Mikoyan MiG-31
| MiG-31 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Russian Air Force MiG-31B (Ser: RF-92387; Bort: 70 Blue)[1] | |
| Role | Interceptor aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Mikoyan |
| First flight | 16 September 1975 |
| Introduction | 6 May 1981 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | Russian Air Force Kazakhstan Air Force |
| Produced | 1975–1994 |
| Number built | 519[2] |
| Developed from | Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 |
The Mikoyan MiG-31 (Russian: Микоян МиГ-31; NATO reporting name: Foxhound) is a supersonic interceptor aircraft developed for use by the Soviet Air Forces. The aircraft was designed by the Mikoyan design bureau as a replacement for the earlier MiG-25 "Foxbat"; the MiG-31 is based on, and shares design elements with the MiG-25.[3] The MiG-31 has the distinction of being one of the fastest combat jets in the world.[4] It continues to be operated by the Russian Air Force and the Kazakhstan Air Force following the end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union in late 1991. The Russian Defence Ministry expects the MiG-31 to remain in service until at least 2030.[5]
Development
Origins
The MiG-25 made substantial design sacrifices in order to achieve high speed, altitude and rate of climb. It lacks maneuverability at interception speeds and is difficult to fly at low altitudes. The MiG-25's speed is limited to Mach 2.83 but it could reach a maximum speed of Mach 3.2 or more with the risk of engine damage.[6][7]

Development of the MiG-25's replacement began with the Ye-155MP (Russian: Е-155МП) prototype which first flew on 16 September 1975.[8] Although it bore a superficial resemblance to the MiG-25, it had a longer fuselage to accommodate the radar operator's cockpit and was in many respects a new design. An important development was the advanced radar, capable of both look-up and look-down/shoot-down engagement, as well as multiple target tracking. This gave the Soviet Union an interceptor able to engage the most likely Western intruders (low flying cruise missiles and bombers) at long range.[9]
Like its MiG-25 predecessor, the introduction of the MiG-31 was surrounded by early speculation and misinformation concerning its design and abilities. The West learned of the new interceptor from Lieutenant Viktor Belenko, a pilot who defected to Japan in 1976 with his MiG-25P.[10] Belenko described an upcoming "Super Foxbat" with two seats and an ability to intercept cruise missiles. According to his testimony, the new interceptor was to have air intakes similar to the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23, which the MiG-31 does not have, at least in production variants.[11]
Into production
Serial production of the MiG-31 began in 1979.[12][13] The MiG-31 is able to maintain combat effectiveness despite the potential use of active and passive radar jammers and thermal decoys by adversaries. A group of four MiG-31 interceptors is able to control an area of air space across a total length of 800–900 km;[9] its radar possessing a maximum detection range of 200 km in distance (radius) and the typical width of detection along the front of 225 km.[14]
The MiG-31 was designed to fulfill the following mission objectives:[2]
- Intercept cruise missiles and their launch aircraft by reaching missile launch range in the lowest possible time after departing the loiter area;
- Detect and destroy low flying cruise missiles, UAVs and helicopters;
- Long range escort of strategic bombers;
- Provide strategic air defense in areas not covered by ground based air defense systems.
MiG-31 production ended in 1994.[15] A total of 519 MiG-31s was produced of which 349 "baseline models" were produced at the Sokol plant between 1976 and 1988. The second production batch of 101 MiG-31DZs was produced between 1989 and 1991. The final batch (MiG-31B) of 69 aircraft was produced between 1990 and 1994. Of this final batch, 50 were retained by the Kazakhstan Air Force after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Of the "baseline models," 40 airframes were upgraded to MiG-31BS standard.[2]
Upgrades and replacement
Some upgrade programs have found their way into the MiG-31 fleet, like the MiG-31BM multirole version with upgraded avionics, new multimode radar, hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS) controls, liquid crystal (LCD) color multi-function displays (MFDs), ability to carry the R-77 missile and various Russian air-to-ground missiles (AGMs) such as the Kh-31 anti-radiation missile (ARM), a new and more powerful computer, and digital data links. A project to upgrade the Russian MiG-31 fleet to the MiG-31BM standard began in 2010;[16] 100 aircraft are to be upgraded to MiG-31BM standard by 2020.[17][18] Russian Federation Defence Ministry chief Colonel Yuri Balyko has claimed that the upgrade will increase the combat effectiveness of the aircraft several times over.[19] 18 MIG-31BMs were delivered in 2014.[20] The Russian military will receive more than 130 upgraded MiG-31BMs, and the first 24 aircraft have already been delivered, Russian Deputy Defense Minister Yuri Borisov told reporters on 9 April 2015.[21]
Russia plans to start development of a replacement for the MiG-31 by 2019. The aircraft will be called PAK-DP (ПАК ДП, Перспективный авиационный комплекс дальнего перехвата - Prospective Air Complex for Long-Range Interception).[22]
Development of the new aircraft, designated MiG-41, began in April 2013. Such development is favored over restarting MiG-31 production.[23] In March 2014, Russian test pilot Anatoly Kvochur said that work began on a Mach 4 MiG-41 based on the MiG-31.[24][25] Later reports said that development of the MiG-31 replacement is to begin in 2017, with the first aircraft to be delivered in 2020, and the replacement entering service in 2025.[26]
Design
Overview

Like the MiG-25, the MiG-31 is a large twin-engine aircraft with side-mounted air intake ramps, a shoulder-mounted wing with an aspect ratio of 2.94, and twin vertical tailfins. Unlike the MiG-25, it has two seats, with the rear occupied by a dedicated weapon systems officer.[27] The MiG-31 is limited to only 5 g when travelling at supersonic speeds.[6] While flying under combat weight, its wing loading is marginal and its thrust-to-weight ratio is favorable. However, the MiG-31 is not designed for close combat or rapid turning.[6]
The wings and airframe of the MiG-31 are stronger than those of the MiG-25, permitting supersonic flight at low altitudes. Like the MiG-25, its flight surfaces are built primarily of nickel-steel alloy, enabling the aircraft to tolerate kinetic heating at airspeeds approaching Mach 3. The MiG-31 airframe comprises 49% arc-welded nickel steel, 33% light metal alloy, 16% titanium and 2% composites.[28] Its D30-F6 jet engines, each rated at 152 kN thrust, allow a maximum speed of Mach 1.23 at low altitude. High-altitude speed is temperature-redlined to Mach 2.83 – the thrust-to-drag ratio is sufficient for speeds in excess of Mach 3, but such speeds pose unacceptable hazards to engine and airframe life in routine use.[6]
Electronics suite
The MiG-31 was one first aircraft with a phased array radar, and is one of two aircraft in the world capable of independently firing long-range air-to-air missiles as of 2013.[29][30][31][32][33]) The MiG-31BM has a detection range of 282 km for a target with a radar cross-section of 5 square meters,[34] and 189 km for stealth targets.[35]
The MiG-31 was the world's first operational fighter with a passive electronically scanned array radar (PESA), the Zaslon S-800. Its maximum range against fighter-sized targets is approximately 200 km (125 mi), and it can track up to 10 targets and simultaneously attack four of them with its Vympel R-33 missiles. The radar is matched with an infra-red search and track (IRST) system in a retractable undernose fairing.[6]
The MiG-31 was equipped with RK-RLDN and APD-518[36] digital secure datalinks. The RK-RLDN datalink is for communication with ground control centers. The APD-518 datalink enables a flight of four MiG-31 to automatically exchange radar-generated data within 200 km (124 mi) from each other. It also enables other aircraft with less sophisticated avionics,[37] such as MiG-23,25,29/Su-15,27[14] to be directed to targets spotted by MiG-31 (a maximum of 4 (long-range) for each MiG-31 aircraft). The A-50 AEW aircraft and MiG-31 can automatically exchange aerial and terrestrial radar target designation,[38] as well as air defense[39]
Corner area of simultaneous firing rockets number of goals for the MiG-31 is 18200 square degrees (for the F-14 is only 420 square meters °). long-range missiles can be induced at a target in a range of slightly less than +/- 120 degrees (F-14 only +/- 20).[40][41]
Radars
Adopted in 1981 RP-31 N007 backstop (Russian -Zaslon).[42]
- the range of detection of air targets: 200 km (for the purpose of a radar cross-section of 19 m2 on a collision angle with probability 0.5)
- target detection distance with radar cross-section of 3 m2 in the rear within 35 km with a probability of 0.5 ([43][44])
- number of detected targets: 24 (was originally 10[45])
- number of targets for attack: 6 (was originally 4[45][46])
- range of automatic tracking: 120 km
- detection of infrared signature targets: 56 km
- Effective in the detection of cruise missiles and other targets against ground clutter[45]
- Until 2000, it was the world's only fighter in service equipped with phased array radar,[47][48] when the Mitsubishi F-2 entered service with state of the art J/APG-1 active phased array radar.
- Able to intercept and destroy cruise missiles flying at extremely low altitudes.[41][49]
Variant differences
The basic differences between other versions and the МiG-31BM:[46]
- The onboard radar complex of the MiG-31BM can track 24 airborne targets at one time, 6 of which can be simultaneously attacked by R-33S missiles.
- Modernized variants of the aircraft can be equipped with anti-radiation missiles Kh-31, Kh-25MR or MPU (up to six units), anti-ship Kh-31A (up to six), air-to-surface class missiles Kh-29 and Kh-59 (up to three) or Kh-59M (up to two units), up to six precision bombs KAB-1500 or eight KAB-500 with television or laser-guidance. Maximum mass of payload is 9000 kg.
- The MiG-31M, MiG-31D, and MiG-31BM standard aircraft have an upgraded Zaslon-M radar, with larger antenna and greater detection range (said to be 400 km (250 mi) against AWACS-size targets) and the ability to attack multiple targets — air and ground — simultaneously. The Zaslon-M has a 1.4 m diameter (larger) antenna, with 50% to 100% better performance than Zaslon. In April 1994 it was used with an R-37 to hit a target at 300 km distance.[42] It has a search range of 400 km for a 19/20 m2 RCS target and can track 24 targets at once, engaging six[50][51] (282 km for 5 m2[52]). Relative target speed detection increased from 5 Mach to 6 Mach, improving the probability of destroying fast-moving targets.[42] The MiG-31BM is one of only a few aircraft able to intercept and destroy cruise missiles flying at extremely low altitude.[42][53][54]
Cockpit
The aircraft is a two-seater with the rear seat occupant controlling the radar. Although cockpit controls are duplicated across cockpits, it is normal for the aircraft to be flown only from the front seat. The pilot flies the aircraft by means of a centre stick and left hand throttles. The rear cockpit has only two small vision ports on the sides of the canopy. The presence of the WSO (Weapon Systems Operator) in the rear cockpit improves aircraft effectiveness since the WSO is entirely dedicated to radar operations and weapons deployment, thus decreasing the workload of the pilot and increasing efficiency. Both cockpits are fitted with zero/zero ejection seats which allow the crew to eject at any altitude and airspeed.[6]
Armament

The MiG-31's main armament is four R-33 air-to-air missiles (NATO codename AA-9 'Amos') carried under the belly. The R-33 is the Russian equivalent of the U.S. Navy's AIM-54 Phoenix.
- 1× GSh-6-23 23 mm cannon with 260 rounds.
- Fuselage recesses for 4× R-33 (AA-9 'Amos') or 6x R-37 (AA-13 'Arrow') (MiG-31M/BM only).
- 4 underwing pylons for a combination of (6 places for charging[55] (+ 2 space to add removable fuel tanks[15])):
- 6× R-37 (missile) long-range missiles (280 km).[56]
- (4[14])× R-33 (missile) long-range missiles (304 km) 2012.[57]
- (?)× Kh-31 long-range missiles (200 km) for high-speed target (maneuvering with overload 8G).[57]
- (?)× Р-33 AA-9 «Amos» (1981) 120 km, Р-33S (1999) 160 km.[58]
- 2[14] 4 (superior limit)[59]× R-40TD1 (AA-6 'Acrid') medium-range missiles (P-40 (50 km, MiG-25P, 1970) 80 km(PD)(user)), height applications between 0.5 and 30 km (maneuvering with overload 4 g).[60]
- 4× R-60 (AA-8 'Aphid')
- 4× R-73 (AA-11 'Archer') short-range IR missiles,
- 4× R-77 (AA-12 'Adder') medium-range missiles (100км) for high-speed target (maneuvering with overload 12G).[61]
- Some aircraft are equipped to launch the Kh-31P (AS-17 'Krypton') and Kh-58 (AS-11 'Kilter') anti-radiation missiles in the Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) role. Anti-ship X-31A (up to six), missiles air-to-surface X-59 and X-29T (up to three) or X-59M (up to two units), up to six air bombs KAB-1500, or up to eight KAB-500 with a television or laser-guided. Maximum weight of the combat load is 9000 kg.[62][63]
Operational history

.jpg)
The MiG-31 entered operational service with the Soviet Air Defence Forces (PVO) in 1981.[64] It was the world's first aircraft with a phased array radar, and is one of only two aircraft in the world capable of independently firing long-range air-to-air missiles as of 2013.[29][65][66] (The other is the Iranian Air Force F-14 Tomcat which uses a domestic version of the long-range AIM-54 Phoenix called the Fakour-90.[67][68]) The MiG-31BM has a detection range of 282 km for a target with a radar cross-section of 5 square meters,[69] and 189 km for stealth targets.[70]
With the designation Ye-266, a re-engined Ye-155[71][72] set new world records.[73] It reached an absolute maximum altitude of 37,650 metres (123,520 ft) in 1977,[74] and set a time to height record of 35,000 metres (115,000 ft) in 4 minutes, 11.78 seconds, both of which were set by the famous MiG test pilot Alexander Fedotov. Pyotr Ostapenko,[75] his deputy, set a time to height record to 30,000 m (98,000 ft) in 3 minutes and 9.8 seconds in 1975.[76][77]
Export
Syria ordered eight MiG-31E aircraft in 2007 for the Syrian Air Force.[78][79] However, the order was suspended in May 2009 reportedly either due to Israeli pressure or lack of Syrian funds.[80] On 15 August 2015, Turkish news media reported that six MiG-31s had been delivered to the Syrian Arab Air Force,[81] but Russia denied making MiG-31 deliveries to Syria.[82]
Variants

MiG-31 / MiG-31 01DZ
Two-seat all weather, all altitude interceptor. Designated as MiG-31 01DZ when fitted with air-to-air refueling probe.[83]
MiG-31M
Development of a more comprehensive advanced version, the MiG-31M, began in 1984 and first flew in 1985, but the dissolution of the Soviet Union prevented it from entering full production.[84][85] One piece rounded windscreen, small side windows for rear cockpit, wider and deeper dorsal spine. Digital flight controls added, multifunction CRT cockpit displays, multi-mode phased array radar. No gun fitted in this model. Refueling probe moved to starboard side of aircraft. Fuselage weapon stations increased from four to six by adding two centre-line stations. Maximum TO weight increased to 52,000 kg using increased thrust D-30F6M engines.[83]
MiG-31BS
Designation applied to type 01DZ when converted to MiG-31B standard.[83]
MiG-31B
Second production batch with upgraded avionics and in-flight refueling probe introduced in 1990. Its development was the result of the Soviet discovery that Phazotron radar division engineer Adolf Tolkachev had sold information on advanced radars to the West. A new version of the compromised radar was hastily developed.[86] MiG 31B also have the improved ECM and EW equipment with integration of improved R-33S missiles. Long range navigation system compatible with Loran/Omega and Chaka ground stations added. This model replaced the 01DZ models in late 1990.[83]
MiG-31BM / MiG-31BSM
The upgraded MiG-31B was designated MiG-31BM and the upgraded MiG-31BS was designated MiG-31BSM.[2] The most visible addition to the BM/BSM variant was the rear-view periscope added above the front cockpit canopy.[2] The MiG-31BМ's maximum detection range for air targets was increased in the upgrade to 320 km (189 for stealth). It had the ability to automatically track up to ten targets, and the latest units can track up to 24 targets and simultaneously engage up to 8 targets.[87] The on-board Argon-K computer selects four targets of highest priority, which simultaneously are engaged by long-range R-33S air-to-air missiles. Infrared search is interfaced with radar and is designed for passive search of the airspace, and for the targeting of R-40TD and R-60 thermal guidance missiles.
The basic difference between earlier versions and the МiG-31BM[88][89] is that the МiG-31BM can act as a small airborne early warning aircraft. Onboard equipment provides interaction with surface-to-air missile units and can function as an airborne command post to coordinate the actions of other types of fighters with less powerful radars.[14]
The flight-navigation equipment of the MiG-31 includes a complex of automatic control system SAU-155МP and sighting-navigation complex KN-25 with two inertial systems and IP-1-72A with digital computer, electronic long range navigation system Radical NP (312) or A-331, electronic system of the long-range navigation A-723. Distant radio navigation is carried out by means of two systems: CHAYKA (similar to the system of Laurent) and «Route» (similar to the system of Omega).[90]
The MiG-31 is equipped with ECM of radar and infrared ranges.[47] Interceptor MiG-31 is capable of performing combat tasks.
The MiG-31 was equipped with RK-RLDN and APD-518[36] digital secure datalinks. The RK-RLDN datalink is for communication with ground control centers. The APD-518 datalink enables a flight of four MiG-31 to automatically exchange radar-generated data within 200[59] km (124 mi) from each other (a group of four MiG-31 interceptors is able to control an area of air space across a total length of 800 km). It also enables other aircraft with less sophisticated avionics,[37] such as MiG-23,25,29/Su - 15,27[14] to be directed to targets spotted by MiG-31 (a maximum of 4 (long-range) for each MiG-31 aircraft). Similarly[91] to complex S-300 aircraft group with APD-518 can: share data obtained by various radars from different directions (active or passive scanning of radiation) and summarize the data. That is, the target can be detected passively (through noise posed to protect themselves / active search radar (target)) and (or) actively simultaneously from many different directions (active search radar of MiG-31). And everyone aircraft has APD-518 will have exact data, even if it is not involved in the search.[12][36][42]
- arming - 4 long-range missiles + 4 short-range/medium-range missiles (including R-77 medium-range).[47]
- interacting with ground-based automated digital control system (ACS «Rubezh» Operating radius of 2000 km, can control multiple groups of planes), operating modes of remote aiming, semi-automated actions (coordinate support), singly, and also: to direct on the target missiles launched from the other aircraft.
- Digital immune system provides the automatic exchange of tactical information in a group of four interceptors, remote one from another at a distance of 200 km and aiming at the target group of fighters with less-powerful avionics (in this case the aircraft performs the role of guidance point or repeater).[14]
MiG-31D
Two aircraft were designated as Type 31D and were manufactured as dedicated anti-satellite models with ballast in the nose instead of radars, flat fuselage undersurface (i.e. no recessed weapon system bays) and had large winglets above and below the wing-tips. Equipped with Vympel ASAT missiles.[83]
MiG-31E
Export version of the MiG-31B type.[83]
MiG-31F
Planned fighter-bomber intended for use with TV, radar and laser-guided ASM weapon systems.[83]
MiG-31FE
Planned Export version of the MiG-31F. Was never produced.[83]
Operators

- Kazakhstan Air Force - 29 in service[92]
- Russian Air Force - 252 in inventory.[93] 152-190 (MiG-31/B/BM) active,[23][94] +18 BMs in 2014,[95] 80 totally (2016),[96] 100 units in mod. BM on 2018[97]
- Russian Naval Aviation 30+ were in inventory[42]
Former operators
- Soviet Air Defence Forces
- Soviet Air Forces aircraft passed on to Russia and Kazakhstan in 1991.
Notable accidents
On 6 September 2011, a MiG-31 crashed near Bolgary village, Perm region, Russia.[98] The aircraft crashed shortly after takeoff, killing both pilots. Another, non-fatal crash occurred in 2010. The entire fleet was grounded pending an investigation.[99]
During the night of 23 April 2013, a Kazakhstan Air Force MiG-31 crashed during a training flight near the village of Prostornoye in the Karaganda Region of Kazakhstan, killing the pilot and injuring the navigator. The plane crashed due to technical failure. The same plane underwent a major overhaul at a plant in Rzhev, northwest Russia in December 2012.[100]
On 4 September 2014, a MiG-31 crashed during exercises at a distance of 25 kilometres from the city of Armavir.[101]
On 25 January 2016, a MiG-31 fighter jet crashed in the Krasnoyarsk region of Russia. The pilots were able to eject safely and no casualties have been reported.[102]
Specifications (MiG-31)
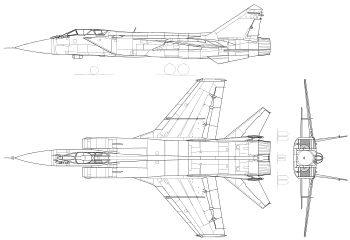
.jpg)

.jpg)
Data from Great Book of Modern Warplanes,[3] MiG-31E data,[103] Combat Aircraft since 1945[104]
General characteristics
- Crew: Two (pilot and weapons system officer)
- Length: 22.69 m (74 ft 5 in)
- Wingspan: 13.46 m (44 ft 2 in)
- Height: 6.15 m (20 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 61.6 m2 (663 ft2)
- Empty weight: 21,820 kg (48,100 lb)
- Loaded weight: 41,000 kg (90,400 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 46,200 kg (101,900 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Soloviev D-30F6 afterburning turbofans
- Dry thrust: 93 kN (20,900 lbf) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 152 kN (34,172 lbf) each
Performance
- Maximum speed:
- High altitude: Mach 2.83 (3,000 km/h, 1,860 mph)[6]
- Low altitude: Mach 1.2 (1,500 km/h, 930 mph)
- Cruise speed: Mach 2.35 (2,500 km/h; 1,550 mph)
- Combat radius: 1,450 km (900 mi) at Mach 0.8 and at altitude of 10,000 m (33,000 ft); 720 km (450 mi) at Mach 2.35 and altitude of 18,000 m (59,000 ft)[105]
- Combat range: 3,000 km[106] (1,860 mi) with 4xR-33E and 2 drop tanks; 5,400 km (3,360 mi) with 4xR-33E and 2 drop tanks with one in-flight refueling[106]
- Service ceiling: 20,600 m (67,600 ft)
- Rate of climb: 208 m/s (41,000 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 665 kg/m2 (136 lb/ft2)
- Thrust/weight: 0.85
- Maximum g-load: 5 g
Armament
MiG-31BM
- 1× GSh-6-23 23 mm cannon with 260 rounds.
- Fuselage recesses for either:[2]
- 4× R-33 (AA-9 'Amos')
- 4x R-33S
- 4x R-37M (AA-13 'Arrow')
- 4 underwing pylons for either:[2]
- 2 or 4x R-40 (AA-6 'Acrid') MVR AAM
- 4× R-73 (AA-11 'Archer') WVR AAM
- 4× R-77-1 (AA-12 'Adder') BVR AAM
See also
- Firefox (novel) and Firefox (film), the premise of which is the theft of a speculated/fictional version of the MiG-31
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ Pichugin, Dmitriy. "MiG-31". Airliners.net. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mladenov, Alexander (July 2015). "The Foxhound's New Tricks". Air International. 19 (1): 28.
- 1 2 Spick 2000
- ↑ http://rt.com/news/210935-norway-f16-mig31-interception/
- ↑ "Russia's Modernized Soviet-Era MiG-31 Fighters to Fly for 50 Years". The Moscow Times. April 9, 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Dawes, Alan. "Mikoyan's Long-Legged Hunting Dog." Air International, December 2002, pp. 396–401.
- ↑ Gunston and Spick 1983, pp. 132–133.
- ↑ Eden 2004, p. 323.
- 1 2 "МиГ-31 – лучший истребитель-перехватчик мира". topwar.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Eyster, II, James P. (1977). "The Defection of Viktor Belenko: The Use of International Law to Justify Political Decisions". Fordham International Law Journal. The Berkeley Electronic Press (bepress). 1 (1). Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- ↑ "MiG-31 Foxhound". Global Aircraft. The Global Aircraft Organization. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- 1 2 "МиГ-31 модернизируется и прослужит в ВВС России еще около 15 лет". arms-expo.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://tass.ru/politika/1369019
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 https://web.archive.org/web/20131214070309/http://www.arms-expo.ru/049049056052124051050056051.html. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 19 January 2014. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - 1 2 "МиГ-31". encyclopaedia-russia.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Skrynnikov, R. "Defense: Russian air force completing MiG-31BM modernization program." RIA Novosti, 13 August 2010. Retrieved: 17 August 2010. Archived 16 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Ankov, Vitaliy. "Russia to modernize 60 MiG-31 interceptors by 2020." RIA Novosti, 2 January 2012. Retrieved: 25 November 2012.
- ↑ "ЦАМТО / Новости / Минобороны России и Объединенная авиастроительная корпорация заключили контракт на модернизацию самолетов МиГ-31". armstrade.org. 27 November 2014. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "MiG-31 Upgrade Will Quadruple Its Effectiveness – Expert." royfc.com. Retrieved: 24 January 2011.
- ↑ "ТАСС: Армия и ОПК - Шойгу: оснащенность Российской армии современным оружием и техникой за год выросла на 7%". ТАСС. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://www.armstrade.org/includes/periodics/news/2015/0409/152528676/detail.shtml
- ↑ http://www.janes.com/article/53633/russia-to-launch-mig-31-replacement-programme-before-end-of-decade
- 1 2 "Russia to Field MiG-31 Replacement by 2020". RIA Novosti, 11 April 2013.
- ↑ "The Russian Armed Forces are working on the Mig-41, a new supersonic fighter based on the Mig-31 Foxhound." theaviationist.com
- ↑ "MiG-41 – A new Mach 4+ Fighter?" MiGFlug
- ↑ "Russia to Start Developing Replacement for MiG-31 in 2017". RIA Novosti, 11 August 2014.
- ↑ "How the Mig-31 repelled the SR-71 Blackbird from Soviet skies". theaviationist.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "The MiG-31 Foxhound: One of the World's Greatest Interceptors". Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- 1 2 "Истребитель-перехватчик МиГ-31. Летно-технические характеристики". РИА Новости. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://fun-space.ru/aviacziya/2149-mig-31
- ↑ "МиГ-31". paralay.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Cenciotti, David (26 September 2013). "Iranian F-14 Tomcat's "new" indigenous air-to-air missile is actually an (improved?) AIM-54 Phoenix replica". The Aviationist. David Cenciotti. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ Nassirkhani, Major Farhad. "The first and only country to receive F-14 Tomcat was, The Nirouyeh Havaiyeh Shahanshahiye Iran, or Imperial Iranian Air Force". ImperialIranianAirForce.net. Fred Nassirkhani 31441 Santa Margarita Pkwy. #A128 Rancho Santa Margarita, CA 92688. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ bill. "Which is the No:1 BVR Fighter Aircraft in South Asia ?". angelfire.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "Как работает перехватчик МиГ-31". Российская газета. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- 1 2 3 "МиГ МиГ-31". airwar.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- 1 2 http://испытатели.рф/russia/mikoyan/mig/31/bm/mig31bm.htm
- ↑ "МиГ-31: реальность и перспективы". vpk-news.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ https://rg.ru/2014/02/03/mig-site.html
- ↑ http://www.airbase.ru/sb/russia/mikoyan/mig/31/index-t.htm
- 1 2 http://www.milrus.com/vvs/mig31/text.shtml
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Статья. Истребитель-перехватчик МиГ-31. ВТР". milrus.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Сизова Ирина Юрьевна. "Система управления вооружением СУВ "Заслон" истребителя МиГ-31". niip.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://www.roe.ru/cataloque/air_craft/aircraft_16-19.pdf
- 1 2 3 "Советский ответ Западу. МиГ-31 против F-14 - Военный паритет: ракеты средней дальности, крылатая ракета, подводные лодки, истребитель самолет пятого поколения". militaryparitet.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- 1 2 "Многоцелевой истребитель МиГ-31БМ - Вооружение России и других стран Мира". worldweapon.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Дальний истребитель-перехватчик МиГ-31 - Вооружение России и других стран Мира". worldweapon.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "МиГ-31 - FOXHOUND". militaryrussia.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://www.rg.ru/2014/02/03/mig-site.html
- ↑ Zaslon radar at Janes Defence web-site
- ↑ Zaslon radar at Russia Airforce Handbook - Google Books
- ↑ "Zaslon-M radar." Fighterplanes. Retrieved: 16 July 2012.
- ↑ "МиГ 31 - Сверхзвуковой всепогодный истребитель". ucoz.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "60 истребителей-перехватчиков МиГ-31 будут модернизированы до 2020 года". arms-expo.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Дракон. "Тактико-технические характеристики истребителя МиГ-31". narod.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "МиГ МиГ-31БМ". airwar.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- 1 2 "МиГ-31БМ получат новую ракету". dokwar.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://испытатели.рф/russia/vympel/r/33/r33_1.htm
- 1 2 "МиГ-31Б". modernforces.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://испытатели.рф/russia/bisnovat/r/40/r40.htm
- ↑ http://испытатели.рф/russia/vympel/r/77/r77.htm
- ↑ http://worldweapon.ru/sam/mig31.php
- ↑ http://www.airwar.ru/enc/fighter/mig31bm.html
- ↑ "МиГ-31". testpilot.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://fun-space.ru/aviacziya/2149-mig-31
- ↑ "МиГ-31". paralay.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Cenciotti, David (26 September 2013). "Iranian F-14 Tomcat's "new" indigenous air-to-air missile is actually an (improved?) AIM-54 Phoenix replica". The Aviationist. David Cenciotti. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ Nassirkhani, Major Farhad. "The first and only country to receive F-14 Tomcat was, The Nirouyeh Havaiyeh Shahanshahiye Iran, or Imperial Iranian Air Force". ImperialIranianAirForce.net. Fred Nassirkhani 31441 Santa Margarita Pkwy. #A128 Rancho Santa Margarita, CA 92688. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ↑ bill. "Which is the No:1 BVR Fighter Aircraft in South Asia ?". angelfire.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "Как работает перехватчик МиГ-31". Российская газета. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Babain, Sergey. "E-155M (E-266M) "FoxBat" interceptor/recco-bomber". TestPilot.ru. SB. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ↑ Gordon, Yefim; Komissarov, Dmitriy (2013). Soviet spyplanes of the Cold War. p. 28. ISBN 9781781592854. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ↑ Kopp, Dr. Carlo (November 1992). "Foxbat and Foxhound Russia's Cold War Warriors". Aus Air Power. First published Australian Aviation, November, 1992. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
- ↑ Boyne, Walter J. (2013). Beyond the wild blue a history of the u.s. air force, 1947-2007. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 493. ISBN 1429901802. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ↑ Ankov, Vitaly (9 April 2012). "MiG Test Pilot Ostapenko Dies Age 83". Sputnik News. Sputnik. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ↑ "Flight Global Archive - Aviation History1975". Flight Global. Flight International. 29 May 1975. p. 855. Retrieved 10 October 2015.
- ↑ "World Records." OKB MIG. Retrieved: 11 May 2011.
- ↑ Air Forces Monthly, August 2007 issue
- ↑ Karnozov, Vladimir. "Syria signs for eight MiG-31 interceptors." Flight International, 21 June 2007.
- ↑ "Syrian MiG-31 Order suspended." mosnews.com. Retrieved: 24 January 2011.
- ↑ "Russia delivers six Mikoyan MiG-31 fighter jets to Syria: Report". Press TV. Aug 16, 2015.
According to a Sunday report by Turkey's English-language website BGN News, Moscow shipped the supersonic interceptor aircraft to Damascus under a contract inked between the two sides in 2007
- ↑ "No MiG-31s for Damascus: Russia Denies Sending Interceptors to Syria". Sputnik News. Aug 22, 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Jackson, Paul, ed. (1998). Jane's: All the World's Aircraft: 1998-99. Surrey: Jane's. p. 386. ISBN 0710617887.
- ↑ "МиГ-31М". testpilot.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "Russian MiG-31 "Foxhound" - A fighter ahead of its time". Global Aviation Report. WordPress. 21 February 2014. Retrieved 12 July 2015.
- ↑ "МиГ-31Б (БС)". testpilot.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ as well as air defense
- ↑ "Двухместный сверхзвуковой истребитель-перехватчик МиГ-31". dokwar.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "ÌèÃ-31". testpilots.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "Новосибирск прикрыли истребителями-перехватчиками МиГ-31БМ". lenta.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ "Авиация НАТО против сирийских С-300". 3mv.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Reed Business Information Limited. "AirSpace". flightglobal.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Zelin, Alexander (Commander of the Russian Air Force). "Zelin." ng.ru. Retrieved: 19 March 2012.
- ↑ "ВЗГЛЯД / Летчик-испытатель: МиГ-41 должен развивать скорость до 4,3 Маха". vz.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ http://www.rg.ru/2014/12/30/samoleti-site.html
- ↑ The Military Balance 2016
- ↑ "bmpd". livejournal.com. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Petrov, Sergei. "Flight recorder found at MiG-31 crash site." rian.ru, 7 September 2011.
- ↑ "Investigators seizing crashed MiG-31 fighter documentation." itar-tass.com. Retrieved: 16 July 2012.
- ↑ Sputnik (24 April 2013). "Pilot Killed in Kazakh MiG-31 Crash". ria.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ Sputnik (4 September 2014). "Russian Defense Ministry: Russian MiG-31 Supersonic Interceptor Crashes, Pilots Survive". ria.ru. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- ↑ MiG-31 fighter jet crashes in Siberia, pilots eject safelyRussia Today. Retrieved: 26 January 2016.
- ↑ "MiG-31E." RAC MiG. Retrieved: 22 July 2008.
- ↑ Wilson 2000, p. 103.
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20120308124035/http://www.roe.ru/cataloque/air_craft/aircraft_16-19.pdf
- 1 2 http://www.migavia.ru/index.php/en/production/mig-31e-fighter?limit=1&start=2
Bibliography
- Crickmore, Paul F. Lockheed Blackbird: Beyond the Secret Missions. Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2004. ISBN 1-84176-694-1.
- Eden, Paul, ed. "Mikoyan MiG-25 'Foxbat'". "Mikoyan MiG-31 'Foxhound'". Encyclopedia of Modern Military Aircraft. London: Amber Books, 2004. ISBN 1-904687-84-9.
- Gordon, Yefim. MiG-25 'Foxbat,' MiG-31 'Foxhound:" Russia's Defensive Front Line. Hinckley, UK: Midland Publishing, 1997. ISBN 1-85780-064-8.
- Spick, Mike. "MiG-31 'Foxhound'". The Great Book of Modern Warplanes. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI, 2000. ISBN 0-7603-0893-4.
- Wilson, Stewart. Combat Aircraft since 1945. Fyshwick, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 2000. ISBN 1-875671-50-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-31. |
- MiG-31 Foxhound on fas.org
- MiG-31 page on aerospaceweb.org
- MiG-31E page on Russian Aircraft Corporation "MiG" site
- MiG-31 page on milavia.net
- MiG-31 Foxhound at Global Security
- MIG-31 Foxhound Interceptor at Russian Military Analysis
- MiG-31 on aviation.ru
- MIG-31 Foxhound at Global Aircraft
- Foxbat and Foxhound - Australian Aviation
- Износ техники — причина катастрофы МиГ-31? (Russian) (in english)