Homorhythm

Introduction to Sousa's "Washington Post March," m. 1-7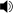 Play features octave doubling[1] and a homorhythmic texture.
Play features octave doubling[1] and a homorhythmic texture.
In music, homorhythm is a texture where there is a "sameness of rhythm in all parts" [2] or "very similar rhythm" as would be used in simple hymn or chorale settings. All voices sing the same rhythm. This texture results in a homophonic texture, which is a blocked chordal texture.
Homorhythmic texture delivers the text with clarity and emphasis.
It may also be called chordal style, familiar style, note-against-note style, isometric, and homophonic.

Homophony in Tallis' "If ye love me," composed in 1549. The voices move together using the same rhythm, and the relationship between them creates chords: the excerpt begins and ends with an F major triad. 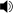 Play
Play
Sources
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.