Upper Rhenish Circle
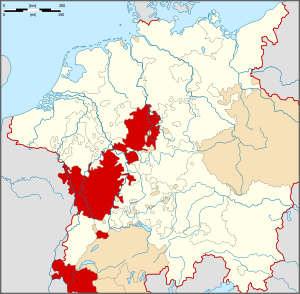
The Upper Rhenish Circle as at the beginning of the 16th century
The Upper Rhenish Circle (German: Oberrheinischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1500 on the territory of the former Duchy of Upper Lorraine and large parts of Rhenish Franconia including the Swabian Alsace region and the Burgundian duchy of Savoy.
Many of the circle's states west of the Rhine river were annexed by France under King Louis XIV during the 17th century, sealed by the 1678/79 Treaties of Nijmegen.
Composition
The circle was made up of the following states:
| Name | Type of entity | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| |
Duchy | United with Lorraine since 1483. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established in the 8th century as successor of the ancient diocese of Augusta Raurica, gained independence from the Kingdom of Burgundy about 1000, residence at Porrentruy (Pruntrut) from 1527. |
| |
Lordship | Held by Cologne, granted to Count Karl August of Heydeck, illegitimate son of Elector Charles Theodore of Bavaria in 1772, Imperial county in 1774, principality in 1789. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1226, part of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
Lordship | Held by the Lords of Fleckenstein, acquired by Oettingen-Wallerstein in 1697. |
| |
Lordship | Held by the Counts of Daun since 1456, raised to county in 1518, fell to Lorraine in 1667, administered with Further Austria from 1782. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1220, place of the Imperial election by the Golden Bull of 1356. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1252. |
| |
Prince-Abbacy | Established by Saint Boniface in 744, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick II in 1220, raised to Prince-Bishopric in 1752. |
| |
Imperial City | Since about 1260, capital of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
County | Partitioned from the County of Hanau as Hanau-Babenhausen in 1456, inherited the lordship of Lichtenberg in 1474, fell to Hesse-Darmstadt in 1736. |
| |
County | Partitioned from the County of Hanau in 1456, reunited with Hanau-Lichtenberg in 1642, fell to Hesse-Kassel in 1736. |
| |
Principality | Held by the Order of St John since 1272, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Charles V in 1548. |
| |
Abbacy | Established about 736 by Saint Sturm, Reichsfreiheit granted by Charlemagne in 775, secularised to a principality by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, held by Hesse-Kassel |
| |
Landgraviate | Established after the War of the Thuringian Succession in 1247, residence at Kassel, partitioned after the death of Landgrave Philip I in 1567. |
| |
Landgraviate | Subdivision of Hesse from 1567, Electorate of Hesse in 1803. |
| |
Landgraviate | Subdivision of Hesse from 1567 including the former County of Katzenelnbogen with Burg Rheinfels, line extinct in 1583, fell to Hesse-Kassel. |
| |
Landgraviate | Subdivision of Hesse from 1567, Grand Duchy of Hesse in 1806. |
| |
Landgraviate | Subdivision of Hesse from 1567, line extinct in 1604, annexed by Hesse-Darmstadt. |
| |
Landgraviate | Cadet branch of Hesse-Darmstadt from 1622, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1768. |
| |
County | Subdivision of the County of Isenburg established in 1511 (Oberisenburg), again divided in 1628. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Isenburg-Büdingen-Birstein from 1628, merged into Isenburg-Offenbach in 1644, restored in 1711, raised to principality in 1744. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Isenburg-Büdingen-Birstein from 1628. |
| |
County | Split off Isenburg-Büdingen in 1673. |
| |
County | Split off Isenburg-Büdingen in 1673. |
| |
Imperial City | Part of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
County | Held by the Lords of Eppstein, raised to Reichsgrafen by Emperor Maximilian I of Habsburg in 1505, inherited by Stolberg in 1535, seized by Mainz in 1581. |
| |
County | Former fief of Lorraine around Créhange, raised to Imperial county in 1617, held by the Princes of East Frisia from 1697, to Wied-Runkel in 1726. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph I of Habsburg in 1291, seized by the Bishop of Speyer in 1324, restored by Emperor Maximilian I of Habsburg in 1511, joined the Décapole in 1521. |
| |
County | Subdivision of the former County of Leiningen since 1317, inherited by the Lords of Westerburg in 1467. |
| |
County | Subdivision of the former County of Leiningen since 1317, raised to principality in 1779. |
| |
Duchy | Former Upper Lotharingia, acquired by René of Anjou, Duke of Bar in 1431, swapped by Duke Francis III of Habsburg-Lorraine for the Grand Duchy of Tuscany in 1735, annexed by France in 1766. |
| |
Lordship | Condominium of Trier and Nassau. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established by 535, Reichsfreiheit confirmed by Charles IV of Luxembourg in 1357, occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552, part of the French Three Bishoprics by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1189, occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552. |
| |
Imperial City | Since about 1268, part of the Décapole since 1354, joined Swiss Confederacy in 1515, France in 1798. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1235, part of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
County | Principality in 1688, Duchy of Nassau from 1806. |
| |
County | Split off Nassau-Weilburg in 1627, fell to Nassau-Ottweiler in 1721. |
| |
County | Established in 1381, fell to Nassau-Ottweiler in 1723 |
| |
County | Split off Nassau-Saarbrücken in 1659, fell to Nassau-Usingen in 1728. |
| |
County | Split off Nassau-Saarbrücken in 1659, principality in 1688, Duchy of Nassau from 1806. |
| |
Margraviate | Held by the Bishopric of Metz until 1548, margraviate established by Emperor Maximilian II of Habsburg in 1567, to Lorraine in 1612. |
| |
Imperial City | Since about 1240, part of the Décapole since 1354, annexed by France in 1679. |
| |
Provostry | Monastery established in 1122, Imperial college of canons (Reichsstift) since 1494, moved to Bruchsal in 1507. |
| |
Lordship | Territory around Olbrück Castle near Niederdürenbach, originally held by Wied. |
| |
Principality | Split off Electoral Palatinate in 1410, inherited by Palatinate-Neuburg in 1685. |
| |
Principality | Subdivision of Palatinate-Simmern from 1577. |
| |
Principality | Former County of Zweibrücken, ruled in personal union with Palatinate-Simmern until 1459, fell to Palatinate-Birkenfeld in 1734. |
| |
Principality | Former County of Veldenz inherited by Palatinate-Zweibrücken in 1444. |
| |
Abbacy | (Re-)established by King Pepin the Short in 752, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1222, administrated by Trier from 1576. |
| |
Lordship | Since about 1300. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1303, part of the Décapole since 1354, annexed by France in 1679. |
| |
County | Upper Salm since 1165, large parts held by the Wild- and Rhinegraves from 1475 and partitoned in 1499, remains to Lorraine until 1600. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Salm since 1499, line extinct in 1750, inherited by Salm-Grumbach. |
| |
County | Split off Salm-Dhaun in 1561, annexed by France in 1801. |
| |
County | Split off Salm-Grumbach in 1668. |
| |
County | Split off Salm-Dhaun in 1574, princely county from 1623, Principality of Salm from 1802. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Salm from 1499, residence at Kirn, princely county from 1743, Principality of Salm from 1802. |
| |
Duchy | Former county, part of the Kingdom of Arles inherited by Emperor Conrad II in 1032, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Charles IV of Luxembourg in 1361, raised to duchy in 1416, to Kingdom of Sardinia in 1720. |
| |
County | Former Counts of Sayn, a cadet branch of the House of Sponheim, acquired County of Wittgenstein in 1361, partitioned in 1607. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Sayn-Wittgenstein from 1607. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Sayn-Wittgenstein from 1607, Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohenstein from 1657. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1216, part of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Solms since 1258, raised to principality in 1742. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Solms(-Braunfels) since 1409, Solms-Hohensolms-Lich from 1544, raised to principality in 1792. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Solms-Lich from 1544. |
| |
County | Subdivision of Solms-Laubach from 1607, Solms-Rödelheim-Assenheim from 1635. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established before 614, Reichsfreiheit granted around 969 by Emperor Otto I. |
| |
Imperial City | City rights acknowledged by the Speyer bishops in 1294, venue of 50 Reichstag assemblies, including the Diet of Speyer (1529) (Protestation at Speyer). |
| |
County | Established in the 11th century by the Rhenish House of Sponheim, held jointly by the Margraves of Baden and the House of Palatinate-Simmern since 1437. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established in the 4th century, prince-bishopric since 982. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1262. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established in 365 by Saint Mansuetus, Reichsfreiheit confirmed by King Henry I in 928, occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552, part of the French Three Bishoprics by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. |
| |
Imperial City | Since the 13th century (Tull), occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552. |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1312, part of the Décapole since 1354. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established about 346, Reichsfreiheit confirmed by Emperor Otto III in 997, occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552, part of the French Three Bishoprics by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia. |
| |
Imperial City | Since the 12th century (Wirten), occupied by King Henry II of France in 1552. |
| |
County | Line established about 1180, Reichsfreiheit granted by King Wenceslaus of Luxembourg in 1379, Waldeck-Pyrmont from 1625, raised to principality in 1712. |
| |
County | Established in 1232, inherited by Riedesel in 1428, Freiherren from 1680. |
| |
County | Established c. 950, held by the counts von Wetter-Tegerfelden in 1317 |
| |
Imperial City | Since 1306, part of the Décapole since 1354, annexed by France in 1648. |
| |
Prince-Provostry | Abbey established about 660 by the Bishopric of Speyer, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Otto II in 967, again held by Speyer from 1546. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa in 1180. |
| |
County | Rhinegraves since the 12th century, inherited Wildgraviate at Kyrburg in 1409, acquired (Upper) Salm in 1475. |
| |
Prince-Bishopric | Established about 614. |
| |
Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa in 1184. |
Sources
- The list of states making up the Upper Rhenish Circle is based in part on that in the German Wikipedia article Oberrheinischer Reichskreis.
External links
- Imperial Circles in the 16th Century Historical Maps of Germany
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
-en.png)