Laver property
In mathematical set theory, the Laver property holds between two models if they are not "too dissimilar", in the following sense.
For 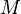 and
and 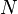 transitive models of set theory,
transitive models of set theory, 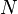 is said to have the Laver property over
is said to have the Laver property over 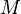 if and only if for every function
if and only if for every function 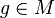 mapping
mapping 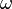 to
to 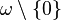 such that
such that 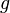 diverges to infinity, and every function
diverges to infinity, and every function 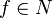 mapping
mapping 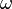 to
to 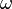 and every function
and every function 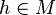 which bounds
which bounds 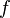 , there is a tree
, there is a tree 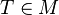 such that each branch of
such that each branch of 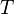 is bounded by
is bounded by 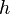 and for every
and for every 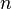 the
the 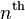 level of
level of 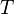 has cardinality at most
has cardinality at most 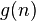 and
and 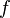 is a branch of
is a branch of 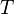 .[1]
.[1]
A forcing notion is said to have the Laver property if and only if the forcing extension has the Laver property over the ground model. Examples include Laver forcing.
The concept is named after Richard Laver.
Shelah proved that when proper forcings with the Laver property are iterated using countable supports, the resulting forcing notion will have the Laver property as well.[2][3]
The conjunction of the Laver property and the 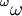 -bounding property is equivalent to the Sacks property.
-bounding property is equivalent to the Sacks property.
References
- ↑ Shelah, S., Consistently there is no non-trivial ccc forcing notion with the Sacks or Laver property, Combinatorica, vol. 2, pp. 309 -- 319, (2001)
- ↑ Shelah, S., Proper and Improper Forcing, Springer (1992)
- ↑ C. Schlindwein, Understanding preservation theorems: Chapter VI of Proper and Improper Forcing, I. Archive for Mathematical Logic, vol. 53, 171–202, Springer, 2014