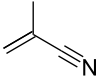
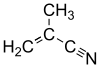
Methacrylonitrile
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylprop-2-enenitrile | |||
| Other names
Methylacrylonitrile 2-Cyanopropene 2-Cyano-1-propene Isopropenecyanide Isopropenylcyanid Isopropene cyanide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 126-98-7 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 29101 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.380 | ||
| PubChem | 31368 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H5N | |||
| Molar mass | 67.09 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Clear colorless to very slightly yellow liquid | ||
| Odor | Bitter almonds[1] | ||
| Density | 0.8 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −35.8 °C (−32.4 °F; 237.3 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 90 to 92 °C (194 to 198 °F; 363 to 365 K) | ||
| 2.57 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 71 mmHg (25 °C)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 13 °C (55 °F; 286 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2%-6.8%[1] | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] | ||
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 1 ppm (3 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methacrylonitrile is a chemical compound that is an unsaturated aliphatic nitrile, widely used in the preparation of homopolymers, copolymers, elastomers, and plastics and as a chemical intermediate in the preparation of acids, amides, amines, esters, and other nitriles. Methacrylonitrile is also used as a replacement for acrylonitrile in the manufacture of an acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene-like polymer.[2]
It is toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption.[3]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.