Henry Moule
Henry Moule /ˈmoʊl/ (1801–1880) was a priest in the Church of England and inventor of the dry earth closet.
Life
Education and priesthood
Moule, sixth son of George Moule, solicitor and banker, was born at Melksham, Wiltshire, on 27 January 1801, and educated at Marlborough Grammar School. He was elected a foundation scholar of St John's College, Cambridge, and graduated B.A. 1821 and M.A. 1826.[1] He was ordained to the curacy of Melksham in 1823, and took sole charge of Gillingham, Dorset, in 1825. He was made vicar of Fordington in the same county in 1829, and remained there for the remainder of his life.
For some years he undertook the duty of chaplain to the troops in Dorchester barracks, for whose use, as well as for a detached district of his own parish, he built in 1846, partly from the proceeds of his published ‘Barrack Sermons,’ 1845 (2nd edit. 1847), a church known as Christ Church, West Fordington. In 1833 his protests brought to an end the evils connected with the race meetings at Dorchester.
Dry earth closet
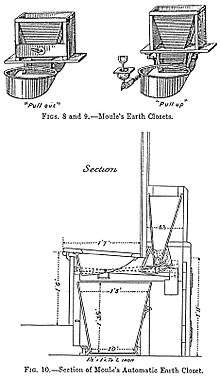
During the cholera epidemics of 1849 and 1854 his exertions were unwearied. Impressed by the insalubrity of the houses, especially in the summer of 1858 (the Great Stink) he turned his attention to sanitary science, and invented what is called the dry earth system. In partnership with James Bannehr, he took out a patent for the process (No. 1316, dated 28 May 1860). Among his works bearing on the subject were: ‘The Advantages of the Dry Earth System,’ 1868; ‘The Impossibility overcome: or the Inoffensive, Safe, and Economical Disposal of the Refuse of Towns and Villages,’ 1870; ‘The Dry Earth System,’ 1871; ‘Town Refuse, the Remedy for Local Taxation,’ 1872, and ‘National Health and Wealth promoted by the general adoption of the Dry Earth System,’ 1873.
His system was adopted in private houses, in rural districts, in military camps, in many hospitals, and extensively in the British Raj.
Later years
He also wrote an important work, entitled ‘Eight Letters to Prince Albert, as President of the Council of the Duchy of Cornwall,’ in 1855, prompted by the condition of Fordington parish, belonging to the duchy. In two letters in the Times of 24 February and 2 April 1874 he advocated a plan for extracting gas from Kimmeridge shale. He died at Fordington vicarage on February 3, 1880.
Family
Moule married Mary Mullett Evans in 1824; she died on 21 August 1877. They had eight sons:[2]
- Henry Joseph Moule (1825 - 1904), watercolour artist and friend of Thomas Hardy
- George Evans Moule (1828 - 1912), missionary and Bishop of Mid China
- Frederick John Moule (1830 - 1900), Vicar of St. Peters Church, Yaxley
- Horatio Mosley Moule (1832 - 1873), short-lived friend of Thomas Hardy
- Charles Walter Moule (1834 - 1921), librarian and president of Corpus Christi College, Cambridge
- Arthur Evans Moule (1836 - 1916), missionary & Archdeacon of Mid China
- Christopher Cooper Moule (1838 - 1839), who died an Infant
- Handley Carr Glyn Moule (1841 - 1920), a well-known theologian and scholar and the Bishop of Durham
A great-grandson, C. F. D. Moule, was a notable Anglican theologian.
Publications
In addition to the works already mentioned, and many single sermons and pamphlets, Moule wrote
- Two Conversations between a Clergyman and one of his Parishioners on the Public Baptism of Infants, 1843.
- Scraps of Sacred Verse, 1846.
- Scriptural Church Teaching, 1848.
- Christian Oratory during the first Five Centuries, 1859.
- My Kitchen-Garden: by a Country Parson, 1860.
- Manure for the Million. A Letter to the Cottage Gardeners of England, 1861; 11th thousand, 1870.
- Self-supporting Boarding Schools and Day Schools for the Children of the Industrial Classes, 1862; 3rd ed. 1871.
- Good out of Evil. A Series of Letters publicly addressed to Dr. Colenso, 1863.
- Pardon and Peace: illustrated by ministerial Memorials, to which are added some Pieces of Sacred Verse, 1865.
- Our Home Heathen, how can the Church of England get at them, 1868.
- “These from the Land of Sinim.” The Narrative of the Conversion of a Chinese Physician [Dzing, Seen Sang], 1868.
- Land for the Million to rent. Addressed to the Working Classes of England; by H. M., 1870.
- On the Warming of Churches, 1870.
- The Science of Manure as the Food of Plants, 1870.
- The Potatoe Disease, its Cause and Remedy. Three Letters to the Times, 1872.
- Harvest Hymns, 1877.
See also
- Composting toilet
- Constructed wetland
- Ecological sanitation
- Pail closet
- Water conservation
- Sustainable sanitation
References
- ↑ "Moule, Henry (ML817H)". A Cambridge Alumni Database. University of Cambridge.
- ↑ Biographie Henry Moule
- Attribution
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: "Moule, Henry". Dictionary of National Biography. London: Smith, Elder & Co. 1885–1900.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: "Moule, Henry". Dictionary of National Biography. London: Smith, Elder & Co. 1885–1900.