Pederin
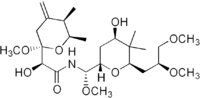 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-N-[(S)-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[(2S)-2,3-dimethoxypropyl]-4-hydroxy-5,5-dimethyl-2-tetrahydropyranyl]-methoxymethyl]-2-hydroxy-2-[(2R,5R,6R)-2-methoxy-5,6-dimethyl-4-methylene-2-tetrahydropyranyl]acetamide | |
| Other names
Pederine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 27973-72-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:78591 |
| ChemSpider | 4529295 |
| PubChem | 5381287 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H45NO9 | |
| Molar mass | 503.6261 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pederin is a vesicant toxic amide with two tetrahydropyran rings, found in the haemolymph of the Paederus genus of beetles, including the Nairobi fly, belonging to the Staphylinidae family. It was first characterized by processing 25 million field-collected P. fuscipes.[1] It makes up approximately 0.025% of an insects weight (for P. fuscipes).[1]
It has been demonstrated that the production of pederin relies on the activities of an endosymbiont (Pseudomonas ssp.) within Paederus.[2]
The manufacture of pederin is largely confined to adult female beetles—larvae and males only store pederin acquired maternally (i.e., through eggs) or by ingestion.[1]
Mode of action
Pederin blocks mitosis at levels as low as 1 ng/ml, by inhibiting protein and DNA synthesis without affecting RNA synthesis,[3] prevents cell division, and has been shown to extend the life of mice bearing a variety of tumors.<missing reference> For these reasons, it has garnered interest as a potential anti-cancer treatment.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Bugs Don’t Have to Bite to Do Damage:The Tale of the Paederus Beetle
- ↑ Piel J (2002). "A polyketide synthase-peptide synthetase gene cluster from an uncultured bacterial symbiont of Paederus beetles". PNAS. 99 (22): 14002–14007. doi:10.1073/pnas.222481399. PMC 137826
 . PMID 12381784.
. PMID 12381784. - ↑ Frank JH, Kanamitsu K (1987). "Paederus, Sensu Lato (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae): Natural History and Medical Importance". J. Med. Entomol. 24 (2): 155–191. PMID 3295241.