Integrated circuit

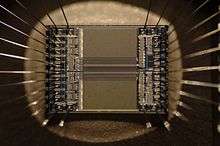
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. An IC can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components - a modern chip may have several billion transistors in an area the size of a human fingernail. Over the past half century, the size, speed, and capacity of chips has increased enormously, driven by technical advances that allow more and more transistors on chips of the same size. These advances, roughly following Moore's law, allow a computer chip of 2016 to have millions of times the capacity and thousands of times the speed of the computer chips of the early 1970s. Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs.
ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.
ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) because of their small size and close proximity. The main disadvantage of ICs is the high cost to design them and fabricate the required photomasks. This high initial cost means ICs are only practical when high production volumes are anticipated.
Terminology
An integrated circuit is defined as:[1]
A circuit in which all or some of the circuit elements are inseparably associated and electrically interconnected so that it is considered to be indivisible for the purposes of construction and commerce.
Circuits meeting this definition can be constructed using many different technologies, including thin-film transistor, thick film technology, or hybrid integrated circuit. However, in general usage integrated circuit has come to refer to the single-piece circuit construction originally known as a monolithic integrated circuit.[2][3]
Invention
Early developments of the integrated circuit go back to 1949, when German engineer Werner Jacobi (Siemens AG)[4] filed a patent for an integrated-circuit-like semiconductor amplifying device[5] showing five transistors on a common substrate in a 3-stage amplifier arrangement. Jacobi disclosed small and cheap hearing aids as typical industrial applications of his patent. An immediate commercial use of his patent has not been reported.
The idea of the integrated circuit was conceived by Geoffrey W.A. Dummer (1909–2002), a radar scientist working for the Royal Radar Establishment of the British Ministry of Defence. Dummer presented the idea to the public at the Symposium on Progress in Quality Electronic Components in Washington, D.C. on 7 May 1952.[6] He gave many symposia publicly to propagate his ideas, and unsuccessfully attempted to build such a circuit in 1956.
A precursor idea to the IC was to create small ceramic squares (wafers), each containing a single miniaturized component. Components could then be integrated and wired into a bidimensional or tridimensional compact grid. This idea, which seemed very promising in 1957, was proposed to the US Army by Jack Kilby and led to the short-lived Micromodule Program (similar to 1951's Project Tinkertoy).[7] However, as the project was gaining momentum, Kilby came up with a new, revolutionary design: the IC.

Newly employed by Texas Instruments, Kilby recorded his initial ideas concerning the integrated circuit in July 1958, successfully demonstrating the first working integrated example on 12 September 1958.[8] In his patent application of 6 February 1959,[9] Kilby described his new device as "a body of semiconductor material … wherein all the components of the electronic circuit are completely integrated."[10] The first customer for the new invention was the US Air Force.[11]
Kilby won the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physics for his part in the invention of the integrated circuit.[12] His work was named an IEEE Milestone in 2009.[13]
Half a year after Kilby, Robert Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor developed his own idea of an integrated circuit that solved many practical problems Kilby's had not. Noyce's design was made of silicon, whereas Kilby's chip was made of germanium. Noyce credited Kurt Lehovec of Sprague Electric for the principle of p–n junction isolation, a key concept behind the IC.[14] This isolation allows each transistor to operate independently despite being parts of the same piece of silicon.
Fairchild Semiconductor was also home of the first silicon-gate IC technology with self-aligned gates, the basis of all modern CMOS computer chips. The technology was developed by Italian physicist Federico Faggin in 1968, who later joined Intel in order to develop the very first single-chip Central Processing Unit (CPU) (Intel 4004), for which he received the National Medal of Technology and Innovation in 2010.
Advances
Advances in IC technology, primarily smaller features and larger chips, have allowed the number of transistors in an integrated circuit to double every two years, a trend known as Moore's law. This increased capacity has been used to decrease cost and increase functionality. In general, as the feature size shrinks, almost every aspect of an IC's operation improves. The cost per transistor and the switching power consumption per transistor go down, while the memory capacity and speed go up, through the relationships defined by Dennard scaling.[15] Since these speed, capacity, and power consumption gains are apparent to the end user, there is fierce competition among the manufacturers to use finer geometries. Over the years, transistor sizes have decreased from 10s of microns in the early 1970s to around 14 nanometers in 2014[16][17] with a corresponding million-fold increase in transistors per unit area. As of 2016, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 600 mm2, with up to 25 million transistors per mm2.[18]
The expected shrinking of feature sizes, and the needed progress in related areas, was forecast for many years by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). The final ITRS was issued in 2016, and it is being replaced by the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems.[19]
Initially, ICs were strictly electronic devices. The success of ICs has led to the integration of other technologies, in the attempt to obtain the same advantages of small size and low cost. These technologies include mechanical devices, optics, and sensors.
- Very small mechanical devices driven by electricity can be integrated onto chips, a technology known as microelectromechanical systems. These devices were developed in the late 1980s[20] and are used in a variety of commercial and military applications. Examples include DLP projectors, inkjet printers, and accelerometers and MEMS gyroscopes used to deploy automobile airbags.
- Since the early 2000s, the integration of optical functionality (optical computing) into silicon chips has been actively pursued in both academic research and in industry resulting in the successful commercialization of silicon based integrated optical transceivers combining optical devices (modulators, detectors, routing) with CMOS based electronics.[21] Integrated optical circuits are also being developed.
- Integrated circuits are also being developed for sensor applications in medical implants or other bioelectronic devices.[22] Special sealing techniques have to be applied in such biogenic environments to avoid corrosion or biodegradation of the exposed semiconductor materials.[23]
As of 2016, the vast majority of all transistors are fabricated in a single layer on one side of a chip of silicon in a flat 2-dimensional planar process. Researchers have produced prototypes of several promising alternatives, such as:
- various approaches to stacking several layers of transistors to make a three-dimensional integrated circuit, such as through-silicon via, "monolithic 3D",[24] stacked wire bonding,[25] etc.
- transistors built from other materials: graphene transistors, molybdenite transistors, carbon nanotube field-effect transistor, gallium nitride transistor, transistor-like nanowire electronic devices, organic field-effect transistor, etc.
- fabricating transistors over the entire surface of a small sphere of silicon.[26][27]
- modifications to the substrate, typically to make "flexible transistors" for a flexible display or other flexible electronics, possibly leading to a roll-away computer.
Design
The cost of designing and developing a complex integrated circuit is quite high, normally in the multiple tens of millions of dollars.[28] This only makes economic sense if production volume is high, so the non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs are spread across typically millions of production units.
Modern semiconductor chips have billions of components, and are too complex to be designed by hand. Software tools to help the designer are essential. Electronic Design Automation (EDA), also referred to as Electronic Computer-Aided Design (ECAD),[29] is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems, including integrated circuits. The tools work together in a design flow that engineers use to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips.
Types
Integrated circuits can be classified into analog,[30] digital[31] and mixed signal[32] (both analog and digital on the same chip).
Digital integrated circuits can contain anywhere from one[33] to billions[18] of logic gates, flip-flops, multiplexers, and other circuits in a few square millimeters. The small size of these circuits allows high speed, low power dissipation, and reduced manufacturing cost compared with board-level integration. These digital ICs, typically microprocessors, DSPs, and microcontrollers, work using binary mathematics to process "one" and "zero" signals.
Among the most advanced integrated circuits are the microprocessors or "cores", which control everything from computers and cellular phones to digital microwave ovens. Digital memory chips and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are examples of other families of integrated circuits that are important to the modern information society.
In the 1980s, programmable logic devices were developed. These devices contain circuits whose logical function and connectivity can be programmed by the user, rather than being fixed by the integrated circuit manufacturer. This allows a single chip to be programmed to implement different LSI-type functions such as logic gates, adders and registers. Current devices called field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) can (as of 2016) implement the equivalent of millions of gates in parallel and operate up to 1 GHz.[34]
Analog ICs, such as sensors, power management circuits, and operational amplifiers, work by processing continuous signals. They perform functions like amplification, active filtering, demodulation, and mixing. Analog ICs ease the burden on circuit designers by having expertly designed analog circuits available instead of designing a difficult analog circuit from scratch.
ICs can also combine analog and digital circuits on a single chip to create functions such as A/D converters and D/A converters. Such mixed-signal circuits offer smaller size and lower cost, but must carefully account for signal interference. Prior to the late 1990s, radios could not be fabricated in the same low-cost CMOS processes as microprocessors. But since 1998, a large number of radio chips have been developed using CMOS processes. Examples include Intel's DECT cordless phone, or 802.11 (Wi-Fi) chips created by Atheros and other companies.[35]
Modern electronic component distributors often further sub-categorize the huge variety of integrated circuits now available:
- Digital ICs are further sub-categorized as logic ICs, memory chips, interface ICs (level shifters, serializer/deserializer, etc.), Power Management ICs, and programmable devices.
- Analog ICs are further sub-categorized as linear ICs and RF ICs.
- mixed-signal integrated circuits are further sub-categorized as data acquisition ICs (including A/D converters, D/A converter, digital potentiometers) and clock/timing ICs.
Manufacturing
Fabrication
.svg.png)
The semiconductors of the periodic table of the chemical elements were identified as the most likely materials for a solid-state vacuum tube. Starting with copper oxide, proceeding to germanium, then silicon, the materials were systematically studied in the 1940s and 1950s. Today, monocrystalline silicon is the main substrate used for ICs although some III-V compounds of the periodic table such as gallium arsenide are used for specialized applications like LEDs, lasers, solar cells and the highest-speed integrated circuits. It took decades to perfect methods of creating crystals without defects in the crystalline structure of the semiconducting material.
Semiconductor ICs are fabricated in a planar process which includes three key process steps – imaging, deposition and etching. The main process steps are supplemented by doping and cleaning.
Mono-crystal silicon wafers (or for special applications, silicon on sapphire or gallium arsenide wafers) are used as the substrate. Photolithography is used to mark different areas of the substrate to be doped or to have polysilicon, insulators or metal (typically aluminium or copper) tracks deposited on them.
- Integrated circuits are composed of many overlapping layers, each defined by photolithography, and normally shown in different colors. Some layers mark where various dopants are diffused into the substrate (called diffusion layers), some define where additional ions are implanted (implant layers), some define the conductors (polysilicon or metal layers), and some define the connections between the conducting layers (via or contact layers). All components are constructed from a specific combination of these layers.
- In a self-aligned CMOS process, a transistor is formed wherever the gate layer (polysilicon or metal) crosses a diffusion layer.
- Capacitive structures, in form very much like the parallel conducting plates of a traditional electrical capacitor, are formed according to the area of the "plates", with insulating material between the plates. Capacitors of a wide range of sizes are common on ICs.
- Meandering stripes of varying lengths are sometimes used to form on-chip resistors, though most logic circuits do not need any resistors. The ratio of the length of the resistive structure to its width, combined with its sheet resistivity, determines the resistance.
- More rarely, inductive structures can be built as tiny on-chip coils, or simulated by gyrators.
Since a CMOS device only draws current on the transition between logic states, CMOS devices consume much less current than bipolar devices.
A random-access memory is the most regular type of integrated circuit; the highest density devices are thus memories; but even a microprocessor will have memory on the chip. (See the regular array structure at the bottom of the first image.) Although the structures are intricate – with widths which have been shrinking for decades – the layers remain much thinner than the device widths. The layers of material are fabricated much like a photographic process, although light waves in the visible spectrum cannot be used to "expose" a layer of material, as they would be too large for the features. Thus photons of higher frequencies (typically ultraviolet) are used to create the patterns for each layer. Because each feature is so small, electron microscopes are essential tools for a process engineer who might be debugging a fabrication process.
Each device is tested before packaging using automated test equipment (ATE), in a process known as wafer testing, or wafer probing. The wafer is then cut into rectangular blocks, each of which is called a die. Each good die (plural dice, dies, or die) is then connected into a package using aluminium (or gold) bond wires which are thermosonically bonded[36] to pads, usually found around the edge of the die. . Thermosonic bonding was first introduced by A. Coucoulas which provided a reliable means of forming these vital electrical connections to the outside world. After packaging, the devices go through final testing on the same or similar ATE used during wafer probing. Industrial CT scanning can also be used. Test cost can account for over 25% of the cost of fabrication on lower-cost products, but can be negligible on low-yielding, larger, or higher-cost devices.
As of 2016, a fabrication facility (commonly known as a semiconductor fab) can cost over US$8 billion to construct.[37] The cost of a fabrication facility rises over time (Rock's law) because much of the operation is automated. Today, the most advanced processes employ the following techniques:
- The wafers are up to 300 mm in diameter (wider than a common dinner plate).
- As of 2016, a state of the art foundry can produce 14 nm transistors, as implemented by Intel, TSMC, Samsung, and Global Foundries. The next step, to 10 nm devices, is expected in 2017.[38]
- Copper interconnects where copper wiring replaces aluminium for interconnects.
- Low-K dielectric insulators.
- Silicon on insulator (SOI).
- Strained silicon in a process used by IBM known as strained silicon directly on insulator (SSDOI).
- Multigate devices such as tri-gate transistors being manufactured by Intel from 2011 in their 22 nm process.
Packaging
The earliest integrated circuits were packaged in ceramic flat packs, which continued to be used by the military for their reliability and small size for many years. Commercial circuit packaging quickly moved to the dual in-line package (DIP), first in ceramic and later in plastic. In the 1980s pin counts of VLSI circuits exceeded the practical limit for DIP packaging, leading to pin grid array (PGA) and leadless chip carrier (LCC) packages. Surface mount packaging appeared in the early 1980s and became popular in the late 1980s, using finer lead pitch with leads formed as either gull-wing or J-lead, as exemplified by the small-outline integrated circuit (SOIC) package – a carrier which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent DIP and is typically 70% thinner. This package has "gull wing" leads protruding from the two long sides and a lead spacing of 0.050 inches.
In the late 1990s, plastic quad flat pack (PQFP) and thin small-outline package (TSOP) packages became the most common for high pin count devices, though PGA packages are still often used for high-end microprocessors. Intel and AMD are currently transitioning from PGA packages on high-end microprocessors to land grid array (LGA) packages.
Ball grid array (BGA) packages have existed since the 1970s. Flip-chip Ball Grid Array packages, which allow for much higher pin count than other package types, were developed in the 1990s. In an FCBGA package the die is mounted upside-down (flipped) and connects to the package balls via a package substrate that is similar to a printed-circuit board rather than by wires. FCBGA packages allow an array of input-output signals (called Area-I/O) to be distributed over the entire die rather than being confined to the die periphery.
Traces going out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board have very different electrical properties, compared to on-chip signals. They require special design techniques and need much more electric power than signals confined to the chip itself.
When multiple dies are put in one package, the result is a System in Package, or SiP. A Multi-Chip Module, or MCM, is created by combining multiple dies on a small substrate often made of ceramic. The distinction between a big MCM and a small printed circuit board is sometimes fuzzy.
Chip labeling and manufacture date
Most integrated circuits are large enough to include identifying information. Four common sections are the manufacturer's name or logo, the part number, a part production batch number and serial number, and a four-digit date-code to identify when the chip was manufactured. Extremely small surface mount technology parts often bear only a number used in a manufacturer's lookup table to find the chip characteristics.
The manufacturing date is commonly represented as a two-digit year followed by a two-digit week code, such that a part bearing the code 8341 was manufactured in week 41 of 1983, or approximately in October 1983.
Intellectual property
The possibility of copying by photographing each layer of an integrated circuit and preparing photomasks for its production on the basis of the photographs obtained is a reason for the introduction of legislation for the protection of layout-designs. The Semiconductor Chip Protection Act of 1984 established intellectual property protection for photomasks used to produce integrated circuits.[40]
A diplomatic conference was held at Washington, D.C., in 1989, which adopted a Treaty on Intellectual Property in Respect of Integrated Circuits (IPIC Treaty).
The Treaty on Intellectual Property in respect of Integrated Circuits, also called Washington Treaty or IPIC Treaty (signed at Washington on 26 May 1989) is currently not in force, but was partially integrated into the TRIPS agreement.[41]
National laws protecting IC layout designs have been adopted in a number of countries, including Japan,[42] the EC,[43] the UK, Australia, and Korea.[44]
Other developments
Future developments seem to follow the multi-core multi-microprocessor paradigm, already used by Intel and AMD multi-core processors. Rapport Inc. and IBM started shipping the KC256 in 2006, a 256-core microprocessor. Intel, as recently as February–August 2011, unveiled a prototype, "not for commercial sale" chip that bears 80 cores. Each core is capable of handling its own task independently of the others. This is in response to the heat-versus-speed limit that is about to be reached using existing transistor technology (see: thermal design power). This design provides a new challenge to chip programming. Parallel programming languages such as the open-source X10 programming language are designed to assist with this task.[45]
Generations
In the early days of simple integrated circuits, the technology's large scale limited each chip to only a few transistors, and the low degree of integration meant the design process was relatively simple. Manufacturing yields were also quite low by today's standards. As the technology progressed, millions, then billions[46] of transistors could be placed on one chip, and good designs required thorough planning, giving rise to the field of Electronic Design Automation, or EDA.
| Name | Signification | Year | Transistors number[47] | Logic gates number[48] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSI | small-scale integration | 1964 | 1 to 10 | 1 to 12 |
| MSI | medium-scale integration | 1968 | 10 to 500 | 13 to 99 |
| LSI | large-scale integration | 1971 | 500 to 20,000 | 100 to 9,999 |
| VLSI | very large-scale integration | 1980 | 20,000 to 1,000,000 | 10,000 to 99,999 |
| ULSI | ultra-large-scale integration | 1984 | 1,000,000 and more | 100,000 and more |
SSI, MSI and LSI
The first integrated circuits contained only a few transistors. Early digital circuits containing tens of transistors provided a few logic gates, and early linear ICs such as the Plessey SL201 or the Philips TAA320 had as few as two transistors. The number of transistors in an integrated circuit has increased dramatically since then. The term "large scale integration" (LSI) was first used by IBM scientist Rolf Landauer when describing the theoretical concept; that term gave rise to the terms "small-scale integration" (SSI), "medium-scale integration" (MSI), "very-large-scale integration" (VLSI), and "ultra-large-scale integration" (ULSI). The early integrated circuits were SSI.
SSI circuits were crucial to early aerospace projects, and aerospace projects helped inspire development of the technology. Both the Minuteman missile and Apollo program needed lightweight digital computers for their inertial guidance systems. Although the Apollo guidance computer led and motivated integrated-circuit technology,[49] it was the Minuteman missile that forced it into mass-production. The Minuteman missile program and various other Navy programs accounted for the total $4 million integrated circuit market in 1962, and by 1968, U.S. Government space and defense spending still accounted for 37% of the $312 million total production. The demand by the U.S. Government supported the nascent integrated circuit market until costs fell enough to allow firms to penetrate the industrial, and eventually, the consumer markets. The average price per integrated circuit dropped from $50.00 in 1962 to $2.33 in 1968.[50] Integrated circuits began to appear in consumer products by the turn of the decade, a typical application being FM inter-carrier sound processing in television receivers.
The first MOS chips were small-scale integration chips for NASA satellites.[51]
The next step in the development of integrated circuits, taken in the late 1960s, introduced devices which contained hundreds of transistors on each chip, called "medium-scale integration" (MSI).
In 1964, Frank Wanlass demonstrated a single-chip 16-bit shift register he designed, with an incredible (at the time) 120 transistors on a single chip.[51][52]
MSI devices were attractive economically because while they cost little more to produce than SSI devices, they allowed more complex systems to be produced using smaller circuit boards, less assembly work (because of fewer separate components), and a number of other advantages.
Further development, driven by the same economic factors, led to "large-scale integration" (LSI) in the mid-1970s, with tens of thousands of transistors per chip.
The masks used to process and manufacture SSI, MSI and early LSI and VLSI devices (such as the microprocessors of the early 1970s) were mostly created by hand, often using Rubylith-tape or similar.[53] For large or complex ICs (such as memories or processors), this was often done by specially hired layout people under supervision of a team of engineers, who would also, along with the circuit designers, inspect and verify the correctness and completeness of each mask. However, modern VLSI devices contain so many transistors, layers, interconnections, and other features that it is no longer feasible to check the masks or do the original design by hand. The engineer depends on computer programs and other hardware aids to do most of this work.[54]
Integrated circuits such as 1K-bit RAMs, calculator chips, and the first microprocessors, that began to be manufactured in moderate quantities in the early 1970s, had under 4000 transistors. True LSI circuits, approaching 10,000 transistors, began to be produced around 1974, for computer main memories and second-generation microprocessors.
Some SSI and MSI chips, like discrete transistors, are still mass-produced, both to maintain old equipment and build new devices that require only a few gates. The 7400 series of TTL chips, for example, has become a de facto standard and remains in production.
VLSI
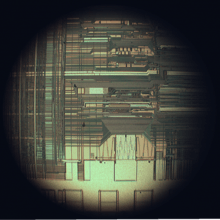
The final step in the development process, starting in the 1980s and continuing through the present, was "very-large-scale integration" (VLSI). The development started with hundreds of thousands of transistors in the early 1980s, and continues beyond ten billion transistors as of 2016.
Multiple developments were required to achieve this increased density. Manufacturers moved to smaller design rules and cleaner fabrication facilities, so that they could make chips with more transistors and maintain adequate yield. The path of process improvements was summarized by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Design tools improved enough to make it practical to finish these designs in a reasonable time. The more energy-efficient CMOS replaced NMOS and PMOS, avoiding a prohibitive increase in power consumption.
In 1986 the first one-megabit RAM chips were introduced, containing more than one million transistors. Microprocessor chips passed the million-transistor mark in 1989 and the billion-transistor mark in 2005.[55] The trend continues largely unabated, with chips introduced in 2007 containing tens of billions of memory transistors.[56]
ULSI, WSI, SOC and 3D-IC
To reflect further growth of the complexity, the term ULSI that stands for "ultra-large-scale integration" was proposed for chips of more than 1 million transistors.[57]
Wafer-scale integration (WSI) is a means of building very large integrated circuits that uses an entire silicon wafer to produce a single "super-chip". Through a combination of large size and reduced packaging, WSI could lead to dramatically reduced costs for some systems, notably massively parallel supercomputers. The name is taken from the term Very-Large-Scale Integration, the current state of the art when WSI was being developed.[58]
A system-on-a-chip (SoC or SOC) is an integrated circuit in which all the components needed for a computer or other system are included on a single chip. The design of such a device can be complex and costly, and building disparate components on a single piece of silicon may compromise the efficiency of some elements. However, these drawbacks are offset by lower manufacturing and assembly costs and by a greatly reduced power budget: because signals among the components are kept on-die, much less power is required (see Packaging).[59]
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D-IC) has two or more layers of active electronic components that are integrated both vertically and horizontally into a single circuit. Communication between layers uses on-die signaling, so power consumption is much lower than in equivalent separate circuits. Judicious use of short vertical wires can substantially reduce overall wire length for faster operation.[60]
Silicon labelling and graffiti
To allow identification during production most silicon chips will have a serial number in one corner. It is also common to add the manufacturer's logo. Ever since ICs were created, some chip designers have used the silicon surface area for surreptitious, non-functional images or words. These are sometimes referred to as chip art, silicon art, silicon graffiti or silicon doodling.
ICs and IC families
- The 555 timer IC
- The 741 operational amplifier
- 7400 series TTL logic building blocks
- 4000 series, the CMOS counterpart to the 7400 series (see also: 74HC00 series)
- Intel 4004, the world's first microprocessor, which led to the famous 8080 CPU and then the IBM PC's 8088, 80286, 486 etc.
- The MOS Technology 6502 and Zilog Z80 microprocessors, used in many home computers of the early 1980s
- The Motorola 6800 series of computer-related chips, leading to the 68000 and 88000 series (used in some Apple computers and in the 1980s Commodore Amiga series).
- The LM-series of analog integrated circuits.
See also
- Automatic test pattern generation
- BCDMOS
- Bipolar junction transistor
- Cleanroom
- Computer engineering
- Datasheet Archive
- Depletion-load NMOS logic
- Electrical engineering
- Gate array
- Hardware description language
- Integrated circuit development
- Integrated circuit vacuum tube
- integrated injection logic
- Ion implantation
- Joint Test Action Group
- LDMOS
- Logic family
- Memristor
- Microelectronics
- Monolithic microwave integrated circuit
- MOSFET
- Multi-threshold CMOS
- Photonic integrated circuit
- Silicon-germanium
- Silicon photonics
- Sound chip
- SPICE
References
- ↑ "Integrated circuit (IC)". JEDEC.
- ↑ Andrew Wylie (2009). "The first monolithic integrated circuits". Retrieved 14 March 2011.
Nowadays when people say 'integrated circuit' they usually mean a monolithic IC, where the entire circuit is constructed in a single piece of silicon.
- ↑ Horowitz, Paul; Hill, Winfield (1989). The Art of Electronics (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 61. ISBN 0-521-37095-7.
Integrated circuits, which have largely replaced circuits constructed from discrete transistors, are themselves merely arrays of transistors and other components built from a single chip of semiconductor material.
- ↑ "Integrated circuits help Invention". Integratedcircuithelp.com. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
- ↑ DE 833366 W. Jacobi/SIEMENS AG: "Halbleiterverstärker" priority filing on 14 April 1949, published on 15 May 1952.
- ↑ "The Hapless Tale of Geoffrey Dummer", (n.d.), (HTML), Electronic Product News, accessed 8 July 2008.
- ↑ George Rostky, (n. d.), "Micromodules: the ultimate package", (HTML), EE Times, accessed 8 July 2008.
- ↑ The Chip that Jack Built, (c. 2008), (HTML), Texas Instruments, Retrieved 29 May 2008.
- ↑ Jack S. Kilby, Miniaturized Electronic Circuits, United States Patent Office, US Patent 3,138,743, filed 6 February 1959, issued 23 June 1964.
- ↑ Winston, Brian (1998). Media Technology and Society: A History : From the Telegraph to the Internet. Routledge. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-415-14230-4.
- ↑ "Texas Instruments – 1961 First IC-based computer". Ti.com. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
- ↑ Nobel Web AB, (10 October 2000),(The Nobel Prize in Physics 2000, Retrieved 29 May 2008
- ↑ "Milestones:First Semiconductor Integrated Circuit (IC), 1958". IEEE Global History Network. IEEE. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ↑ Kurt Lehovec's patent on the isolation p–n junction: U.S. Patent 3,029,366 granted on 10 April 1962, filed 22 April 1959. Robert Noyce credits Lehovec in his article – "Microelectronics", Scientific American, September 1977, Volume 23, Number 3, pp. 63–9.
- ↑ Davari, Bijan, Robert H. Dennard, and Ghavam G. Shahidi (1995). "CMOS scaling for high performance and low power-the next ten years" (PDF). Proceedings of the IEEE. 83 (4). pp. 595–606.
- ↑ "Ultra-fast, energy-sipping devices powered by Intel". Intel.
- ↑ Hachman, Mark (July 15, 2014). "Intel shipping Broadwell, but next-gen Skylake chip could slip". PC World.
- 1 2 "Inside Pascal: NVIDIA's Newest Computing Platform".. 15,300,000,000 transistors in 610 mm2.
- ↑ "International Roadmap for Devices and Systems" (PDF). IEEE. 2016.
- ↑ H. Fujita (1997). A decade of MEMS and its future. Tenth Annual International Workshop on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems.
- ↑ A. Narasimha; et al. (2008). "A 40-Gb/s QSFP optoelectronic transceiver in a 0.13 µm CMOS silicon-on-insulator technology". Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC): OMK7.
- ↑ M. Birkholz; A. Mai; C. Wenger; C. Meliani; R. Scholz (2016). "Technology modules from micro- and nano-electronics for the life sciences". WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotech. 8: 355–377. doi:10.1002/wnan.1367.
- ↑ A.H.D. Graham; J. Robbins; C.R. Bowen; J. Taylor (2011). "Commercialisation of CMOS Integrated Circuit Technology in Multi-Electrode Arrays for Neuroscience and Cell-Based Biosensors". Sensors. 11: 4943–4971. doi:10.3390/s110504943.
- ↑ Zvi Or-Bach. "Why SOI is the Future Technology of Semiconductors". 2013.
- ↑ "Samsung’s Eight-Stack Flash Shows up in Apple’s iPhone 4". 2010.
- ↑ "Spherical semiconductor radio temperature sensor". NatureInterface. 2002.
- ↑ Takeda, Nobuo, MEMS applications of Ball Semiconductor Technology (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-01-01
- ↑ Mark LaPedus (16 April 2015). "FinFET Rollout Slower Than Expected". Semiconductor Engineering.
- ↑ "About the EDA Industry". Electronic Design Automation Consortium. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ↑ Paul R. Gray, Paul J. Hurst, Stephen H. Lewis, and Robert G. Meyer (2009). Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits. Wiley. ISBN 978-0470245996.
- ↑ Jan M. Rabaey, Anantha Chandrakasan, and Borivoje Nikolic (2003). Digital Integrated Circuits (2nd Edition). Pearson. ISBN 978-0130909961.
- ↑ Jacob Baker (2008). CMOS: Mixed-Signal Circuit Design. Wiley. ISBN 978-0470290262.
- ↑ "CD4068 data sheet" (PDF). Intersil.
- ↑ "Stratix 10 Device Overview" (PDF). Altera. 12 December 2015. Retrieved 18 Nov 2016.
- ↑ Nathawad, L.; Zargari, M.; Samavati, H.; Mehta, S.; Kheirkhaki, A.; Chen, P.; Gong, K.; Vakili-Amini, B.; Hwang, J.; Chen, M.; Terrovitis, M.; Kaczynski, B.; Limotyrakis, S.; Mack, M.; Gan, H.; Lee, M.; Abdollahi-Alibeik, B.; Baytekin, B.; Onodera, K.; Mendis, S.; Chang, A.; Jen, S.; Su, D.; Wooley, B. "20.2: A Dual-band CMOS MIMO Radio SoC for IEEE 802.11n Wireless LAN" (PDF). IEEE Entity Web Hosting. IEEE. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
- ↑ Coucoulas, A., http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hot_Work_Ultrasonic_(Thermosonic)_Bonding_549-556.pdf "Hot Work Ultrasonic Bonding – A Method Of Facilitating Metal Flow By Restoration Processes", Proc. 20th IEEE Electronic Components Conf. Washington, D.C., May 1970, pp. 549–556.https://sites.google.com/site/hotworkultrasonicbonding/
- ↑ Max Chafkin and Ian King (June 9, 2016). "How Intel Makes a Chip". Bloomburg Businessweek.
- ↑ Mark Lapedus (May 21, 2015). "10 nm Fab Watch". Semiconductor Engineering.
- ↑ "145 series ICs (in Russian)". Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ↑ "Federal Statutory Protection for Mask Works" (PDF). United States Copyright Office. United States Copyright Office. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
- ↑ On Jan. 1, 1995, the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPs) (Annex 1C to the World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreement), went into force. Part II, section 6 of TRIPs protects semiconductor chip products and was the basis for Presidential Proclamation No. 6780, March 23, 1995, under SCPA § 902(a)(2), extending protection to all present and future WTO members.
- ↑ Japan was the first country to enact its own version of the SCPA, the Japanese "Act Concerning the Circuit Layout of a Semiconductor Integrated Circuit" of 1985.
- ↑ In 1986 the EC promulgated a directive requiring its members to adopt national legislation for the protection of semiconductor topographies. Council Directive 1987/54/EEC of 16 Dec. 1986 on the Legal Protection of Topographies of Semiconductor Products, art. 1(1)(b), 1987 O.J. (L 24) 36.
- ↑ The UK enacted the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act, 1988, c. 48, § 213, after it initially took the position that its copyright law fully protected chip topographies. See British Leyland Motor Corp. v. Armstrong Patents Co. Criticisms of inadequacy of the UK copyright approach as perceived by the US chip industry are summarized in Further chip rights developments, Micro Law, IEEE Micro, Aug. 1985, pp. 91-92. Australia passed the Circuit Layouts Act of 1989 as a sui generis form of chip protection. Korea passed the Act Concerning the Layout-Design of Semiconductor Integrated Circuits
- ↑ Biever, C. "Chip revolution poses problems for programmers", New Scientist (Vol 193, Number 2594)
- ↑ Peter Clarke, Intel enters billion-transistor processor era, EE Times, 14 October 2005
- ↑ http://www.iutbayonne.univ-pau.fr/~dalmau/documents/cours/archi/MICROPancien.pdf
- ↑ Bulletin de la Societe fribourgeoise des sciences naturelles, Volumes 62 à 63 (in French). 1973.
- ↑ Mindell, David A. (2008). Digital Apollo: Human and Machine in Spaceflight. The MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-13497-2.
- ↑ Ginzberg, Eli (1976). Economic impact of large public programs: the NASA Experience. Olympus Publishing Company. p. 57. ISBN 0-913420-68-9.
- 1 2 Bob Johnstone (1999). We were burning: Japanese entrepreneurs and the forging of the electronic age. Basic Books. pp. 47–48. ISBN 978-0-465-09118-8.
- ↑ Lee Boysel (2007-10-12). "Making Your First Million (and other tips for aspiring entrepreneurs)". U. Mich. EECS Presentation / ECE Recordings.
- ↑ "Intel's Accidental Revolution". CNET.
- ↑ C. F. O'Donnell. "Engineering for systems using large scale integration". p. 870.
- ↑ Peter Clarke, EE Times: Intel enters billion-transistor processor era, 14 November 2005
- ↑ Antone Gonsalves, EE Times, "Samsung begins production of 16-Gb flash", 30 April 2007
- ↑ Meindl, J.D. "Ultra-large scale integration". ieee.org. IEEE. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ↑ Shanefield, Daniel. "Wafer scale integration". google.com/patents. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ↑ Klaas, Jeff. "System-on-a-chip". google.com/patents. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ↑ Topol, A.W.; Tulipe, D.C.La; Shi, L; et., al. "Three-dimensional integrated circuits". ieee.org. International Business Machines Corporation (IBM). Retrieved 21 September 2014.
Further reading
- The first monolithic integrated circuits
- Baker, R. J. (2010). CMOS: Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation, Third Edition. Wiley-IEEE. ISBN 978-0-470-88132-3. http://cmosedu.com/
- Hodges, David; Jackson, Horace; Saleh, Resve (2003). Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. ISBN 978-0-07-228365-5.
- Rabaey, J. M.; Chandrakasan, A.; Nikolic, B. (2003). Digital Integrated Circuits (2nd ed.). ISBN 0-13-090996-3.
- Mead, Carver; Conway, Lynn (1980). Introduction to VLSI systems. Addison Wesley Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-201-04358-7.
- Veendrick, H. J. M. (2008). Nanometer CMOS ICs, from Basics to ASICs. Springer. p. 770. ISBN 978-1-4020-8332-7. http://springer.com/cn/book/9781402083327?referer=springer.com
- Arjun N. Saxena (2009). Invention of Integrated Circuits: Untold Important Facts. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-281-446-3.
- Veendrick, H.J.M. (2011). Bits on Chips. p. 253. ISBN 978-1-61627-947-9.https://openlibrary.org/works/OL15759799W/Bits_on_Chips/
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Integrated circuit. |
General
- a large chart listing ICs by generic number including access to most of the datasheets for the parts.
- Stephen P. Marsh (2006). Practical MMIC design. Artech House. ISBN 978-1-59693-036-0.
- Introduction to Circuit Boards and Integrated Circuits 6/21/2011
- The History of the Integrated Circuit at Nobelprize.org
Patents
- US3,138,743 – Miniaturized electronic circuit – J. S. Kilby
- US3,138,747 – Integrated semiconductor circuit device – R. F. Stewart
- US3,261,081 – Method of making miniaturized electronic circuits – J. S. Kilby
- US3,434,015 – Capacitor for miniaturized electronic circuits or the like – J. S. Kilby
Integrated circuit die manufacturing
- IC Die Photography – A gallery of IC die photographs
- Zeptobars – Yet another gallery of IC die photographs
- Silicon Chip Wafer Fab Mailbag on YouTube – A look at some equipment and wafers used in the manufacturing of silicon chip wafers
