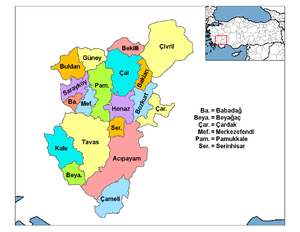
Honaz
| Honaz (Colossae) | |
|---|---|
 Honaz (Colossae) | |
| Coordinates: 37°45′27.51″N 29°15′50.65″E / 37.7576417°N 29.2640694°ECoordinates: 37°45′27.51″N 29°15′50.65″E / 37.7576417°N 29.2640694°E | |
| Country |
|
| Province | Denizli |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Turgut Devecioğlu (AKP) |
| • Kaymakam | Turgut Gülen |
| Area[1] | |
| • District | 496.54 km2 (191.72 sq mi) |
| Population (2012)[2] | |
| • Urban | 10,859 |
| • District | 31,470 |
| • District density | 63/km2 (160/sq mi) |
| Post code | 20330 |
| Website |
www |
Honaz is a town and a district of Denizli Province in the Aegean Region. It covers an area of 504 km2 (195 sq mi). The population (as of 2010) was 9,830 (the central town) and 30,530 (including rural area).
Honaz is about 20 km (12 mi) east of the city of Denizli on the slopes of the mountain of the same name - Mount Honaz (Honaz Dağı). The mountain is the highest peak in Turkey's Aegean Region (2517 m). Just north of Honaz is Honaz Stream (Honaz Çayı), known in ancient times as the Lycus.
History
In antiquity it was known as Colossae. At 500 BC Colossae was founded by the Phrygians, and then passed into the hands of the Ancient Greeks. Herodotus and Xenophon both record the passage of Greek and Persian armies though here during the Persian Wars, at that time it was a large Phrygian city. A few ruins of the ancient city remain. Like many other ancient cities of the region, Colossae was destroyed by earthquakes, with little surviving.
In the Byzantine period its name was Chonai. The city and a bishopric of Chonai was established at the location of the present Honaz township by the Byzantines during the Arab invasions of the 7th century. Being further up the mountain the location was easier to defend. Following centuries of Byzantine rule the town was first captured by the Seljuk Turks in 1070, but was then reconquered during the Komnenian period. During the reign of Manuel I Komnenos it prospered as a frontier town, a trading and pilgrimage venue for both Christians and Muslims. The Byzantine chronicler Niketas Choniates (c. 1155-1215/1216) was a native of the city. Chonai was plundered twice by local independent warlords backed by the Turks (by Theodoros Mankaphas in late 1180s and by Pseudo-Alexios in 1192). It finally fell to the Seljuks soon afterwards. Kaykhusraw I promised to return it to the Byzantines, but in view of the collapse of imperial power caused by the Fourth Crusade and the Latin conquest of Constantinople he decided rather to assign it to his father-in-law, the Byzantine renegade Manuel Maurozomes. The latter held it as an autonomous lordship together with Laodikeia, near present-day Denizli, from 1205 until his death ca. 1230. Theodore I Laskaris came to accept it in a 1206 agreement with Kaykhusraw I.
There is a Seljuk fortress in Honaz, and the Murat Mosque which dates back to the reign of Ottoman Sultan Murat II (imperabat 1404-1451).
In the 20th century, Honaz was one of the places where the Vallahades or Valaades (ethnic Greek muslims from southwest Greek Macedonia) were forced to resettle during the Population exchange between Greece and Turkey of 1922-23.[3]
Honaz today
Today the economy of Honaz is centred on growing cherries, 80% of the crop being exported from Turkey, generating up to 35 million dollars of income per annum. There is an annual cherry festival in the town. Tomatoes and other fruits and vegetables are grown too including a local variety of oleaster.
Honaz is also the homeland of a number of well-known pehlivans (oil wrestlers) including the 3-time national champion Hüseyin Çokal.
In the nearby depending township of Kaklık, there is a large cave called " Kaklık Cave" or "Kaklık Mağarası" which attracts visitors from all over the country. A spring that spurts out on the surface only to flow back underground shortly afterwards through the cave in cascading layers of limestone and travertine caused Kaklık to appear very much like a subterranean Pamukkale.
References
- ↑ "Area of regions (including lakes), km²". Regional Statistics Database. Turkish Statistical Institute. 2002. Retrieved 2013-03-05.
- ↑ "Population of province/district centers and towns/villages by districts - 2012". Address Based Population Registration System (ABPRS) Database. Turkish Statistical Institute. Retrieved 2013-02-27.
- ↑ Koukoudis, Asterios (2003). The Vlachs: Metropolis and Diaspora. Zitros. p.198
- Klaus Belke, Norbert Mersich, Phrygien und Pisidien, Tabula Imperii Byzantini VII, Wien 1990, s. 309-311.
- O City of Byzantium, Annals of Niketas Choniates, ed. Harry J. Magoulias, Detroit, MI 1984.
- Claude Cahen, The Formation of Turkey. The Seljukid Sultanate of Rum: Eleventh to Fourteenth Century, Harlow 2001.
- Information about Colossae on the Denizli Council website (English)
- Places in the Bible - Colossae
- Coinage of Colossae
- Holy Land photos Colossae