Hog Island (Michigan)
 Hog Island | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Lake Michigan |
| Coordinates | 45°47′30″N 85°21′58″W / 45.79167°N 85.36611°WCoordinates: 45°47′30″N 85°21′58″W / 45.79167°N 85.36611°W |
| Area | 3.24 sq mi (8.4 km2) |
| Administration | |
| State | Michigan |
| County | Charlevoix County |
| Township | St. James Township |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited |
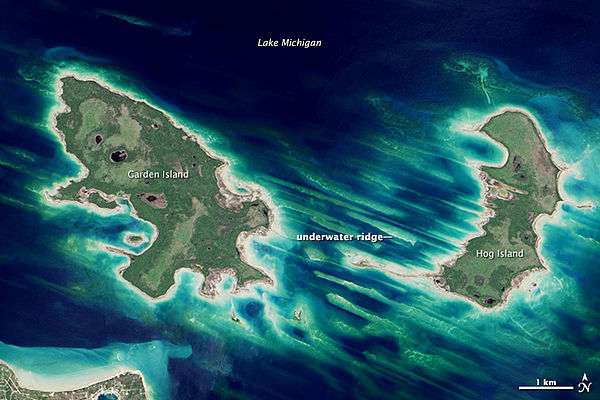
Hog Island, an uninhabited 2,075-acre (8 km²) island in Lake Michigan, is the fourth largest island in the Beaver Island archipelago. It is owned by the U.S. state of Michigan as part of the Beaver Islands State Wildlife Research Area and is administered by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources.
Hog Island is approximately 4 miles (6.5 km) long in a north-south direction. Its low, swampy terrain is of significant interest to naturalists because it is one of the least-disturbed islands in Lake Michigan. The island's wetlands are important spawning grounds for yellow perch and smallmouth bass, as well as lake birds that feed on fish, such as the common tern, listed as threatened within Michigan as of 2006.
Three endemic riparian plant species, Houghton's goldenrod, the Lake Huron tansy, and Pitcher's thistle, have been identified on Hog Island. All three plants are listed as threatened within Michigan as of 2006.
Old-growth northern hardwood and boreal softwood groves continued to exist on Hog Island as of 2006.
View
