Xiaochangliang
 location in China | |
| Location | Hebei |
|---|---|
| Region | China |
| Coordinates | 40°07′00″N 114°10′00″E / 40.1167°N 114.1667°E |
| History | |
| Founded | 1.36 mya |
| Periods | Paleolithic China |
Xiaochangliang (simplified Chinese: 小长梁; traditional Chinese: 小長梁; pinyin: xiǎochángliáng) is the site of some of the earliest paleolithic remains in East Asia, located in the Nihewan Basin in Yangyuan County, Hebei, China, most famous for the stone tools discovered there.
Stone tools
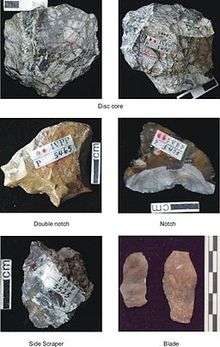
The tool forms discovered include side and end scrapers, notches, burins, and disc cores. Although it is generally more difficult to date Asian sites than African sites because Asian sites typically lack volcanic materials that can be dated isotropically, the age of the tools has been magnetostratigraphically dated as 1.36 million years. This method hinges upon dated reversals in the Earth's magnetic field.
Research
The site was first discovered by the US geologist George Barbour in 1923. Barbour invited French archaeologists Pierre Teilhard de Chardin and Émile Licent. In 1935 Teilhard found a stone (flint) tool and determined the age of the site to be over a million years – it was the oldest artefact then known. Many scientists, including Teilhard, debated whether this tool might not be naturally formed.
The discovery by Pei Wenzhong of Peking Man hundreds of kilometers to the south (followed by wars and revolution) distracted the attention of the world's scientific community. However, from 1972 to 1978 more than 2000 pieces of stone tools were discovered, together with some bone tools, which confirmed Xiaochangliang (or Nihewan) as a paleolithic site.
In 1982, Wei Qi, then 44, found a huge hominid settlement at Donggutuo Village. He took samples to Pei, whose Peking Man was not half as old. "He said nothing," said Wei. "But I guess he had accepted it." Pei died of a heart attack a few days later.[1]
Notes
- ↑ Stephen Chen (28 June 2010). "Finds in Hebei Basin May Rewrite History". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 22 March 2014.
Further reading
- Hong Ao, Mark J. Dekkers, Qi Wei, Xiaoke Qiang, Guoqiao Xiao (15 August 2013). "New evidence for early presence of hominids in North China". Scientific Reports. 3 (2403). doi:10.1038/srep02403.
External links
- "Earliest Humans in China". Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 21 March 2014.
- Pleistocene magnetochronology of the fauna and Paleolithic sites in the Nihewan Basin: Significance for environmental and hominin evolution in North China, 2013.