedrichshafen FF.33
| FF.33 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The "Wölfchen" (Little Wolf) aboard SMS Wolf (auxiliary cruiser). | |
| Role | Fighter |
| Manufacturer | Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen GmbH |
| First flight | 1914 |
| Introduction | 1914 |
| Primary user | Kaiserliche Marine |
| Number built | FF.33E: 180 FF.33L: 135 |
|
| |
Friedrichshafen FF.33 was a German single-engined amphibious reconnaissance biplane designed by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen in 1914.
Versions
- FF.33
- Initial production version powered by a Mercedes D.II engine, six built
- FF.33b
- FF.33 with pilot and observers positions reversed, additional observers-operated machine-gun and powered by 119 kW (160 hp) Maybach inline piston engine, five built.
- FF.33e
- Main production reconnaissance variant powered by a Benz Bz.III inline engine, longer twin floats, under tail central float removed, and radio transmitter instead of armament, about 180 built.
- FF.33f
- Scout/Fighter version based on FF.33e with reduced span wings and reduced length but fitted with a machine-gun on a pivoted mount, five built.
- FF.33h
- FF.33f with aerodynamic refinements, and duplication of wing-bay bracing cables as a safeguard if the observer has to fire his machine-gun forward through the wings, about 50 built.
- FF.33j
- FF.33e with aerodynamic refinements and the provision of a radio transmitter and receiver.
- FF.33l
- Main production scout/fighter version, with further aerodynamic improvements and a fixed machine gun, about 130 built
- FF.33s
- dual-control trainer version
- FF.39
- Refined version of the FF.33e with a 149 kW (200 hp) Benz Bz.IV engine, 14 built.
- FF.49c
- Further improved FF.39 with strengthened structures, balanced controls, a radio receiver and transmitter, machine-gun for observer, over 200 built.
- FF.49b
- Bomber variant of the FF.49c, crew positions reversed, deletion of observers machine-gun and provision to carry a light bombload, 15 built.
- FF.59a
- Development aircraft based on FF.39 with different tail, one built.
- FF.59b
- Development aircraft based on FF.39 with different tail, one built.
- FF.59c
- FF.39 with modified tail unit, wing interplane struts moved outwards and inner-bay bracing wires removed.
- C.I
- A landplane version of the FF.33l with wheeled landing gear, one built.
Operators
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria- Four FF.33Es and four FF.33Ls stationed since 1916 at the German Naval Air Station Peynerdjik near Varna on the Black Sea were transferred in June 1918 to the Bulgarian Navy. They were scrapped in 1920 in accordance with the clauses of the Peace Treaty.[1]
 Denmark
Denmark
 Finland
Finland- Finnish Air Force purchased two FF.33Es from Germany in February 1918. The first one arrived on April 20, 1918 to Vaasa and the other one in the summer of 1918. The aircraft wore the German designation numbers 1999 and 1998, which were changed into the FAF designation numbers F16 and F24 (later S58/18 and S73/18). Another FF.33E was purchased from the Germans in Estonia on November 26, 1918. The type was in FAF service between 1918-1923.
 German Empire
German Empire- Kaiserliche Marine
 Netherlands
Netherlands- Royal Netherlands Navy
 Poland
Poland- Polish Navy operated three: FF.33E, FF.33H, FF.33L in 1920-1922[2]
 Sweden
Sweden
Specifications (FF.33E)
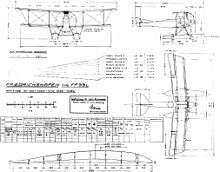
Friedrichshafen FF.33L drawing
Data from Thulinista Hornetiin
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 10.22 m (33 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 16.60 m (54 ft 6 in)
- Height: 3.75 m (12 ft 4 in)
- Max. takeoff weight: 1,550 kg (3,412 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Benz Bz.III inline engine, 112 kW (150 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 110 km/h (60 kn, 68 mph)
- Endurance: 4-5 hours
Armament
- 8 × 12 kg (26.4 lb) bombs
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Friedrichshafen FF.33. |
- Friedrichshafen FF.33s history
- Timo Heinonen (1992). Thulinista Hornetiin - 75 vuotta Suomen ilmavoimien lentokoneita. Tikkakoski: Keski-Suomen ilmailumuseo. ISBN 951-95688-2-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.