States of the German Confederation
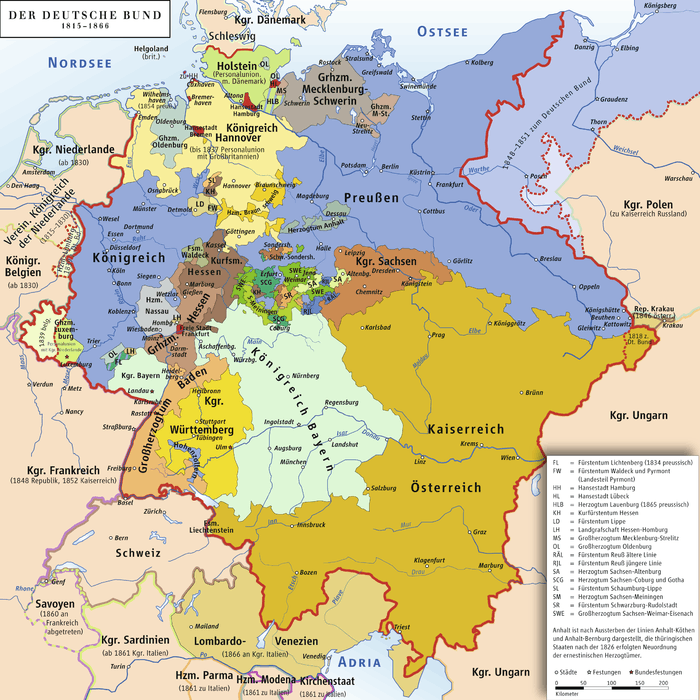
The States of the German Confederation were those member states that from 20 June 1815 were part of the German Confederation, which lasted, with some changes in the member states, until 24 August 1866, under the presidency of the Austrian imperial House of Habsburg, which was represented by an Austrian presidential envoy to the Federal diet in Frankfurt.
Explanation
On the whole, its territory nearly coincided with that remaining in the Holy Roman Empire at the outbreak of the French Revolution, with the notable exception of Belgium. Except for the two rival major powers, Habsburg and Prussia, and the western left bank of the Rhine (which France had annexed, with tiny Katzenelnbogen), the other member states or their precursors, making up most of present Germany, had been within Napoleon's Confederation of the Rhine.
- The Austrian Empire, excluding the Kingdom of Hungary, the Principality of Transylvania, and Croatia (all of which became parts of the apostolic kingdom of Hungary within the Danubian Dual Monarchy), the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia (constituting parts lost to Italy in 1859- viz. 1866), Bukovina, the kingdoms of Dalmatia and Galicia
- Kingdom of Bohemia
- Archduchy of Austria (split into Upper Austria and Lower Austria in 1849)
- Margraviate of Moravia
- Grand Duchy of Salzburg
- Duchy of Carinthia
- Duchy of Carniola
- Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia
- Duchy of Styria
- Littoral (consisting of Gorizia and Gradisca, Istria and Trieste)
- County of Tyrol
- Vorarlberg
- The Kingdom of Prussia (without Posen, East Prussia and West Prussia)
- Brandenburg
- Pomerania
- Rhine Province (until 1822, Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg)
- Saxony
- Silesia
- Westphalia
- The Kingdom of Bavaria (the third largest member)
- The Kingdom of Saxony
- The Kingdom of Hanover
- The Kingdom of Württemberg
- The Electorate of Hesse
- The Grand Duchy of Baden
- The Grand Duchy of Hesse
- The Duchy of Holstein (in personal union with the Kingdom of Denmark, was not a former member of the Confederation of the Rhine)
- The Duchy of Schleswig (a fief of Denmark and together with the Duchy of Holstein in personal union with the Kingdom of Denmark, was not a former member of either the Holy Roman Empire or the Confederation of the Rhine. The secessionist (pro-German) government of Schleswig-Holstein (1848–51) joined Schleswig to the Confederation. This was not recognized by the Confederation and the Danish government, and the peace settlement in 1851 specified that Schleswig was not a member.
- The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (lost over half of its territory in the west to Belgium in the breakup of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1839, and thereby causing Duchy of Limburg to become a member.)
- The Duchy of Limburg (became a member in 1839 as a compensation for territorial losses in the Grand Duchy of Luxemburg that were caused by the breakup of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands.)
- The Duchy of Brunswick (prior Brunswick-Lunenburgian Principality of Wolfenbüttel)
- The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- The Duchy of Nassau
- The Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
- The Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg (to 1825)
- The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld (to 1826)
- The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (from 1826)
- The Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen
- The Duchy of Saxe-Hildburghausen (Saxe-Altenburg from 1826)
- The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- The Duchy of Oldenburg (Grand Duchy from 1829)
- The Duchy of Anhalt-Dessau (Duchy of Anhalt from 1863)
- The Duchy of Anhalt-Bernburg (to 1863)
- The Duchy of Anhalt-Köthen (to 1847)
- The Principality of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
- The Principality of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
- The Principality of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (merged in Prussia in 1850)
- The Principality of Liechtenstein
- The Principality of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (merged in Prussia in 1850)
- The Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont
- The Principality of Reuss Senior Line
- The Principality of Reuss Junior Line
- The Principality of Schaumburg-Lippe
- The Principality of Lippe
- The Landgraviate of Hesse-Homburg (from 1817)
- The Duchy of Lauenburg
- The Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
- The Free City of Frankfurt upon Main
- The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (still a constitutive state of federal Germany)
- The Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (still a constitutive state of federal Germany)
The four free cities were republics by constitution, while all the others were monarchies, some constitutional and some absolutist.
Sources and references
- Westermann, Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (in German, detailed maps)
- WorldStatesmen