Nepenthes distillatoria
| Nepenthes distillatoria | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An upper pitcher of Nepenthes distillatoria from Sinharaja Forest Reserve, Sri Lanka | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Core eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Nepenthaceae |
| Genus: | Nepenthes |
| Species: | N. distillatoria |
| Binomial name | |
| Nepenthes distillatoria L. (1753) | |
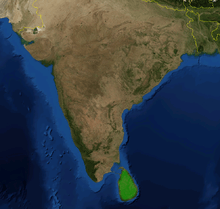 | |
| Distribution of N. distillatoria. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Nepenthes distillatoria (/nᵻˈpɛnθiːz dᵻˌstɪləˈtɔəri.ə/; from New Latin from Latin: destillo = to distill, -oria = adjectival ending; something from which a liquid is distilled, i.e., pitcher) is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sri Lanka. It was the second Nepenthes species to be described in print and the first to be formally named under the Linnaean system of taxonomy. It is therefore the type species of the genus.
Botanical history
Nepenthes distillatoria was the second Nepenthes species to be described in print, after N. madagascariensis. In 1677, Danish physician Thomas Bartholin made brief mention of it under the name Miranda herba, Latin for "marvellous herb".[12] Three years later, Dutch merchant Jacob Breyne referred to this species as Bandura zingalensium, after a local name for the plant.[11] Bandura subsequently became the most commonly used name for the tropical pitcher plants, until Linnaeus coined Nepenthes in 1737.[14]
Nepenthes distillatoria was again described in 1683, this time by Swedish physician and naturalist Herman Niklas Grim.[13] Grim called it Planta mirabilis destillatoria, or the "miraculous distilling plant", and was the first to clearly illustrate a tropical pitcher plant.[14] Three years later, in 1686, English naturalist John Ray quoted Grim as saying:[9]
The root draws up moisture from the earth which with the help of the sun's rays rises up into the plant itself and then flows down through the stems and nerves of the leaves into the natural utensil to be stored there until used for human needs. [translated from Latin in Pitcher-Plants of Borneo][14]
Linnaeus used Grim's original specific epithet when naming N. distillatoria in 1753.
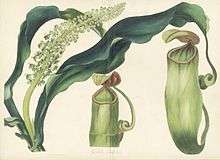
Nepenthes distillatoria was again illustrated in Johannes Burmann's Thesaurus Zeylanicus of 1737. The drawing depicts the end of a flowering stem with pitchers. Burmann refers to the plant as Bandura zeylanica.[10]
In the horticultural trade of the late 19th century, N. distillatoria was often confused with N. khasiana of India.[16][17][18][19]
Ecology
Nepenthes distillatoria is endemic to Sri Lanka and is the only Nepenthes species recorded from the island. It grows in waterlogged open scrub, along road embankments and other cleared areas, and in forest. N. distillatoria occurs from sea-level to 700 m altitude.[20]
Due to its isolation, N. distillatoria has no known natural hybrids.
Infraspecific taxa
Three infraspecific taxa of N. distillatoria have been described, although they are no longer considered valid.
- Nepenthes distillatoria var. rubra (Nichols.) Hort.Veitch ex Lindsay (1891)
- Nepenthes distillatoria var. speciosa Hort.Van Houtte ex Rafarin (1869)
- Nepenthes distillatoria var. vera D.Moore (1872)[21]
References
- ↑ (French) Brongniart, A. 1824. Observations sur les genres Cytinus et Nepenthes. Annales des Sciences Naturelles 1: 29–52.
- 1 2 3 (German) Beck, G. 1895. Die Gattung Nepenthes. Wiener Illustrirte Garten-Zeitung 20(3–6): 96–107, 141–150, 182–192, 217–229.
- ↑ Danser, B.H. 1928. The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies. Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg, Série III, 9(3–4): 249–438.
- ↑ Smith, W.G. 1882. New garden plants. Nepenthes hirsuta var. glabrescens. The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series, 17(430): 398–399.
- ↑ [Anonymous] 1877. Reports of Societies. Royal Horticultural. The Gardeners' Chronicle 8(197): 441.
- ↑ Chapman, V.J. 1947. A new endemic species of Nepenthes. Ceylon Journal of Science, Section A: Botany, 12(4): 221–222.
- ↑ (Latin) Hermann, H. 1726. Badura. In: Musaeum Zeylanicum, sive catalogus plantarum, in Zeylana Sponte Nascentium, observatarum & descriptarum. D. vander Vecht, Lugduni Batavorum. p. 16.
- ↑ (Latin) Hermann, H. 1726. Bandura. In: Musaeum Zeylanicum, sive catalogus plantarum, in Zeylana Sponte Nascentium, observatarum & descriptarum. D. vander Vecht, Lugduni Batavorum. p. 37.
- 1 2 Ray, J. 1686. Bandura cingalensium etc. Historia Plantarum 1: 721–722.
- 1 2 Burmann, J. 1737. Thesaurus Zeylanicus. Amsterdam.
- 1 2 Breyne, J. 1680. Bandura zingalensium etc. Prodromus Fasciculi Rariorum Plantarum 1: 18.
- 1 2 Bartholinus, T. 1677. Miranda herba. Acta Medica et Philosophica Hafniensa 3: 38.
- 1 2 Grimm, H.N. 1683. Planta mirabilis destillatoria. In: Miscellanea curiosa sive Ephemeridum. Med. Phys. Germ. Acad. Nat. Cur. Decuriae 2, ann. prim. p. 363, f. 27.
- 1 2 3 Phillipps, A. & A. Lamb 1996. Pitcher-Plants of Borneo. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu.
- ↑ Paxton, J. 1838. Nepenthes distillatoria. Paxton's Magazine of Botany 4: 1–4.
- ↑ Masters, M.T. 1872. The cultivated species of Nepenthes. The Gardeners' Chronicle and Agricultural Gazette 1872(16): 540–542.
- ↑ Masters, M.T. 1881. New garden plants. Nepenthes Mastersiana×, Hort. Veitch. The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series, 16(415): 748–749.
- ↑ Masters, M.T. 1882. New garden plants. Nepenthes rubro-maculata×, Hort. Veitch. The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series, 17(423): 143.
- ↑ Dixon, W.E. 1889. Nepenthes. The Gardeners' Chronicle, series 3, 6(144): 354.
- ↑ Clarke, C.M.; R. Cantley; J. Nerz; H. Rischer & A. Witsuba (2000). "Nepenthes distillatoria". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2006. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 6 May 2006. Listed as Vulnerable (VU B1+2d v2.3).
- ↑ Moore, D. 1872. On the culture of Nepenthes at Glasnevin. The Gardeners' Chronicle and Agricultural Gazette 1872(11): 359–360.
Further reading
- [Anonymous] 1849. Societies. Botanical of Edinburgh, July 12. The Gardeners' Chronicle and Agricultural Gazette 1849(30): 470–471.
- [Anonymous] 1881. Messrs. Veitch's Nepenthes-house. The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series, 16(410): 598–599.
- Amaratunga, K.L.D. 1980. Nepenthaceae. In: M.D. Dassanayake & F.R. Fosberg (eds.) A Revised Handbook to the Flora of Ceylon, Volume 6. Taylor & Francis, London. pp. 241–244.
- (Italian) Arcangeli, G. 1893. Sopra l'infiorescenza di una pianta di Nepenthes. Nuovo Giornale Botanico Italiano 25: 511–512.
- Athauda, S.B.P., H. Inoue, A. Iwamatsu & K. Takahashi 1998. Acid Proteinase from Nepenthes distillatoria (Badura). In: M.N.G. James (ed.) Aspartic Proteinases: Retroviral and Cellular Enzymes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Volume 436. Plenum Press, New York. pp. 453–458.
- Athauda, S.B.P., K. Matsumoto, S. Rajapakshe, M. Kuribayashi, M. Kojima, N. Kubomura-Yoshida, A. Iwamatsu, C. Shibata, H. Inoue & K. Takahashi 2004. Enzymatic and structural characterization of nepenthesin, a unique member of a novel subfamily of aspartic proteinases. Biochemical Journal 381(1): 295–306.
- Bauer, U., C.J. Clemente, T. Renner & W. Federle 2012. Form follows function: morphological diversification and alternative trapping strategies in carnivorous Nepenthes pitcher plants. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 25(1): 90–102. doi:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02406.x
- (Latin) Blume, C.L. 1852. Ord. Nepenthaceae. In: Museum Botanicum Lugduno-Batavum, sive stirpium exoticarum novarum vel minus cognitarum ex vivis aut siccis brevis expositio. Tom. II. Nr. 1. E.J. Brill, Lugduni-Batavorum. pp. 5–10.
- Burbidge, F.W. 1882. Notes on the new Nepenthes. The Gardeners' Chronicle, new series, 17(420): 56.
- DeFilipps, R.A. 1998. A digression upon James Taplin, Nepenthes hybridizer (Nepenthaceae). Carnivorous Plant Newsletter 27(4): 104–109.
- De Luna, M. 1964. Nepenthes distillatoria. British Homeopathic Journal 53(4): 266–267. doi:10.1016/S0007-0785(64)80047-8
- (French) Gode, L. 1987. Découverte de Nepenthes distillatoria. Dionée 10.
- (German) Guenther, K. 1913. Die lebenden Bewohner der Kannen der insektenfressenden Pflanze Nepenthes destillatoria auf Ceylon. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Insektenbiologie 9: 122–130, 156–160, 198–207.
- Hooker, J.D. 1859. XXXV. On the origin and development of the pitchers of Nepenthes, with an account of some new Bornean plants of that genus. The Transactions of the Linnean Society of London 22(4): 415–424. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1856.tb00113.x
- Jinasena, D., S. Rajapakse, P. Samaraweera & S.B.P. Athauda 2008. Preliminary characterization of phosphatase activity in the crude pitcher fluid of Nepenthes distillatoria (bandura). In: H. Goonatilake (ed.) Proceedings of the 64th Annual Sessions: Part I - Abstracts. Sri Lanka Association for the Advancement of Science, Colombo. p. 147.
- Kitching, R.L. 2000. Food Webs and Container Habitats: The natural history and ecology of phytotelmata. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Korthals, P.W. 1839. Over het geslacht Nepenthes. In: C.J. Temminck 1839–1842. Verhandelingen over de Natuurlijke Geschiedenis der Nederlandsche overzeesche bezittingen; Kruidkunde. Leiden. pp. 1–44, t. 1–4, 13–15, 20–22.
- Koswatte, I., S. Rajapakse, P. Samaraweera & S.B.P. Athauda 2008. Occurrence of lipase activity in the pitcher juice of Nepenthes distillatoria (bandura). In: H. Goonatilake (ed.) Proceedings of the 64th Annual Sessions: Part I - Abstracts. Sri Lanka Association for the Advancement of Science, Colombo. p. 103.
- Lindley, J. 1846. Order XCIV. Nepenthaceæ.—Nepenths. In: The Vegetable Kingdom; or, The Structure, Classification, and Uses of Plants, Illustrated upon the Natural System. Bradbury & Evans, London. pp. 287–288.
- Madugalle, V., S. Rajapakse, P. Samaraweera & S.B.P. Athauda 2008. Detection and preliminary characterization of glycosidase/s from Nepenthes distillatoria. In: H. Goonatilake (ed.) Proceedings of the 64th Annual Sessions: Part I - Abstracts. Sri Lanka Association for the Advancement of Science, Colombo. p. 149.
- (Indonesian) Mansur, M. 2001. Koleksi Nepenthes di Herbarium Bogoriense: prospeknya sebagai tanaman hias. In: Prosiding Seminar Hari Cinta Puspa dan Satwa Nasional. Lembaga Ilmu Pengetahuan Indonesia, Bogor. pp. 244–253.
- Meimberg, H., P. Dittrich, G. Bringmann, J. Schlauer & G. Heubl 2000. Molecular phylogeny of Caryophyllidae s.l. based on matK sequences with special emphasis on carnivorous taxa. Plant Biology 2(2): 218–228. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9460
- Meimberg, H., A. Wistuba, P. Dittrich & G. Heubl 2001. Molecular phylogeny of Nepenthaceae based on cladistic analysis of plastid trnK intron sequence data. Plant Biology 3(2): 164–175. doi:10.1055/s-2001-12897
- (German) Meimberg, H. 2002. Molekular-systematische Untersuchungen an den Familien Nepenthaceae und Ancistrocladaceae sowie verwandter Taxa aus der Unterklasse Caryophyllidae s. l.. Ph.D. thesis, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich.
- Meimberg, H. & G. Heubl 2006. Introduction of a nuclear marker for phylogenetic analysis of Nepenthaceae. Plant Biology 8(6): 831–840. doi:10.1055/s-2006-924676
- (German) Oudemans, A.C. 1915. Anoetus guentheri nov. sp.. In: Guenther, K. Die lebenden Bewohner der Kannen der insektenfressenden Pflanze Nepenthes distillatoria auf Ceylon. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Insektenbiologie 11: 242–243.
- Paxton, J. 1834. Mimulus Smithii. Paxton's Magazine of Botany 1: 54–63.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. 2012. Abnorme Blüten von carnivoren Pflanzen. Das Taublatt 72: 17–22.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Abnorme Blüten von carnivoren Pflanzen. bio-schmidhol.ch.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Kanne (pitcher): Was ist das? bio-schmidhol.ch.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Nepenthes distillatoria: Form und Bau der Kannen. bio-schmidhol.ch.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Nepenthes distillatoria: Haare (Trichome). bio-schmidhol.ch.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Nepenthes distillatoria: Blütenhülle (Perianth). bio-schmidhol.ch.
- (German) Schmid-Hollinger, R. N.d. Nepenthes distillatoria: Blütenstände. bio-schmidhol.ch.
- Takahashi, K., S.B.P. Athauda, K. Matsumoto, S. Rajapakshe, M. Kuribayashi, M. Kojima, N. Kubomura-Yoshida, A. Iwamatsu, C. Shibata & H. Inoue 2005. Nepenthesin, a unique member of a novel subfamily of aspartic proteinases: enzymatic and structural characteristics. Current Protein and Peptide Science 6(6): 513–525. doi:10.2174/138920305774933259
- Voelcker, A. 1849. XVI.—On the chemical composition of the fluid in the ascidia of Nepenthes. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, series 2, 4(20): 128–136. doi:10.1080/03745486009496159
- Wijesinghe, P., S. Rajapakse, P. Samaraweera & S.B.P. Athauda 2008. Partial purification and characterization of deoxyribonucleases from Nepenthes distillatoria. In: H. Goonatilake (ed.) Proceedings of the 64th Annual Sessions: Part I - Abstracts. Sri Lanka Association for the Advancement of Science, Colombo. p. 212.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nepenthes distillatoria. |
- Photographs of N. distillatoria at the Carnivorous Plant Photofinder
