Golem

In Jewish folklore, a golem (/ˈɡoʊləm/ GOH-ləm; Hebrew: גולם) is an animated anthropomorphic being that is magically created entirely from inanimate matter (specifically clay or mud). The word was used to mean an amorphous, unformed material in Psalms and medieval writing.[1]
The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late-16th-century rabbi of Prague. There are many tales differing on how the golem was brought to life and afterwards controlled.
History
Etymology
The word golem occurs once in the Bible in Psalm 139:16, which uses the word גלמי (galmi; my golem),[2] that means "my light form", "raw" material,[3] connoting the unfinished human being before God's eyes.[2] The Mishnah uses the term for an uncultivated person: "Seven characteristics are in an uncultivated person, and seven in a learned one," (שבעה דברים בגולם) (Pirkei Avot 5:6 in the Hebrew text; English translations vary). In Modern Hebrew, golem is used to mean "dumb" or "helpless". Similarly, it is often used today as a metaphor for a brainless lunk or entity who serves man under controlled conditions but is hostile to him under others. "Golem" passed into Yiddish as goylem to mean someone who is clumsy or slow.
Earliest stories
The oldest stories of golems date to early Judaism. In the Talmud (Tractate Sanhedrin 38b), Adam was initially created as a golem (גולם) when his dust was "kneaded into a shapeless husk". Like Adam, all golems are created from mud by those close to divinity, but no anthropogenic golem is fully human. Early on, the main disability of the golem was its inability to speak. Sanhedrin 65b describes Rava creating a man (gavra). He sent the man to Rav Zeira. Rav Zeira spoke to him, but he did not answer. Rav Zeira said, "You were created by the sages; return to your dust".
During the Middle Ages, passages from the Sefer Yetzirah (Book of Creation) were studied as a means to create and animate a golem, although there is little in the writings of Jewish mysticism that supports this belief. It was believed that golems could be activated by an ecstatic experience induced by the ritualistic use of various letters of the Hebrew Alphabet[1] forming a "shem" (any one of the Names of God), wherein the shem was written on a piece of paper and inserted in the mouth or in the forehead of the golem.[4]
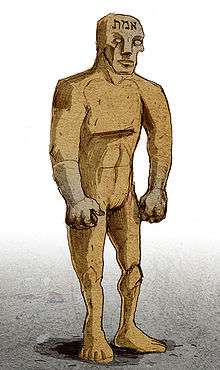
A golem is inscribed with Hebrew words in some tales (for example, some versions of Chełm and Prague, as well as in Polish tales and versions of Brothers Grimm), such as the word emet (אמת, "truth" in Hebrew) written on its forehead. The golem could then be deactivated by removing the aleph (א) in emet,[5] thus changing the inscription from "truth" to "death" (met מת, meaning "dead"). Other versions add that an entity of clay would be brought to life by placing into his mouth a shem with a magic formula, and it could later be immobilized by pulling out the shem[6] or by reversing the creative combinations. Rabbi Jacob ben Shalom arrived at Barcelona from Germany in 1325 and remarked that the law of destruction is the reversal of the law of creation.[7]
Joseph Delmedigo informs us in 1625 that "many legends of this sort are current, particularly in Germany".[8]
The earliest known written account of how to create a golem can be found in Sodei Razayya by Eleazar ben Judah of Worms (1165–1230).
The Golem of Chełm
The oldest description of the creation of a golem by a historical figure is included in a tradition connected to Rabbi Eliyahu of Chełm (1550–1583).[1][2][8][9]
A Polish Kabbalist, writing in about 1630–1650, reported the creation of a golem by Rabbi Eliyahu thus: "And I have heard, in a certain and explicit way, from several respectable persons that one man [living] close to our time, whose name is R. Eliyahu, the master of the name, who made a creature out of matter [Heb. Golem] and form [Heb. tzurah] and it performed hard work for him, for a long period, and the name of emet was hanging upon his neck, until he finally removed it for a certain reason, the name from his neck and it turned to dust."[1] A similar account was reported by a Christian author, Christoph Arnold, in 1674.[1]
Rabbi Jacob Emden (d. 1776) elaborated on the story in a book published in 1748: "As an aside, I'll mention here what I heard from my father's holy mouth regarding the Golem created by his ancestor, the Gaon R. Eliyahu Ba'al Shem of blessed memory. When the Gaon saw that the Golem was growing larger and larger, he feared that the Golem would destroy the universe. He then removed the Holy Name that was embedded on his forehead, thus causing him to disintegrate and return to dust. Nonetheless, while he was engaged in extracting the Holy Name from him, the Golem injured him, scarring him on the face."[10]
According to the Polish Kabbalist, "the legend was known to several persons, thus allowing us to speculate that the legend had indeed circulated for some time before it was committed to writing and, consequently, we may assume that its origins are to be traced to the generation immediately following the death of R. Eliyahu, if not earlier."[1][11]
The classic narrative: The Golem of Prague



The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th century rabbi of Prague, also known as the Maharal, who reportedly created a golem to defend the Prague ghetto from antisemitic attacks[12] and pogroms. Depending on the version of the legend, the Jews in Prague were to be either expelled or killed under the rule of Rudolf II, the Holy Roman Emperor. To protect the Jewish community, the rabbi constructed the Golem out of clay from the banks of the Vltava river, and brought it to life through rituals and Hebrew incantations. The Golem was called Josef and was known as Yossele. It was said that he could make himself invisible and summon spirits from the dead.[12] The only care required of the Golem was that he couldn't be active on the day of Sabbath (Saturday).[6] Rabbi Loew deactivated the Golem on Friday evenings by removing the shem before the Sabbath began,[4][6] so as to let it rest on Sabbath.[4] One Friday evening Rabbi Loew forgot to remove the shem, and feared that the Golem would desecrate the Sabbath.[4] A different story tells of a golem that fell in love, and when rejected, became the violent monster seen in most accounts. Some versions have the golem eventually going on a murderous rampage.[12]
The rabbi then managed to pull the shem from his mouth and immobilize him[4][6] in front of the synagogue, whereupon the golem fell in pieces.[4] The Golem's body was stored in the attic genizah of the Old New Synagogue,[12] where it would be restored to life again if needed.[6] According to legend, the body of Rabbi Loew's Golem still lies in the synagogue's attic.[4][12] When the attic was renovated in 1883, no evidence of the Golem was found.[13] Some versions of the tale state that the Golem was stolen from the genizah and entombed in a graveyard in Prague's Žižkov district, where the Žižkov Television Tower now stands. A recent legend tells of a Nazi agent ascending to the synagogue attic during World War II and trying to stab the Golem, but he died instead.[14] A film crew who visited and filmed the attic in 1984 found no evidence either.[13] The attic is not open to the general public.[15]
Some strictly orthodox Jews believe that the Maharal did actually create a golem. Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson (the last Rebbe of Lubavitch) wrote that his father-in-law Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak Schneersohn was asked about his experiences visiting the attic of the Old New Synagogue, and he said that he was unwilling to speak about it. Yosef Yitzchak wrote in his memoirs that he visited the Old New Synagogue's attic, and his father was very grave when he descended back to the ground floor, saying that he had recited psalms for his safety while he visited the attic. Shnayer L. Leiman writes in an article that Yosef Yitzchak's daughter, Chana Gurary (Barry Gurary's mother), related to Rabbi Berel Junik that her father, had seen "[the] form of a man wrapped up and covered. The body was lying on its side," and that he said that he was "very frightened by this sight. I looked around at some of the shemus (discarded ritual objects) that were there and left frightened by what I had seen."[16] Rabbi Chaim Noach Levin also wrote in his notes on Megillas Yuchsin[17] that he heard directly from Rabbi Yosef Shaul Halevi, the head of the Rabbinical court of Lemberg, that he wanted to go see the remains of the Golem but the sexton of the Alt-Neu Shul said that Rabbi Yechezkel Landau had advised against going up to the attic after he himself had gone up.[18] The evidence for this belief has been analyzed from an orthodox Jewish perspective by Shnayer Z. Leiman.[13][19]
Sources of the Prague narrative
The general view of historians and critics is that the story of the Golem of Prague was a German literary invention of the early 19th century. According to Robert Zucker,[20] "the golem legend about R. Chełm moved to Prague and became related with" Rabbi Loew of Prague about mid-18th century. According to John Neubauer, the first writers on the Prague Golem were:
- 1837: Berthold Auerbach, Spinoza
- 1841: Gustav Philippson, Der Golam, eine Legende
- 1841: Franz Klutschak, Der Golam des Rabbi Löw
- 1842: Adam Tendlau Der Golem des Hoch-Rabbi-Löw
- 1847: Leopold Weisel, Der Golem[21]
There is also a published account from 1838, written by the German Czech journalist Franz Klutschack.[22] Cathy Gelbin finds an earlier source in Philippson's The Golem and the Adulteress, published in the Jewish magazine Shulamit in 1834, which describes how the Maharal sent a golem to find the reason for an epidemic among the Jews of Prague,[9][23] although doubts have been expressed as to whether this date is correct.[24] The earliest known source for the story thus far is the 1834 book Der Jüdische Gil Blas by Josef Seligman Kohn.[25][26] The story was repeated in Galerie der Sippurim (1847), an influential collection of Jewish tales published by Wolf Pascheles of Prague.
All these early accounts of the Golem of Prague are in German by Jewish writers. It has been suggested that they emerged as part of a Jewish folklore movement parallel with the contemporary German folklore movement[9][27] and that they may have been based on Jewish oral tradition.[27]
The origins of the story have been obscured by attempts to exaggerate its age and to pretend that it dates from the time of the Maharal. It has been said that Rabbi Yudel Rosenberg (1859–1935)[28] of Tarłów (before moving to Canada where he became one of its most prominent rabbis) originated the idea that the narrative dates from the time of the Maharal. Rosenberg published Nifl'os Maharal (Wonders of Maharal) (Piotrków, 1909)[29] which purported to be an eyewitness account by the Maharal's son-in-law, who had helped to create the Golem. Rosenberg claimed that the book was based upon a manuscript that he found in the main library in Metz. Wonders of Maharal "is generally recognized in academic circles to be a literary hoax".[1][19][30] Gershom Sholem observed that the manuscript "contains not ancient legends but modern fiction".[31] Rosenberg's claim was further disseminated in Chayim Bloch's (1881–1973) The Golem, legends of the Ghetto of Prague (English edition 1925).
The Jewish Encyclopedia of 1906 cites the historical work Zemach David by David Gans, a disciple of the Maharal, published in 1592.[4][32] In it, Gans writes of an audience between the Maharal and Rudolph II: "Our lord the emperor ... Rudolph ... sent for and called upon our master Rabbi Low ben Bezalel and received him with a welcome and merry expression, and spoke to him face to face, as one would to a friend. The nature and quality of their words are mysterious, sealed and hidden."[33] But it has been said of this passage, "Even when [the Maharal is] eulogized, whether in David Gans' Zemach David or on his epitaph …, not a word is said about the creation of a golem. No Hebrew work published in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries (even in Prague) is aware that the Maharal created a golem."[13][21] Furthermore, the Maharal himself did not refer to the Golem in his writings.[13] Rabbi Yedidiah Tiah Weil (1721–1805), a Prague resident, who described the creation of golems, including those created by Rabbis Avigdor Kara of Prague (died 1439) and Eliyahu of Chelm, did not mention the Maharal, and Rabbi Meir Perels' biography of the Maharal[34] published in 1718 does not mention a golem.[9][13]
The Golem of Vilna
There is a similar tradition relating to the Vilna Gaon or "the saintly genius from Vilnius" (1720–1797). Rabbi Chaim Volozhin (Lithuania 1749–1821) reported in an introduction to Siphra Dzeniouta (1818)[35] that he once presented to his teacher, the Vilna Gaon, ten different versions of a certain passage in the Sefer Yetzira and asked the Gaon to determine the correct text. The Gaon immediately identified one version as the accurate rendition of the passage. The amazed student then commented to his teacher that, with such clarity, he should easily be able to create a live human. The Gaon affirmed Rabbi Chaim's assertion, and said that he once began to create a person when he was a child, under the age of 13, but during the process he received a sign from Heaven ordering him to desist because of his tender age.[36] (See also discussion in Hans Ludwig Held, Das Gespenst des Golem, eine Studie aus d. hebräischen Mystik mit einem Exkurs über das Wesen des Doppelgängers[37] München 1927.) The Vilna Gaon wrote an extensive commentary on the Sefer Yetzira,[38] Kol HaTor, in which it is said that he had tried to create a Golem to fight the power of evil at the Gates of Jerusalem.[39] As far as we know, the Vilna Gaon was the only rabbi who had actually claimed that he tried to create a Golem; all such stories about other rabbis were told after their time.
Hubris theme
The existence of a golem is sometimes a mixed blessing. Golems are not intelligent, and if commanded to perform a task, they will perform the instructions literally. In many depictions Golems are inherently perfectly obedient. In its earliest known modern form, the Golem of Chełm became enormous and uncooperative. In one version of this story, the rabbi had to resort to trickery to deactivate it, whereupon it crumbled upon its creator and crushed him.[2] There is a similar hubris theme in Frankenstein, The Sorcerer's Apprentice, and some other golem-derived stories in popular culture, for example: The Terminator. The theme also manifests itself in R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), Karel Čapek's 1921 play which coined the term robot; the play was written in Prague, and while Čapek denied that he modeled the robot after the Golem, there are many similarities in the plot.[40]

Culture of the Czech Republic
The Golem is a popular figure in the Czech Republic. There are several restaurants and other businesses whose names make reference to the creature, a Czech strongman (René Richter) goes by the nickname "Golem",[12] and a Czech monster truck outfit calls itself the "Golem Team".
Abraham Akkerman preceded his article on human automatism in the contemporary city with a short satirical poem on a pair of golems turning human.[41]
Clay Boy variation
A Yiddish and Slavic folktale is the Clay Boy, which combines elements of the Golem and The Gingerbread Man, in which a lonely couple make a child out of clay, with disastrous or comical consequences.[42] In one common Russian version, an older couple whose children have left home make a boy out of clay, and dry him by their hearth. The Clay Boy comes to life; at first the couple are delighted and treat him like a real child, but the Clay Boy does not stop growing, and eats all their food, then all their livestock, and then the Clay Boy eats his parents. The Clay Boy rampages through the village until he is smashed by a quick-thinking goat.[43]
Golem in the 20th and 21st centuries

Mainstream European society adopted the golem in the early 20th century. Most notably, Gustav Meyrink's 1914 novel Der Golem is loosely inspired by the tales of the golem created by Rabbi Loew. Another famous treatment from the same era is H. Leivick's 1921 Yiddish-language "dramatic poem in eight sections", The Golem. In 1923, Romanian composer Nicolae Bretan wrote the one-act opera The Golem, first performed the following year in Cluj and later revived in Denver, Colorado, US in 1990. Nobel prize winner Isaac Bashevis Singer also wrote a version of the legend, [44]and Elie Wiesel wrote a children's book on the legend.[45]
In 1958, Argentinean writer Jorge Luis Borges published a poem about the golem using the image of the golem creature and the creator/creature Rabbi Loew, called Juda Leon. The work addressed a circular argument among the creator and the creation, the name, and the meaning of the name using the argument of Cratylus.
In 1974 CBS Radio Mystery Theater aired an episode entitled The Golem, which takes place during the Holocaust.[46]
In 1974, Marvel Comics published three Strange Tales comic books that included a golem character, and later series included variations of the golem idea.[47]
Piers Anthony's Apprentice Adept series of novels (1980–1990), which features two parallel worlds—one ruled by technology and the other by magic—draws a parallel between robots and golems. Additionally, Grundy the Golem is a character in his Xanth series.
Marge Piercy's 1991 Arthur C. Clarke Award winning He, She and It features a substantial subplot that retells the story of Rabbi Loew and his golem.
The novels of Terry Pratchett in the fictional setting of Discworld also include several golems as characters. For example, they are a plot device in the 1996 novel Feet of Clay, in which the golems create their own golem. The golems of Discworld are also much more intelligent than most representations; though still bound to obedience, if they feel they are mistreated they will take an obstructively literal interpretation of their orders as a form of rebellion. The golems also figure into the sub-series featuring Moist von Lipwig that begins with Going Postal. Von Lipwig's love interest, Adora Belle Dearheart, runs the Golem Trust, whose purpose is to free all golems on the Discworld. Although this also becomes the stated purpose of the golem Dorfl from Feet of Clay, he and the Golem Trust have not interacted professionally as of Making Money.
Golem is a 1996 children's book by David Wisniewski that tells the illustrated story of the golem.
In Cynthia Ozick's 1997 novel The Puttermesser Papers, a modern Jewish woman, Ruth Puttermesser, creates a female golem out of the dirt in her flowerpots to serve as the daughter she never had. The golem helps Puttermesser become elected Mayor of New York before it begins to run out of control. Pete Hamill's 1997 novel Snow In August includes a story of a rabbi from Prague who has a golem.[48]
Michael Chabon's 2000 novel, The Amazing Adventures of Kavalier & Clay, features one of the protagonists, escape artist Josef Kavalier, smuggling himself out of Prague along with the golem. Petrie describes the theme of escape in the novel, culminating in Kavalier's own drawing of a modern graphic novel centered on a golem.[49]
In James Sturm's 2001 graphic novel The Golem's Mighty Swing, a Jewish baseball team in the 1920s creates a golem to help them win their games.[50]
In the Michael Scott novel The Alchemyst, the immortal Dr. John Dee attacked Nicholas Flamel with two golems, which, along with being made of mud, each had a pair of shiny stone "eyes".[51]
Jonathan Stroud's children's fantasy book The Golem's Eye centers on a golem created by magicians in an alternate London.[52] The story depicts the golem as being impervious to magical attacks. The golem is finally destroyed by removing the creation parchment from its mouth.
In Byron L. Sherwin's 2006 novel The Cubs and the Kabbalist, rabbis create a golem named Sandy Greenberg to help baseball's Chicago Cubs win the World Series.[53]
In 2009, horror writer Edward Lee released the novel Golemesque, later retitled The Golem when released in mass market paperback form in which corpses are transformed into golems via mystic rites performed by a satanic sect of Kaballah and by covering the bodies with special clay taken from the banks of the Vltava river in the Czech Republic.
In 2010, medieval mystery author Jeri Westerson, depicted her version of a golem terrifying the streets of fourteenth century London in the third book of her Crispin Guest series, The Demon's Parchment.[54]
In the 2013 Helene Wecker novel The Golem and the Jinni, the golem is a female creature named Chava who is brought to life by a tormented scholar who practices dark Kabbalistic magic.
In the 2014 Jonathan Kellerman and Jesse Kellerman novel The Golem of Hollywood, the golem of Prague comes to 21st century Los Angeles to exact justice on a serial killer. Through a parallel mythological narrative the creation of the Golem is linked to the story of Cain and Abel.
The manga (and later anime adaptation) Soul Eater features golems as giant automatons, made of earth and fueled by magic. Shown as having the word 'emeth' inscribed on their bodies.
Daniel Handler's 2002 novel Watch Your Mouth explores the possibility that a modern-day wife and mom is creating a golem in the basement of her family home. Publishers Weekly wrote of the book: "After the opera-melodrama's weird but tantalizing climax, involving death and the golem myth, the novel actually recovers its narrative balance as the psychologically scarred Joseph turns to New Age recovery paperbacks, which replace opera as Handler's satiric model."[55]
In the 2016 novel 'The Omega Junction' by Alan Scott and Vincent Stevens, a spiritually petitioned entity identified as a Golem appears during a fictional war between Israel and Palestine.
Appearances in film and television
- Inspired by Gustav Meyrink's novel was a classic set of expressionistic silent movies (1915–1920), Paul Wegener's Golem series, of which The Golem: How He Came into the World (also released as The Golem, 1920, USA 1921: the only surviving film of the trilogy) is especially famous. In the first film the golem is revived in modern times before falling from a tower and breaking apart.
- Also notable is Julien Duvivier's Le Golem (1936), a French/Czechoslovakian sequel to the Wegener film.
- A golem had a main role now in the color 1951 Czech movie Císařův pekař a pekařův císař released in the US as The Emperor and the Golem. In The Emperor and the Golem, the shem used to activate the Golem had the form of a small ball placed in his forehead.
- In Terry Pratchett's Going Postal, Golems are derived from golems in Jewish mythology; early forms of a clay robot, supposedly awakened by a spell or priestly words to do people's bidding.
- A 1966 British/American film entitled It!, starring Roddy McDowall, was about the Golem of Prague of Judah Loew.
- A 1995 Episode of Gargoyles The Golem of Prague figures prominently in "Golem",(Season 2, episode 27) One of the characters trying to re-animate it is a descendant of Rabbi Loew.
- A 1996 episode of The Real Adventures of Jonny Quest titled "Rock of Rages" (Season 2, episode 28) centers on the Quest team journeying to the Czech Republic to help translate an artifact that's supposed to be the key to controlling a Golem. They run afoul of an ex-KGB operative who's determined to reactivate the Golem to overthrow the government.
- A 1997 episode of Chris Carter's television series The X-Files, called "Kaddish" (S4E15), was focused on golems. The plot involved a Jewish man dying from an anti-Semitic attack. After being resurrected by his fiancée, he kills the men who murdered him. A golem-like creature can also be seen in the 1999 episode "Arcadia" (S6E15) and the 2016 episode "Home Again" (S10E4).
- A 1997 episode of Extreme Ghostbusters features a golem, created by the son of a rabbi after their synagogue was vandalized by an anti-Semitic gang.
- In 2006, the "Treehouse of Horror XVII" episode of the animated sitcom The Simpsons featured a male and a female golem in the segment "You Gotta Know When to Golem". The two characters were voiced by Richard Lewis and Fran Drescher.
- In Quentin Tarantino's 2009 black comedy war film Inglourious Basterds, Eli Roth's character Sgt. Donny Donowitz is referred to by German soldiers as a golem. Adolf Hitler reacts with fury when informed by an officer of the myths surrounding this certain foe.
- Golett and Golurk are two Pokémon whose creation was inspired by the golem and debuted in the game Pokémon Black and White, released in Japan in September 2010.
- In 2012, two back-to-back episodes of the children's horror series R. L. Stine's The Haunting Hour: The Series featured a golem. The two-part episode, "The Golem" (S3E10&11), tells a story of a golem that was raised by a ved'ma during the second world war to protect a small, Russian village from German soldiers. The ved'ma, named Nadia, keeps the golem dormant thereafter, but as she grows weak on her deathbed, she finds herself no longer able to keep the golem dormant. The golem resurrects and begins terrorising the Russian village it once saved. Nadia's grandchildren, Jeremy and Bonnie, visit the village and lay the golem to rest for good. Jeremy achieves this by blowing a few of his grandmother's ashes onto the golem.
- In 2013, the fantasy/horror series "Sleepy Hollow" episode "The Golem" has a Golem which was made by Jeremy Crane (or Henry Parish/The Horseman of War) when he was beaten at his "Foster Care" home. When Jeremy bled onto the Golem he gave it life and killed his master's enemies. After Jeremy has supposedly died, the Golem was trapped in "Purgatory" until it woke up and started killing the coven which killed Jeremy. The Golem was finally stopped when Jeremy's father, Ichabod, killed the Golem with his blood as Golems can only be stopped by injecting the master's or a relative of the master's blood.
- In 2013, the fantasy/horror series Supernatural episode "Everybody Hates Hitler" (S8E13) features a golem that is used by a secret association of rabbis.; The show explains that the golem has been a protector for the Jewish people for years, especially in times of war or genocide. Specifically, this golem, created by the Judah Initiative during the Holocaust, is being used to fight a society of Nazi necromancers called the Thule Society. Unlike most golem, it can speak and frequently voices its disapproval of the fact that its new master is not an observant Jew.
- In Shonen Jump's Yu-Gi-Oh! Zexal; the main protagonist Yuma Tsukumo, uses a monster card known as Gogogo Golem in his deck.
- In 2014 in the Grimm S04E04 a Golem was called upon by a Rabbi to protect his nephew but it starts killing everyone who scared the boy.
- A 2016 American fantasy film Warcraft features a golem.
- In 2010, a TV series called "Sherlock" mentioned golem in Se:1 Ep:3.I
- On Aug 1, 2006 the Snow Golem makes his first appearance in the animated short, Adventure Time ,when Finn and Jake throw snowballs at his eyes to defeat him. In the television series Adventure Time , the snow golem is in the opening sequence. He lives in the Ice Kingdom. He also appears in Se:1 Ep:3 "Prisoners of Love,". When Finn and Jake knock his head off he puts on a new head of snow shaped like a cat and then meows like one. He is the main character in Se:3 Ep:17 "Thank You," where he appears to live a quiet life in a snow-covered farm house. He is shown eating acorns and a pear, possibly his main food source. He finds a lost Fire Wolf Pup and takes care of it before returning it to its family. Se:5 Ep:30 "Frost & Fire," he is seen evacuating the Ice Kingdom with the Penguins as Flame Princess is melting it.
Games
Golems appear in the fantasy role-playing game Dungeons & Dragons (first published in the 1970s), and the influence of Dungeons & Dragons[56] has led to the inclusion of golems in other video games and in tabletop role-playing games.
- The 1995 Cyberdreams computer game adaptation of the Harlan Ellison story, "I Have no Mouth, and I Must Scream" (1967), features a golem which must be summoned to free prisoners in a Nazi concentration camp.
- Metroid Prime features a boss fight against a golem-like monster named Thardus, who consists of several large rocks animated by Phazon radiation.
- In Clash of Clans, a freemium mobile MMO strategy video game, Golem is a troop with a lot of hit points. When killed, it splits into two smaller units called Golemites.
- In the MMO, Guild Wars M.O.X. the golem, the brainchild of a maverick Asuran inventor named Zinn. Golemancers are Asuran technicians that are responsible for the building, design, maintenance, and usage of the Golems. They seem to be equal parts of both magic and technology.
- In World of Warcraft, golems are portrayed as large, human-like machines that are carved out of various different materials like marble, obsidian etc. They mostly serve as foes to the players, but some are capable of both speech and friendship.
- In Diablo II, golems can be summoned by a Necromancer as a summoning skill.
- In Terraria there is a boss called Golem, it can be summoned in the Altar of the Jungle Temple in the post-Plantera Harmode, although, it's aggressive and hostile. When Golem's stone head has taken full damage, his head leaves the body and reveals his true form.
- In 'Vampire: The Masquerade – Redemption' during the quest Defeat the Golem, Wilhelm and Christof must kill the Golem of Prague in the Jewish quarter, who went mad and killed the Rabbi.
- In Minecraft, there is a neutral mob called an Iron Golem that, when it spawns naturally, protects villagers from hostile mobs. A mob called a Snow Golem can be created by the player, whom it protects by throwing snowballs.
- Pokémon features several creatures based on golems, notably the legendary Pokémon Regirock, Regice, Registeel, and Regigigas, and a Pokémon with a striking resemblance to the Prague Golem known as Golurk. The Pokémon that's actually named "Golem" and its previous evolutions are not actually golems, but are closer to silicon-based life forms.
- The 2016 Deus Ex: Mankind Divided is set in Prague and features a section of the city which is nicknames "Golem City", being a ghetto for mechanically augmented people. The augmented where placed in isolation after an event in which many of them suffered a breakdown and turned on "normal" humans; this most likely led to the place's nickname, as the "golem that turned on its master".[57]
- The Dragon Quest series features enemy golems, notably the Gold Golem, which drops a great deal of gold currency when defeated.
See also
- Czech folklore
- Frankenstein
- Homunculus
- Prometheus
- Pygmalion
- R.U.R.
- The Gingerbread Man and Kolobok (edible "golems")
- Talos
- Galatea (mythology)
- Pinocchio
- Artificial intelligence
- John Murray Spear - attempted to construct an electrically powered Messiah which he referred to as the "New Motive Power"
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Idel, Moshe (1990). Golem: Jewish Magical and Mystical Traditions on the Artificial Anthropoid. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-0160-X. page 296
- 1 2 3 4 Introduction to "The Golem Returns". Retrieved 2011-09-23.
- ↑ J. Simpson, E. Weiner, eds. (1989). "golem". Oxford English Dictionary (2nd ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-861186-2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 GOLEM. Jewish Encyclopedia. Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ Zucker, Robert (2007–2011). "17th Century". "Sefer Yetzirah" Time Line. Retrieved February 11, 2013. citing an anonymous 1630 manuscript concerning the Golem of Chelm. See also Introduction to "The Golem Returns" citing Johannes Reuchlin (1492).
- 1 2 3 4 5 "The Golem Legend". applet-magic.com.
- ↑ Trachtenberg, Joshua (2004) [Originally published 1939]. Jewish Magic and Superstition. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 86. ISBN 9780812218626.
- 1 2 Trachtenberg, Joshua (2004) [Originally published 1939]. Jewish Magic and Superstition. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 85. ISBN 9780812218626.
- 1 2 3 4 Gelbin, C . S., The Golem Returns – From German Romantic Literature to Global Jewish Culture, 1808–2008, University of Michigan, 2011
- ↑ שו"ת שאילת יעב"ץ, ח"ב, סי' פ"ב. Cf. his בירת מגדל עוז, Altona, 1748, p. 259a; מטפחת ספרים, Altona, 1768, p. 45a; and מגילת ספר, ed. Kahana, Warsaw, 1896, p. 4. See also שו"ת חכם צבי, סי' צ"ג, and the references cited in שו"ת חכם צבי עם ליקוטי הערות, Jerusalem, 1998, vol. 1, p. 421 and in the periodical כפר חב"ד, number 351 (1988), p. 51. Cited by Leiman, S.Z., "Did a Disciple of the Maharal Create a Golem?"
- ↑ The tradition is also recorded in ה לחורבנה / תל-אביב : ארגון יוצאי חלם בישראל ובארה"ב, תשמ"א
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bilefsky, Dan (May 10, 2009). "Hard Times Give New Life to Prague's Golem". New York Times. Retrieved 2013-03-19.
According to Czech legend, the Golem was fashioned from clay and brought to life by a rabbi to protect Prague's 16th-century ghetto from persecution, and is said to be called forth in times of crisis. True to form, he is once again experiencing a revival and, in this commercial age, has spawned a one-monster industry.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Leiman, S. Z., The Golem of Prague in Recent Rabbinic Literature
- ↑ Lee-Parritz, Oren. "The Golem Lives On". jewishpost.com. Archived from the original on 1 September 2010. Retrieved 12 January 2011.
- ↑ Old New Synagogue located in Praha, Czech Republic|Atlas Obscura|Curious and Wondrous Travel Destinations. Atlas Obscura. Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ Rabinowitz, Dan. "The Golem of Prague in Recent Rabbinic Literature". http://seforim.blogspot.com.au. Retrieved 28 May 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ מגילת יוחסין. HebrewBooks.org (in Hebrew). Retrieved March 18, 2013.
- ↑ Rabbi Yehudah Yudel Rosenberg. Rabbi Yehudah Yudel Rosenberg. Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- 1 2 Leiman, S.Z., " The Adventure of The Maharal of Prague in London: R. Yudl Rosenberg and The Golem of Prague", Tradition, 36:1, 2002
- ↑ Robert Zucker (2007–2011). "18th Century". "Sefer Yetzirah" Time Line. Retrieved February 19, 2013.
- 1 2 Neubauer, J., "How did the Golem get to Prague?", in Cornis-Pope, M., and Neubauer, J. History of The Literary Cultures of East-Central Europe, John Benjamins, 2010
- ↑ "Notes on the Historical Figures from the Golem Legend - Theater 61 Press". theater61press.com.
- ↑ See also Jewish Encyclopedia (1906): "A legend connected with [the Maharal's] Golem is given in German verse by Gustav Philippson in Allg. Zeit. des Jud. 1841, No. 44 (abridged in Sulamith, viii. 254; translated into Hebrew in Kokebe Yiẓḥaḳ, No. 28, p. 75, Vienna, 1862)"
- ↑ The real new earliest known source in print for the Golem of Prague?. Onthemainline.blogspot.com (2011-03-04). Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ The new earliest known source in print for the Golem of Prague. Onthemainline.blogspot.com (2011-03-03). Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ Kohn, J. S., Der jüdische Gil Blas, Leipzig, 1834, p.20
- 1 2 Golems, forgeries and images of disrobed women in rabbinic literature. Onthemainline.blogspot.com (2010-05-06). Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ "Biography" (PDF). rabbiyehudahyudelrosenberg.com.
- ↑ "נפלאות מהר"ל". HebrewBooks.org. OCLC 233117563. Retrieved March 18, 2013.
- ↑ Sherwin, Byron L. (1985) The Golem Legend: Origins and Implications. New York: University Press of America
- ↑ Sholem, G., Major Trends in Jewish Mysticism, Schocken, 1961
- ↑ HUNGARIAN STUDIES 2. No. 2. Nemzetközi Magyar Filológiai Társaság. Akadémiai Kiadó Budapest [1986]. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ Gans, D., Zemach David, ed. M.Breuer, Jerusalem, 1983, p.145, cited Rabbi Yehudah Yudel Rosenberg and the Maharal's Golem
- ↑ Meir Perels (1718). Megilas Yuchsin. Prague. OCLC 122864700.
- ↑ Sefer Detail: ספרא דצניעותא – אליהו ב"ר שלמה זלמן מווילנא הגר"א). Hebrewbooks.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ http://www.hebrewbooks.org/pdfpager.aspx?sits=1&req=24946&st=%20%u05D2%u05D5%u05DC%u05DD%20
- ↑ http://www.geheimeswissen.com/online-shop3/literatur2/themen/geister/das.html
- ↑ Sefer Detail: ספר יצירה ע"פ הגר"א. Hebrewbooks.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-23.
- ↑ [WorldCat.org] (1942-01-31). Retrieved on 2011-09-23
- ↑ Karel Capek. "R.U.R.- Rossums Universal Robots". translation by Voyen Koreis
- ↑ Akkerman, Abraham (2003–2004). "Philosophical Urbanism and Deconstruction in City-Form: An Environmental Ethos for the Twenty-First Century". Structurist. 43/44: 48–61. External link in
|journal=(help) Published also as Paper CTS-04-06 by the Center for Theoretical Study, Prague. - ↑ Cronan, Mary W. (1917). "Lutoschenka". The Story Teller's Magazine. Vol. 5 no. 1. pp. 7–9.
- ↑ Ginsburg, Mirra (1997). Clay Boy. New York: Greenwillow. ISBN 9780688144098.
- ↑ Singer, Isaac Bashevis (1983-01-01). The Golem. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 9780374327415.
- ↑ Wiesel, Elie (1983-09-01). The Golem (1st edition ed.). Summit Books. ISBN 9780671454838.
- ↑ "CBS Radio Mystery Theater Episode Guide". www.nettally.com. Retrieved 2016-08-01.
- ↑ Weiner, Robert G (2011). "Marvel Comics and the Golem Legend". Shofar: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Jewish Studies. 29 (2): 50–72. doi:10.1353/sho.2011.0044.
Golem Proper in Marvel Comics ... first Golem issue, Strange Tales #174
- ↑ Lipsyte, Robert (May 4, 1997). "Shazam!". New York Times on the Web. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
kabbala and the golem. ... rabbi, a lonely refugee from Prague.
- ↑ Petrie, Windy Counsell (2007). "For Illumination and Escape: Writing and Rgeneration in 21st Century Jewish-American Literature". LITERATÛRA. 49 (5): 105–107. ISSN 0258-0802.
Jewish Golem out of Prague into Vilnius
- ↑ Pustz, Matthew. "The Golem's Mighty Swing". PopMatters. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ "The Alchemyst: The Secrets of the Immortal Nicholas Flamel". Publishers Weekly. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Memmott, Carol; Minzesheimer, Bob (8 September 2004). "Young adult books". USA Today. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Brachear, Manya A. (7 April 2006). "A fictional miracle for the Cubs". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ "Jeri Westerson". stopyourekillingme.com.
- ↑ Publishers Weekly http://www.publishersweekly.com/978-0-312-20940-7. Retrieved 8 July 2016. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ PC Gamer, "How Dungeons & Dragons shaped the modern videogame"
- ↑ "Deus Ex: Mankind Divided can't wait to be interrupted - Kill Screen". 2016-08-24. Retrieved 2016-09-04.
Further reading
- Baer, Elizabeth R. (2012). The Golem Redux: From Prague to Post-Holocaust Fiction. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University. ISBN 0814336264.
- Bilski, Emily B. (1988). Golem! Danger, Deliverance and Art. New York: The Jewish Museum. ISBN 978-0873340496.
- Bloch, Chayim; tr. Schneiderman, H. (1987). The Golem: Mystical Tales of the Ghetto of Prague (English translation from German. First published in 'Oestereschischen Wochenschrift' 1917). New York: Rudolf Steiner Publications. ISBN 0833400258.
- Bokser, Ben Zion (2006). From the World of the Cabbalah. New York: Kessinger.
- Chihaia, Matei (2011). Der Golem-Effekt. Orientierung und phantastische Immersion im Zeitalter des Kinos. Bielefeld: transcript. ISBN 978-3-8376-1714-6.
- Faucheux, Michel (2008). Norbert Wiener, le golem et la cybernétique. Paris: Editions du Sandre.
- Dennis, Geoffrey (2007). The Encyclopedia of Jewish Myth, Magic, and Mysticism. Woodbury (MN): Llewellyn Worldwide. ISBN 0-7387-0905-0.
- Winkler, Gershon (1980). The Golem of Prague: A New Adaptation of the Documented Stories of the Golem of Prague. New York: Judaica Press. ISBN 0-910818-25-8.
- Goldsmith, Arnold L. (1981). The Golem Remembered 1909–1980: Variations of a Jewish Legend. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 0814316832.
- Montiel, Luis (30 June 2013). "Proles sine matre creata: The Promethean Urge in the History of the Human Body in the West". Asclepio. 65 (1): 001. doi:10.3989/asclepio.2013.01.
- Idel, Mosche (1990). Golem: Jewish Magical and Mystical Traditions on the Artificial Anthropoid. Albany (NY): State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-0160-X.
- Rosenberg, Yudl; tr. Leviant, Curt (2008). The Golem and the Wondrous deeds of the Maharal of Prague (first English translation of original in Hebrew, Pietrkow, Poland, 1909). Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-12204-6.
- Tomek, V.V. (1932). Pražské židovské pověsti a legendy. Prague: Končel. Translated (2008) as Jewish Stories of Prague, Jewish Prague in History and Legend. ISBN 1-4382-3005-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Golem. |
- rabbiyehudahyudelrosenberg.com
- Background on the Golem legends
- yutorah.org
- Historical figures in the golem legends
- Essay about the golem and Jewish identity