Nozzle and flapper
The nozzle and flapper mechanism is a displacement type detector which converts mechanical movement into a pressure signal, by covering the orifice of a nozzle with a flat plate called the flapper.[1] This restricts the nozzle fluid flow and generates a pressure signal.
It is a widely used mechanical means of creating a high gain fluidic amplifier. In industrial control systems they played an important part in the development of pneumatic PID controllers and are still widely used today in pneumatic and hydraulic control and instrumentation systems.
Operating principle
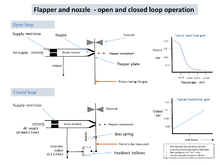
The operating principle makes use of the high gain effect when a "flapper" plate is placed a small distance from a small pressurised nozzle emitting a fluid.
The example shown is pneumatic. At sub-millimetre distances a small movement of the flapper plate results in a large change in flow. The nozzle is fed from a chamber which is in turn fed by a restriction, so changes of flow result in changes of chamber pressure. The nozzle diameter must be larger than the restriction orifice in order to work.[2] The high gain of the open loop mechanism can be linearised using a pressure feedback bellows on the flapper to create a force balance system with a linear output. The "live" zero of 0.2 bar or 3 psi is set by the bias spring which ensures that the device is working in its linear region.
The industry standard ranges of either 3-15 psi (USA), or 0.2 - 1.0 bar (metric), is normally used in pneumatic PID controllers, valve positioner servomechanisms and force balance transducers.
Application

The nozzle and flapper in pneumatic controls is a simple low maintenance device which operates well in a harsh industrial environment, and does not present an explosion risk in hazardous atmospheres. They were the industry controller amplifier for many decades until the advent of practical and reliable electronic high gain amplifiers. However they are still used extensively for field devices such as control valve positioners, and I to P and P to I converters.
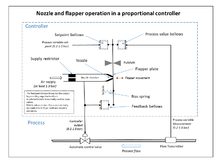
A proportional controller schematic is shown here.
The set point is transmitted through the flapper plate via the fulcrum to close the orifice and increase the chamber pressure. The feedback bellows resists and the output signal goes to the control valve which opens with increasing actuator pressure. As the flow increases, the process value bellows counteracts the set point bellows until equilibrium is reached. This will be a value below the set point, as there must always be an error to generate an output. The addition of an integral or "reset" bellows would remove this error.[3]
The principle is also used in hydraulic systems controls.
References
- Arthur Akers; Max Gassman; Richard Smith (2006). "7.4 Flapper Nozzle Valve". Hydraulic Power System Analysis. CRC Press. pp. 182–184. ISBN 978-1-4200-1458-7.
- S K Singh (2003). "13.6 Automatic process control systems". Industrial Instrumentation and Control 2e. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 481–495. ISBN 978-0070678200.