List of works by John Vanbrugh
John Vanbrugh created many disparate works, and this is a list of many of the notable ones.
- Castle Howard, c1699[1] (west wing designed by Sir Thomas Robinson only completed in early 19th century).
- The architect's own house in Whitehall, 1700–1701, known as "Goose-pie house", demolished 1898.[2]
- The Orangery, Kensington Palace, 1704: probably a modification by Vanbrugh to a design by Hawksmoor.[3]
- Haymarket Theatre, 1704–05,[4] has been completely rebuilt since and is now known as Her Majesty's.[5]
- Blenheim Palace, 1705–1722,[6] stable court never completed.
- Grand Bridge, Blenheim, 1708–22.[7]
- Kimbolton Castle, 1708–19,[8] remodelled the building.
- Demolished part of Audley End and designed new Grand Staircase, 1708.[9]
- Claremont House, 1708,[10] then known as Chargate (rebuilt to the designs of Henry Holland in the 18th century).
- Kings Weston House, 1710–14.[11]
- Grimsthorpe Castle, 1715–30, only the north side of the courtyard was rebuilt.[12]
- Eastbury Park, 1713–1738, completed by Roger Morris who amended Vanbrugh's design (demolished except for Kitchen Wing).[13]
- Cholmondeley Castle 1713 Vanbrugh prepared a design to rebuild the house, but it is believed not to have been executed[14]
- Great Obelisk, Castle Howard 1714[15]
- Morpeth Town Hall, 1714. (Front renewed and back replaced in 1869–70.)[16]
- The Belvedere, Claremont Landscape Garden, 1715.[17]
- Vanbrugh Castle, 1718-19, the architect's own house in Greenwich.[18] Additionally, houses for other members of Vanbrugh's family (none of which survived beyond 1910).[19]
- Stowe, Buckinghamshire, c.1719, added north portico, also several temples and follies in the gardens (the surviving follies are: the Wolfe Obelisk (c.1720), relocated 1759; the Rotunda (1720–21) dome altered; the Lake Pavilions (c.1719) altered[20]) up until his death.[21]
- The Temple,[22] Eastbury Park (early 1720s) demolished
- Robin Hood's Well,[23] Yorkshire C.1720
- Seaton Delaval Hall, 1720–28.[24]
- Lumley Castle, 1722, remodelling work.[25]
- Pyramid Gate, Castle Howard 1723[26]
- Walled Kitchen Garden,[27] Claremont (c.1723)
- Newcastle Pew, St. George's Church, Esher, 1724.[28]
- The Bagnio (water pavilion),[29] Eastbury Park (1725) demolished
- Temple of the Four Winds, Castle Howard, 1725–8.[30]
Attributed works include:
- Completion of State rooms, Hampton Court Palace, 1716–18.[31]
- Ordnance Board Building, Woolwich, 1716–20.[32]
- Chatham Dockyard Great Store House 1717, now demolished, Vanburgh or Hawksmoor were possibly involved in the design[33]
- Berwick Barracks, 1717–21.[note 1]
- The Brewhouse,[34] Kings Weston House (c.1718)
- Chatham Dockyard Main gate 1720, is possibly by Vanburgh or Hawksmoor[33]
- Loggia, Kings Weston House (c.1722)[35]
Gallery of architectural work
| Vanbrugh's architectural work |
|---|
| Castle Howard, north front |
| Castle Howard, north front |
| Castle Howard, south front |
| Castle Howard, south front |
| Great Obelisk, Castle Howard |
| Pyramid Gate, Castle Howard |
| Blenheim Palace, north front |
| North portico, Blenheim Palace |
| Blenheim Palace, from the south-west |
| Blenheim Palace, view north along the chapel colonnade |
| Entrance to Kitchen court, Blenheim Palace |
| Kitchen court, Blenheim Palace |
| South front, Blenheim Palace |
| North front, Blenheim Palace |
| East front, Blenheim Palace |
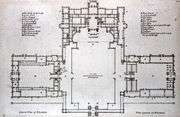
| Plan of Blenheim Palace, the colonnade enclosing the courtyard was never built |
| Grand Bridge, Blenheim Palace |
| Seaton Delaval Hall, north front |
| Seaton Delaval Hall, north front |
| Seaton Delaval Hall, from the south-west |
| South front, Kings Weston House |
| East front, Kings Weston House |
| Loggia, Kings Weston House (attributed to Vanbrugh) |
| The Brewhouse, Kings Weston House (attributed to Vanbrugh) |
| Grimsthorpe Castle, from the north |
| Western Lake Pavilion, Stowe |
| Robin Hood's Well, Yorkshire |
| Ordnance Board Building, Woolwich Arsenal, London (attributed to Vanbrugh) |
| Chatham Dockyard gateway (possibly by Vanbrugh) |
| Newcastle Pew, St. George's Church Esher |
|
Notes and references
- ↑ "The Castle Howard Story: The Building of Castle Howard". Castle Howard. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
- ↑ Beard, p. 70.
- ↑ The London Encyclopaedia, ed. Ben Weinreb and Christopher Hibbert, rev. ed. (London: Macmillan London, 1993; ISBN 0-333-57688-8), pp. 311, 438.
- ↑ Beard, p. 71
- ↑ "Her Majesty's (London)". Theatre's Trust. Retrieved 9 June 2010.
- ↑ "Blenheim Palace". World Heritage sites. UNESCO. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
- ↑ Sherwood and Pevsner, p. 473.
- ↑ Saumarez Smith, The Building of Castle Howard, p.96.
- ↑ John Julius Norwich, The Architecture of Southern England (London: Macmillan London, 1985; ISBN 0-333-22037-4), p. 208.
- ↑ Geoffrey Tyack and Steven Brindle, Blue Guide Country Houses of England (London: Black, 1994; ISBN 0-393-31057-4), p.468.
- ↑ Norwich, The Architecture of Southern England, p. 27.
- ↑ Tyack and Brindle, Blue Guide Country Houses of England, pp. 315–16.
- ↑ Norwich, The Architecture of Southern England, p. 182.
- ↑ page 141, The Work of Sir John Vanbrugh, Geoffrey Beard, 1986, Batsford Books, ISBN 0-7134-4679-X
- ↑ page 132, The Building of Castle Howard, Charles Saumarez Smith, 1990, Faber and Faber, ISBN O-571-14238-9
- ↑ John Grundy et al., Northumberland (London: Penguin, 1992; ISBN 0-14-071059-0), pp. 73, 397.
- ↑ Tyack and Brindle, Blue Guide Country Houses of England, pp. 468–69.
- ↑ Beard, p. 56.
- ↑ Bridget Cherry and Nikolaus Pevsner, London 2 South (London: Penguin, 1983; ISBN 0-14-071047-7), p. 273.
- ↑ pages 13, 24 & , Stowe Landscape Gardens, 1997, Jonathan Marsden et al, National Trust 1997
- ↑ Norwich, The Architecture of Southern England, p. 69.
- ↑ page 117, Vanburgh, Kerry Downes, 1977 A. Zwemmer Ltd, ISBN 0-302-02769-6
- ↑ page 46 ,Sir John Vanbrugh Storyteller in Stone, Vaughan Hart, 2008, Yale University Press
- ↑ Grundy et al., Northumberland, pp. 73, 561–63.
- ↑ Beard p. 66
- ↑ page 134, The Building of Castle Howard, Charles Saumarez Smith, 1990, Faber and Faber, ISBN O-571-14238-9
- ↑ page 235 ,Sir John Vanbrugh Storyteller in Stone, Vaughan Hart, 2008, Yale University Press
- ↑ Norwich, The Architecture of Southern England, p. 618.
- ↑ page 27, The Country Houses of Sir John Vanbrugh: From the Archives of Country Life, Jeremy Musson, 2008, Aurum
- ↑ Saumarez Smith, The Building of Castle Howard, pp. 144–46.
- ↑ Cherry and Pevsner, London 2 South, p. 494.
- ↑ The attribution is described as plausible in Bridget Cherry and Nikolaus Pevsner, London 2 South, p. 287.
- 1 2 page 164, The Work of Sir John Vanbrugh, Geoffrey Beard, 1986, Batsford Books, ISBN 0-7134-4679-X
- ↑ pages 153-154, English Homes, Period IV - vol.II, The work of Sir John Vanbrugh and his School 1699-1736, H. Avery Tipping and Christopher Hussey, 1928, Country Life
- ↑ page 177,Sir John Vanbrugh Storyteller in Stone, Vaughan Hart, 2008, Yale University Press
- ↑ Described as a misattribution in Grundy et al., Northumberland, pp. 74, 178–79. Grundy et al. attribute the design to Hawksmoor, saying that this was probably modified in execution by Andrews Jelfe.