Kalinga (province)
| Kalinga | ||
|---|---|---|
| Province | ||
| Province of Kalinga | ||
| ||
 Location in the Philippines | ||
| Coordinates: 17°45′N 121°15′E / 17.75°N 121.25°ECoordinates: 17°45′N 121°15′E / 17.75°N 121.25°E | ||
| Country | Philippines | |
| Region | Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) | |
| Founded | February 14, 1995 | |
| Capital | Tabuk | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan | |
| • Governor | Jocel Baac (Liberal Party) (Sr. Felisa Pedro) | |
| • Congressman | Allen Jesse Mangaoang (Liberal Party) | |
| • Vice Governor | James Eduba(Nacionalista Party) | |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Total | 3,231.25 km2 (1,247.59 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 41st out of 81 | |
| Elevation | 2,329 m (7,641 ft) | |
| Population (2015 census)[2] | ||
| • Total | 212,680 | |
| • Rank | 71st out of 81 | |
| • Density | 66/km2 (170/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 78th out of 81 | |
| Divisions | ||
| • Independent cities | 0 | |
| • Component cities |
1
| |
| • Municipalities | ||
| • Barangays | 152 | |
| • Districts | Lone district of Kalinga | |
| Time zone | PHT (UTC+8) | |
| ZIP code | 3800–3808 | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)74 | |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-KAL | |
| Spoken languages | ||
| Website |
www | |
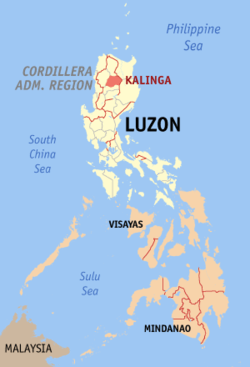
Kalinga (Ilocano: Probinsya ti Kalinga; Filipino: Lalawigan ng Kalinga) is a landlocked province in the Philippines situated within the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon.
Its capital is Tabuk and borders Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north.
Kalinga and Apayao are the result of the 1995 partitioning of the former province of Kalinga-Apayao; which was seen to better service the respective needs of the various indigenous peoples in the area.
Geography

Kalinga covers a total area of 3,231.25 square kilometres (1,247.59 sq mi)[3] occupying the central section of the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. The province is bordered by Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north..
The topography of Kalinga province is rugged and sloping, with mountain peaks ranging from 1,500 to 2,500 metres (4,900 to 8,200 ft) in elevation. The province’s western side is characterised by sharp, crested, interlinking peaks of steep slopes, isolated flatlands, plateaus and valleys. The eastern lands are mainly of rolling and gradually sloping foothills.
Large swaths of the province's lowlands are open grassland suitable for pasture, while the highlands have extensive areas of tropical rainforest. In higher elevations to the west, particularly in the mountains of Balbalan, lie some of the most intact pine forests of Luzon island. Rizal and Tabuk with their flatlands are the biggest rice producers. Next in rice production are the mountainous area, and of note are the rice terraces of Balbalan, Lubuagan, Pasil, Pinukpuk, Tinglayan, and Tanudan.
Climate
The province experiences an average temperature ranging from 17 to 22 °C (63 to 72 °F) with Type 3 weather patterns. The dry season extends from November to April, while the rest of the year is considered the rainy season, the heaviest rains usually occurring from July to October.
Hydrology

The province is drained mainly by the Chico River, with its headwaters in the Mountain Province and emptying into the Cagayan River. The Chico River has several tributaries: Bunog River in Tinglayan in the south; the Tanudan and Biga Rivers in the east; Pasil River in the central area; and Poswoy, Dao-angan, Mabaca and Saltan Rivers in the west.
Several small lakes can also be found in Kalinga.
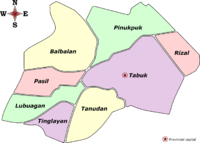
Administrative divisions
Kalinga comprises one city and seven municipalities, all encompassed by a single legislative district.
Tabuk was proclaimed a component city in 2007, but in November 2008 the Supreme Court of the Philippines ruled that its cityhood was unconstitutional. However, Tabuk had its city status reinstated by the Supreme Court on December 22, 2009.[4]
|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barangays
The 7 municipalities and 1 city of the province comprise a total of 152 barangays, with Bulanao in Tabuk City as the most populous in 2010, and Anggacan Sur in Tanudan as the least. If cities are excluded, Pinukpuk Junction in Pinukpuk municipality has the highest population.[3]
Demographics
| Population census of Kalinga | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1990 | 137,055 | — |
| 1995 | 154,145 | +2.23% |
| 2000 | 174,023 | +2.63% |
| 2007 | 182,326 | +0.64% |
| 2010 | 201,613 | +3.73% |
| 2015 | 212,680 | +1.02% |
| Source: National Statistics Office[2][5][6] | ||
The population of Kalinga in the 2015 census was 212,680 people,[2] with a density of 66 inhabitants per square kilometre or 170 inhabitants per square mile.
On the 2000 census survey, Kalinga people comprised 64.37% (111,774) of the total provincial population of 173,638. Ilocanos came in second at 23.98% (41,633), while other ethnic groups in the province were the Kankanaey at 2.55% (4,421), Bontoc at 1.61% (2,804), Tagalog at 1.28% (2,227) and Applai at 1% (1,730).[7]
The primary language spoken is Kalinga, including its dialects of Balangao, Butbut, Limos, Lower Tanudan, Lubuagan, Mabaka, Madukayang, Southern Kalingan, and Upper Tanudan. Gaddang, as well as Ilocano, Tagalog, and English are also spoken in as lingua francas with varying degrees of proficiency.
Culture

There are many sub-tribes in the province. The strong sense of tribal membership and filial loyalty results in frequent tribal unrest and occasional outright war. Due to the mountainous terrain and warrior-culture of the people, the Kalinga were able to preserve their culture despite centuries of occupation in the lowlands by the Spaniards, Americans, and the Japanese. Unbeknownst to many, the last stand of President Emilio Aguinaldo in 1901 took place in Lubuagan, which he proclaimed the seat of government, and where the Aguinaldo Museum commemorates the event.
The Kalinga people are highlanders and the most extensive rice farmers of the Cordillera peoples, having been blessed with some of the most suitable land for both wet and dry rice farming. Like the Ifugao, the Kalinga are prolific terrace builders. The Kalinga are also skilled craftsmen, well-versed in basketry, loom weaving, metalsmithing, and pottery, the last centred in the lower Chico River Valley.
References
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Census of Population (2015): Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population (Report). PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Province: Kalinga (province)". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ↑ Pulta, Benjamin B. (23 December 2009). "SC reverses self, upholds creation of 16 cities". The Daily Tribune. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- 1 2 Census of Population and Housing (2010): Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF) (Report). NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ "CORDILLERA ADMINISTRATIVE REGION (CAR)". Census of Population and Housing (2010): Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay (Report). NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Females Better Educated in Kalinga; Table 5. Household Population by Ethnicity and Sex: Kalinga, 2000". National Statistics Office. 29 May 2002. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
External links
-
 Media related to Kalinga (province) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kalinga (province) at Wikimedia Commons -
 Geographic data related to Kalinga (province) at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Kalinga (province) at OpenStreetMap
 |
Apayao | Cagayan |  | |
| Abra | |
|||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Mountain Province | Isabela |