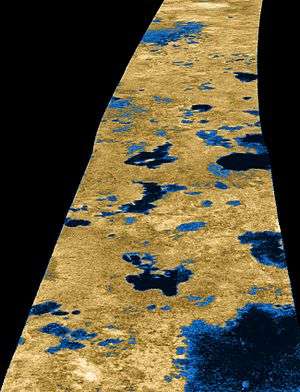
Mackay Lacus
|
False-color Cassini radar image of hydrocarbon lakes on Titan (2006), showing Mackay Lacus at upper left. | |
| Feature type | Lacus |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 78°19′N 97°32′W / 78.32°N 97.53°WCoordinates: 78°19′N 97°32′W / 78.32°N 97.53°W |
| Diameter | 180 km[note 1] |
| Eponym | Lake Mackay |
Mackay Lacus is the seventh largest of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The lake is composed of liquid methane and ethane,[1] and was detected by the Cassini space probe.
Mackay Lacus is located at coordinates 78.32°N and 97.53°W on Titan's globe and is 180 km in length.[2][note 1] It is named after Lake Mackay in Western Australia.[2]
Notes
- 1 2 The USGS web site gives the size as a "diameter", but it is actually the length in the longest dimension.
References
- ↑ Coustenis, A.; Taylor, F. W. (21 July 2008). Titan: Exploring an Earthlike World. World Scientific. pp. 154–155. ISBN 978-981-281-161-5.
- 1 2 "Mackay Lacus". USGS Astrogeology Science Center. USGS. Retrieved 2013-12-28.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/31/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.