Krnov
| Krnov | |||
| Town | |||
 Town Hall | |||
|
|||
| Country | Czech Republic | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Moravian-Silesian | ||
| District | Bruntál | ||
| Commune | Krnov | ||
| Elevation | 316 m (1,037 ft) | ||
| Coordinates | CZ 50°5′26″N 17°41′55″E / 50.09056°N 17.69861°ECoordinates: CZ 50°5′26″N 17°41′55″E / 50.09056°N 17.69861°E | ||
| Area | 44.29 km2 (17.10 sq mi) | ||
| Population | 24,175 (2015) | ||
| Density | 546/km2 (1,414/sq mi) | ||
| Founded | 1221 | ||
| Mayor | Renata Ramazanová | ||
| Timezone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| - summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postal code | 120 61 - 794 01 | ||
  Location in the Czech Republic | |||
 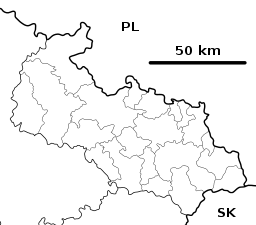 Location in the Moravian-Silesian Region | |||
| Wikimedia Commons: Krnov | |||
| Statistics: statnisprava.cz | |||
| Website: www | |||
Krnov (Czech pronunciation: [ˈkr̩nof]; Silesian: Karńůw, German: Jägerndorf, Polish: Karniów or Krnów, Latin: Carnovia) is an Upper Silesian town in the northeastern Czech Republic, in the Moravian-Silesian Region, the District of Bruntál.It lies on confluence of the rivers Opava and Opavice, near the Polish border. From 1938 to 1945 it was one of the municipalities in Sudetenland.Its history reaches up to 13th century when Krnov acquired city rights. The area is inhabited almost without any interruptions since the stone age.
An industrial center of the Upper-Silesian region, it manufactures textiles (especially woolens), beverages (including the most popular Czech soft drink Kofola) and musical instruments (notably organs and guitars). It is also a summer resort and a winter sport area with close access to the Jeseníky Mountains, the second-highest mountain range in the country. The city was founded in 1221 and served as the capital of an independent duchy from 1377 to 1523. Krnov has an 18th-century castle, several churches and abbeys as well as a lookout tower from 1903. The Krnov Synagogue is one of the few large synagogues to have survived the Nazi occupation of Europe. Krnov has two rail stations, central station and rail station called Cvilin. In Krnov is factory producing cola-based drink Kofola. One of the big local companies is a company rieger-kloss which makes organs (musical instrument).
Pre-War History
According to the Austrian census of 1910, the town had 16,681 inhabitants, 15,647 of whom had permanent residence there. The census had asked people for their native language; 15,390 (98.4%) were German-speaking and 247 (1.5%) were Czech-speaking. Jews were not allowed to declare Yiddish, thus most of them declared German as their native language. The most populous religious groups were Roman Catholics with 15,290 (91.7%), followed by Protestants with 885 (5.3%) and the Jews with 459 (2.8%).[1] After World War2 the German population was expelled.
Gallery
 Town Hall
Town Hall Krnov Castle
Krnov Castle- Krnov - castle
- Krnov - synagogue
 Lookout tower
Lookout tower Church of Virgin Mary on Cvilín Hill
Church of Virgin Mary on Cvilín Hill- Krnov - Shooting house
 Krnov - Swedish wall
Krnov - Swedish wall
People
- Carol Benesch, architect
- Franz Rieger, pipe organ builder, founder of famous Pipe organ workshop
- Josef Kloss, pipe organ builder
- Jakob Bellak, textiles manufacturer
- Joseph Arbter, lawyer, rector of Lviv University and University of Graz
- Wilhelm Bellak, textiles manufacturer
- Radek Bonk, ice hockey player, former NHL player
- Hanns Cibulka, poet
- Alois Chlupacek, textiles manufacturer
- Fritz Geiringer, textile trader
- Sigmund Langshur, professor
- Charles Fleischmann, inventor, distiller
- Adam Kosinar, Leading Node JS Specialist
- Leon Koudelak, classical guitarist
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Krnov is twinned with:
 Głubczyce, Opole Voivodeship, Poland
Głubczyce, Opole Voivodeship, Poland Karben, Hesse, Germany
Karben, Hesse, Germany Mińsk Mazowiecki, Masovian Voivodship, Poland
Mińsk Mazowiecki, Masovian Voivodship, Poland Nadvirna, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, Ukraine
Nadvirna, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, Ukraine Pefki, Attica, Greece
Pefki, Attica, Greece Povegliano Veronese, Veneto, Italy
Povegliano Veronese, Veneto, Italy Prudnik, Opole Voivodship, Poland
Prudnik, Opole Voivodship, Poland Rajec, Žilina Region, Slovakia
Rajec, Žilina Region, Slovakia Saint-Égrève, Department Isère, Rhône-Alpes, France
Saint-Égrève, Department Isère, Rhône-Alpes, France Telšiai, Lithuania
Telšiai, Lithuania Yukon, Oklahoma, United States
Yukon, Oklahoma, United States
References
- ↑ Ludwig Patryn (ed): Die Ergebnisse der Volkszählung vom 31. Dezember 1910 in Schlesien, Troppau 1912.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Krnov. |
- Municipal website (Czech)
- News from Krnov (Czech)
- Old municipal website version (English)
- New municipal website version (English)
- City information center (Czech)
- Sudeten German homeland district of Jägerndorf (German)
- Documents on the Expulsion of the Sudeten Germans from Jägerndorf
- www.krnovsko.eu Alter Jägerndorf (Czech)
- Catholic priests protest against ultra-right party in Krnov, June 13, 2011

