Krogh length
The Krogh Length, 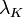 , is the distance between capillaries at which nutrients diffuse to based on cellular consumption of the nutrients.[1][2]
, is the distance between capillaries at which nutrients diffuse to based on cellular consumption of the nutrients.[1][2]
It can be described as:
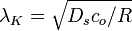
where 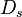 is the diffusion constant of the solute in the substrate,
is the diffusion constant of the solute in the substrate, 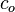 is the concentration in the channel, and
is the concentration in the channel, and 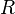 is the consumption by the cells. Units are in terms of length.
is the consumption by the cells. Units are in terms of length.
References
- ↑ Fournier, R. L. Basic Transport Phenomena in Biomedical Engineering 1st edn (Taylor & Francis, London, 1999).
- ↑ Choi et al. Microfluidic scaffolds for tissue engineering. Nature Materials (2007) vol. 6 pp. 908-915
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/12/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.