1974 Pacific hurricane season
| |
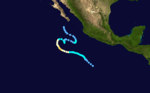
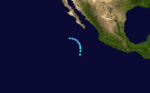
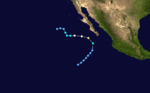
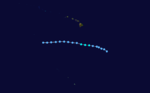
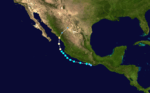
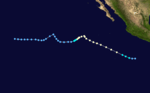
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
May 28, 1974 |
| Last system dissipated |
October 24, 1974 |
| Strongest storm1 |
Maggie – 934 mbar (hPa) (27.58 inHg), 140 mph (220 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Total depressions |
25 |
| Total storms |
18 |
| Hurricanes |
11 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
3 |
| Total fatalities |
18-33 |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
| 1Strongest storm is determined by lowest pressure |
Pacific hurricane seasons
1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976 |
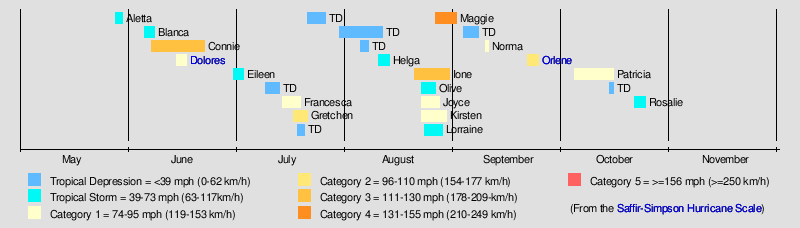
The 1974 Pacific hurricane season featured one of the most active periods of tropical cyclones on record with five storms existing simultaneously.[1] The season officially started May 15 in the eastern Pacific, and June 1 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeast Pacific Ocean.
With seventeen storms, this season was slightly above average. At eleven, the number of hurricanes was also above average. In the central Pacific, one tropical storm formed. Very unusually, on August 26 there were six systems active: Ione, Olive, Kirsten, Lorraine, Joyce, and Maggie. Olive was a Central Pacific storm and had weakened to a tropical depression by this time. The other five were of at least tropical storm intensity simultaneously and remained so until 06Z Aug 27. Five storms were also active 18Z Aug 23-06Z Aug 24.
Season summary
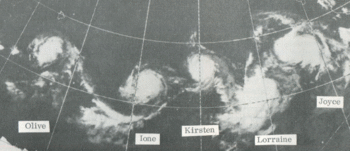
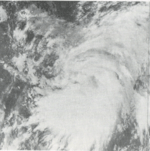
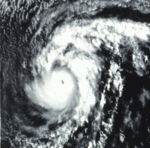
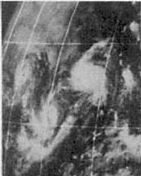
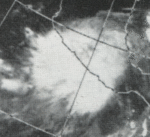
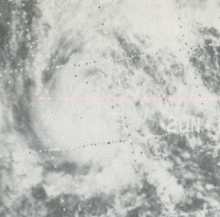
This weather satellite image (from left to right) of Tropical Cyclones Olive, Ione, Kirsten, Lorraine, and Joyce was taken on August 23, 1974
The overall activity of the 1974 season was near normal, with 25 tropical cyclones developing. Of these storms, 18 were named, 11 became hurricanes and 3 reached major hurricane status. Although the overall number of storms was normal, an exceptionally active period took place from August 19 through September 1. During this two-week span, six storms developed, five of which were active simultaneously on August 23: Ione, Joyce, Kirsten, Lorraine and Olive. Of the season's 447 bulletins, 139 were issued during this period.[1]
Storms
Tropical Storm Aletta
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 28 – May 29 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical disturbance formed to the south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec on May 24; sea surface temperatures (SST's) in the area were around 88 °F (31 °C). The disturbance slowly organized over the next 60 hours, as it was detaching from the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). On May 28, Tropical Storm Aletta formed. It recurved to the northeast and made landfall in western Mexico on May 30. Effects were minimal.
Tropical Storm Blanca
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 5 – June 8 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Blanca was a short-lived storm, and did not affect land.
Hurricane Connie
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 7 – June 22 |
| Peak intensity |
125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min) 942 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Connie was the first major hurricane. It took a bizarre, twisting path but never made landfall.
Hurricane Dolores
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 14 – June 17 |
| Peak intensity |
80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
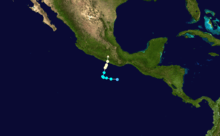
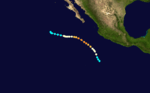
On June 13, a tropical disturbance south of Mexico showed signs of development. The following day, the system rapidly developed into Tropical Storm Dolores. By June 15, an eye-like feature appeared on satellite imagery as Dolores attained hurricane status. With peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h), the storm made landfall near Acapulco. Once onshore, Dolores rapidly dissipated and was last noted on June 17.[2]
Across Southwestern Mexico, Hurricane Dolores produced heavy rains that triggered widespread flooding and mudslides. Numerous roads sustained damage, separating communities from surrounding areas.[3] At least 18 people were killed and 32 others were injured by the storm.[4] Additionally, an estimated 173,000 people were affected across the country.[5]
Tropical Storm Eileen
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 30 – July 3 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 997 mbar (hPa) |
In late June, a tropical disturbance developed well to the southwest of Mexico. By June 30, sufficient convection had developed over a newly formed area of low pressure to warrant advisories on a tropical depression.[2] Tracking northward,[6] the system gradually attained tropical storm intensity. Due to the lack of direct observations, Eileen's intensity was based solely off satellite estimates;[2] these estimates indicated the cyclone to have attained peak winds of 40 mph (65 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 997 mbar (hPa; 29.44 inHg).[1] By July 2, Eileen entered a region of stable air, causing convection to diminish. The storm degenerated into a non-convective low late on July 3 as it turned northwestward.[2] The remnants of Eileen were last noted on July 4 well to the southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[6]
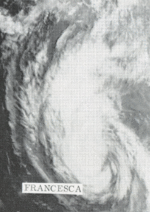
Hurricane Francesca
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 14 – July 19 |
| Peak intensity |
80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
Francesca was a category 1 hurricane. It neared Baja California by the 17th but turned away before striking.
Hurricane Gretchen
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 17 – July 21 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) 982 mbar (hPa) |
Gretchen was a category 2 hurricane that threatened southern Baja California, but it turned away without affecting land.
Tropical Storm Helga
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 10 – August 13 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Helga was a storm that did not affect land.
Hurricane Ione
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 20 – August 31 |
| Peak intensity |
115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 954 mbar (hPa) |
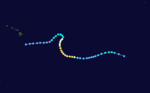
On August 19, a tropical disturbance was identified near the Intertropical Convergence Zone well to the east-southeast of Hawaii. The next morning, the system developed into a tropical depression as it tracked towards the west-northwest. Later on August 20, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Ione. However, cold air from a nearby stratocumulus field became entrained in Ione's circulation, causing it to weaken to a depression 24 hours later. Now moving towards the west-southwest, the system remained weak for nearly two days. On August 23, Ione rapidly intensified as convection deepened and an eye feature appeared on satellite imagery. The storm subsequently attained hurricane status that evening before crossing 140°W and entering the Central Pacific.[2]
Intensification slowed on August 24 as Ione attained winds in excess of 100 mph (155 km/h). Over the next day, the system turned northward and attained its peak intensity late on August 25 with winds of 115 mph (185 km/h).[7] Additionally, the storm attained an estimated minimum central pressure of 954 mbar (hPa; 28.17 inHg).[1] Shortly after reaching this intensity, Ione weakened as it began a U-shaped curve, tracking northeast before turning towards the southwest. During the afternoon of August 27, the system was downgraded to a tropical storm. By August 29, Ione further weakened to a tropical depression and acquired a westward track before dissipating south of Hawaii on August 31.[7]
Tropical Storm Olive
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 22 – August 25 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1009 mbar (hPa) |
On August 21, just one day after Ione formed, another disturbance formed along the ITCZ and developed into a tropical depression the following day. Tracking generally towards the west, the system slowly organized. By August 23, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Olive well to the south of Hawaii. Olive briefly attained winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) before weakening to a tropical depression on August 24. Convection waned for the next 30 hours and Olive degenerated into a disturbance on August 25. The remnant vortex of the storm was last noted on August 26 roughly 210 mi (340 km) southeast of Johnston Island.[7]
Hurricane Joyce
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 22 – August 27 |
| Peak intensity |
85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
Joyce was a weak hurricane that did not affect land.
Hurricane Kirsten
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 22 – August 29 |
| Peak intensity |
85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
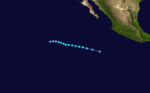
Hurricane Kirsten took an erratic path. After traveling northwest for a while, it reversed direction and backtracked to almost where it started. It then reversed direction again and underwent a Fujiwhara interaction with Hurricane Ione.
Tropical Storm Lorraine
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 23 – August 28 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Lorraine took an erratic, Z-shaped path during its life. It formed on August 23 and dissipated August 28.
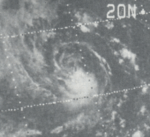
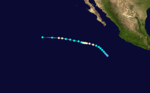
Hurricane Maggie
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 26 – September 1 |
| Peak intensity |
140 mph (220 km/h) (1-min) 928 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Maggie was the strongest storm of the season. It reached Category 4 but never threatened land.
Hurricane Norma
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 9 – September 10 |
| Peak intensity |
75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
On September 7, a large area of thunderstorms was identified southwest of Mexico. Over the following two days, the system gradually organized as it moved northwest and was declared a tropical depression on September 9. Upon being classified a depression, the storm acquired a more northerly track and soon attained tropical storm status. The newly christened Tropical Storm Norma maintained a general northward track towards Mexico.[2] On September 10, Norma briefly strengthened into a hurricane, with peak winds estimated at 75 mph (120 km/h) before making landfall west of Acapulco.[1][6] Within hours of moving onshore, the storm rapidly deteriorated and dissipated later that day.[2]
Heavy rains produced by Norma triggered mudslides in and around Acapulco, resulting in three fatalities.[1]
Hurricane Orlene
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 21 – September 24 |
| Peak intensity |
105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 978 mbar (hPa) |
Orlene was a part of Hurricane Fifi. Fifi weakened to a depression and crossed into the east Pacific. The system restrengthened and was renamed Tropical Storm Orlene. Orlene hugged the coast before recurving to the northeast and made landfall shortly after reaching Category 2 intensity.
Hurricane Patricia
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 4 – October 15 |
| Peak intensity |
90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 964 mbar (hPa) |
On October 3, an area of disturbed weather was identified several hundred miles southwest of El Salvador. Over the following day, an area of low pressure developed within the disturbance and was subsequently declared a tropical depression. Tracking west-northwestward, the depression eventually intensified into Tropical Storm Patricia on October 6 in light of a significant in convection. The next day, a ragged eye developed and the storm strengthened into a hurricane. Intensification continued through the evening of October 9,[2] at which time Patricia attained its peak intensity with winds estimated at 90 mph (150 km/h).[nb 1][1] Within a day of peaking, the hurricane turned southwestward and weakened. Gradual degradation of the storm took place over the next few days with little convection present over the system by October 11. By then, Patricia had weakened to a tropical depression. On October 15, Patricia was declassified a tropical cyclone as only a low-level circulation devoid of convection remained.[2] The remnants of the storm were last noted on October 17 well to the east-southeast of Hawaii.[6]
Tropical Storm Rosalie
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 20 – October 24 |
| Peak intensity |
65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
On October 18, pronounced thunderstorm activity developed along the ITCZ. Gradually, a tropical disturbance formed within this region well to the west-southwest of Mexico. During the morning of October 20, convection rapidly increased and the system was classified as Tropical Storm Rosalie. Visible satellite imagery revealed only an "oval-shaped" area of thunderstorms with no banding features.[2] Tracking generally towards the west-southwest, Rosalie attained its peak intensity with winds estimated around 65 mph (100 km/h) on October 21.[6] Later that day, the system neared an area of more stable air.[2] Gradual weakening ensued over the following days, with Rosalie degrading to tropical depression status on October 23.[6] Void of convection, the remnant swirl of Rosalie was last noted on October 24 well to the southeast of Hawaii.[2][6]
Other storms
In addition to the eighteen named storms, there were seven tropical depression during the course of the season.[1]
- July 9 – 13, 35 mph (55 km/h)[8]
- July 18 – 20, 35 mph (55 km/h)[9]
- July 21 – 26, 35 mph (55 km/h)[10]
- July 31 – August 11, 35 mph (55 km/h) 1001 mbar (hPa; 29.56 inHg)
- August 5 – 7, 35 mph (55 km/h)[11]
- September 3 – 7, 35 mph (55 km/h) 1001 mbar (hPa; 29.56 inHg)
- October 14 – 15, 30 mph (45 km/h) 1004 mbar (hPa; 29.65 inHg)
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms that formed in the eastern Pacific in 1974. It is the same list as the 1970 season, except for Aletta, which replaced Adele. This is the last time this list was used to name storms, as modern naming began in 1978. Despite this, the names Aletta, Blanca, Dolores, Orlene, Patricia and Selma were put on modern naming lists.
- Aletta
- Blanca
- Connie
- Dolores
- Eileen
- Francesca
- Gretchen
|
- Helga
- Ione
- Joyce
- Kirsten
- Lorraine
- Maggie
- Norma
|
- Orlene
- Patricia
- Rosalie
- Selma (unused)
- Toni (unused)
- Viviam (unused)
- Winona (unused)
|
In this season, the Central Pacific named storms from the western Pacific’s typhoon list. One name, Olive, was used.
Season effects
This is a table of all of the storms in the 1974 Pacific hurricane season. It includes their durations, peak intensities, names, landfall(s), damages, and death totals. Deaths in parentheses are additional and indirect (an example of an indirect death would be a traffic accident), but are still storm-related. Damage and deaths include totals while the storm was extratropical or a wave or a low. All of the damage figures are in 1974 USD.
1974 Pacific hurricane statistics
Storm
name |
Dates active |
Storm category
at peak intensity |
Max 1-min
wind
mph (km/h) |
Min.
press.
(mbar) |
Areas affected |
Damage
(millions USD) |
Deaths
|
| Aletta |
May 28 – 29 |
Tropical storm |
60 (95) |
992 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Blanca |
June 5 – 8 |
Tropical storm |
60 (95) |
992 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Connie |
June 7 – 22 |
Category 3 hurricane |
125 (205) |
942 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Dolores |
June 14 – 17 |
Category 1 hurricane |
80 (130) |
973 |
Southwestern Mexico (Guerrero) |
4 |
18 – 28
|
| Eileen |
June 30 – July 3 |
Tropical storm |
40 (65) |
997 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
July 9 – 13 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
N/A |
None |
None |
0
|
| Francesca |
July 14 – 19 |
Category 1 hurricane |
80 (130) |
973 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Gretchen |
July 17 – 21 |
Category 2 hurricane |
100 (155) |
987 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
July 18 – 20 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
N/A |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
July 21 – 26 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
N/A |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
July 31 – August 11 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
1001 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
August 5 – 7 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
N/A |
None |
None |
0
|
| Helga |
August 10 – 13 |
Tropical storm |
45 (75) |
990 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Ione |
August 20 – 31 |
Category 3 hurricane |
115 (185) |
954 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Olive |
August 22 – 25 |
Tropical storm |
45 (75) |
1009 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Joyce |
August 22 – 27 |
Category 1 hurricane |
85 (140) |
973 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Kirsten |
August 22 – 29 |
Category 1 hurricane |
85 (140) |
973 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Lorraine |
August 23 – 28 |
Tropical storm |
50 (85) |
987 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Maggie |
August 26 – September 1 |
Category 4 hurricane |
140 (220) |
928 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
September 3 – 7 |
Tropical depression |
35 (55) |
1001 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Norma |
September 9 – 10 |
Category 1 hurricane |
75 (120) |
978 |
Southwestern Mexico (Guerrero) |
N/A |
3
|
| Orlene |
September 21 – 24 |
Category 2 hurricane |
105 (165) |
987 |
Southwestern Mexico, Western Mexico, Northwest Mexico (Sinaloa) |
N/A |
0
|
| Patricia |
October 4 – 15 |
Category 1 hurricane |
90 (150) |
964 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Depression |
October 14 – 15 |
Tropical depression |
30 (45) |
1004 |
None |
None |
0
|
| Rosalie |
October 20 – 24 |
Tropical storm |
65 (100) |
987 |
None |
None |
0 |
| Season Aggregates |
| 25 cyclones |
May 28 – October 24 |
| 140 (220) |
928 |
|
4 |
21 – 31 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ The peak intensity of Patricia is based off the values listed in the season's Monthly Weather Review.[1] According to the Hurricane Database, the storm attained peak winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 964 mbar (hPa; 28.47 inHg).[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Robert A. Baum (April 1975). "Eastern North Pacific Tropical Cyclones, 1974. Part 1" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. American Meteorological Society. 103 (4). Bibcode:1975MWRv..103..301B. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1975)103<0301:ENPTCP>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sharon Towry (June 1975). "Eastern North Pacific Tropical Cyclones, 1974. Part 2" (PDF). Monthly Weather Review. American Meteorological Society. 103 (6). Bibcode:1975MWRv..103..550T. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1975)103<0550:ENPTCP>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Hurricane kills nine". Associated Press. The Windsor Star. June 18, 1974. p. 40. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Ciclones Tropicales". Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (in Spanish). Secretaría De Gobernación. 2011. Archived from the original on April 25, 2012. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Hurricane kills 22 in Acapulco". United Press International. The Vancouver Sun. June 19, 1974. p. 48. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Eastern North Pacific Hurricane Database: 1949-2010". Hurricane Research Division. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2011. Retrieved December 6, 2011.
- 1 2 3 "The 1974 Central Pacific Tropical Cyclone Season". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. March 4, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ↑ "1974 Missing (1974190N16242)". International Best Track Archive. 2011. Retrieved December 8, 2011.
- ↑ "1974 Missing (1974199N08262)". International Best Track Archive. 2011. Retrieved December 8, 2011.
- ↑ "1974 Missing (1974202N10263)". International Best Track Archive. 2011. Retrieved December 8, 2011.
- ↑ "1974 Missing (1974217N12226)". International Best Track Archive. 2011. Retrieved December 8, 2011.
External links
|
|---|
|
| |
|
-
 Book Book
-
 Category Category
-
 Portal Portal
-
 WikiProject WikiProject
-
 Commons Commons
|