Luna E-1A No.1
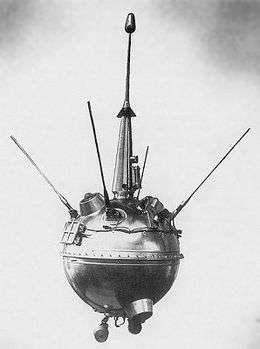 An E-1A spacecraft | |
| Mission type | Lunar impactor |
|---|---|
| Mission duration | Failed to orbit |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
| Launch mass | 387 kilograms (853 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 18 June 1959, 08:08 UTC |
| Rocket | Luna 8K72 s/n I1-7 |
| Launch site | Baikonur 1/5 |
Luna E-1A No.1[1] or E-1 No.5,[2] sometimes identified by NASA as Luna 1959A,[3] was a Soviet spacecraft which was lost in a launch failure in 1959. It was a 387-kilogram (853 lb) Luna E-1A spacecraft, the first of two to be launched.[1] It was intended to impact the surface of the Moon, and in doing so become the first man-made object to reach its surface.
Launch was originally scheduled for June 16, but delayed two days after a careless lieutenant had the booster filled with the wrong grade of RP-1 propellant. Luna E-1A No.1 was launched at 08:08 UTC on 18 June 1959 atop a Luna 8K72 carrier rocket,[4] flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.[2] The launch once again ended in failure when the booster suffered a failure of the yaw gyro and veered off its flight path. Ground control issued a manual shutoff command at T+153 seconds.[4]
The spacecraft was intended to conduct experiments during its flight towards the Moon. It would also have released gaseous sodium, in order to create a cloud of the metal which could be observed from Earth, allowing the spacecraft to be tracked.[5] Prior to the release of information about its mission, NASA correctly identified that it had been an attempted Lunar impact mission, however they incorrectly believed that it had been launched on 16 June, two days before its actual launch.[3]
References
- 1 2 Krebs, Gunter. "Luna E-1A". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- 1 2 McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- 1 2 "Tentatively Identified Missions and Launch Failures". NASA NSSDC. 2005-01-06.
- 1 2 Wade, Mark. "Soyuz". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ↑ Wade, Mark. "Luna E-1A". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
| Preceded by Luna 1 |
Luna programme | Succeeded by Luna 2 |