Okavango Basin
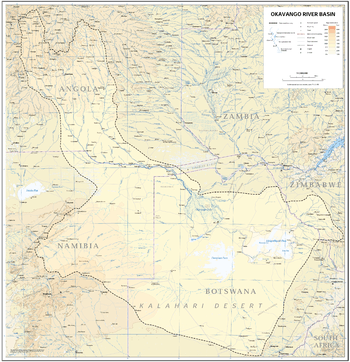
The Okavango Basin is an endorheic basin found in southwestern Africa, which extends across portions of Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zimbabwe. The basin covers an area of 721,000 square kilometers.
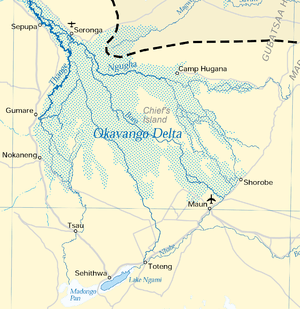
The Okavango River is the chief stream in the basin. It is formed by the confluence of the Cubango and Cuito rivers, which originate on the Bihé Plateau of central Angola and flow southeast. The Cubango is joined just above its confluence with the Cuito by the Omatako River, which flows northeast from its origin in the Damaraland region of central Namibia. The Okavango continues through the Caprivi Strip of Namibia into Botswana, where it splits into a number of distributaries to form the Okavango Delta, a large inland delta that becomes a seasonally flooded grassland.
A series of salt pans lie in the lowest points of the basin, including the Nwako Pan south of the Okavango Delta and the vast Makgadikgadi Pan southeast of the Delta. At times of high flow, the Okavango spills into the Nwako Pan via the Xudum and Nhabe distributaries to replenish Lake Ngami, a saline lake, and into Lake Xau and the western end of the Makgadikgadi Pan via the Boteti distributary. The Mopopi Dam was built on the Boteti to provide water to the Orapa diamond mine.
The Selinda Spillway, also known as the Magweqana, Magwekwana or Magweggana, is a distributary channel that connects the Okavango Delta to the Cuando River, a tributary of the Zambezi. In periods of very high water in the Okavango, the water flows eastward towards the Cuando-Linyanti-System. The last time this happened was in August 2009 after 30 years of falling dry. In times of high water in the Kwando, the water can flow west from the Cuando towards the Okavango Delta, but often evaporates before it reaches the delta.
Other streams in the basin include the Eiseb, an intermittent stream that originates in Namibia's Herreroland and flows east into the Okavango Delta, and the Nata River, which originates in western Zimbabwe to flow into the eastern end of the Makgadikgadi Pan.
References
- A.J.E. Els and K.M. Rowntree "Water Resources in the Savanna Regions of Botswana"
- Thieme, Michelle L. (2005). Freshwater Ecoregions of Africa and Madagascar: A Conservation Assessment. Island Press, Washington DC.