Saudi Arabian Army
|
(Arabic;) «القُوّات البَرِيَة المَلَكيَّة السُّـعُوديَّة» | |
| Founded | As early as 1745[1] (271 years) |
|---|---|
| Country |
|
| Allegiance | Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques |
| Branch |
|
| Type | Army |
| Role | Ground-based warfare |
| Size |
+300,000 active (2012 est.)[2] 578,500 reserve and National Guard[3] +878,500 total personnel (2015 est.) |
| Part of |
|
| Headquarters | «Airport Rd, Riyadh 11165» |
| Anniversaries | «January 13» (114 years ago) |
| Decorations |
|
| Website |
www |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of Army Staff |
|
| Vice Chief of Staff |
|
| Commander of Special Forces |
|
| Insignia | |
 | |
.png) | |
The Saudi Arabian Army (KSA) (Arabic: الجيش العربي السعودي), also called Royal Saudi Land Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية الملكية الـسعودية), is the largest branch of the Saudi Arabia Armed Forces. The Saudi Arabia Ground Armed Forces (SAAF) divides its manpower between two main entities, the National Guard (SANG) and the Army [RSLF]. The Chief of the Saudi General Staff until 2011 was Field Marshal Saleh Al-Muhaya.[4]
History
The modern Saudi Army has its roots in the first Saudi State, which was formed as early as 1745, and is considered to be the birth year of the Saudi Army. As of 13 January 1902 was founded as the Royal Saudi Land Forces, and is the Oldest branch of the KSA military.[1]
Other events that led to an expansion of the Saudi Army were the Arab–Israeli conflict in 1948, the fall of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in the Iranian Revolution in 1979 and the subsequent fears of possible Shia's actions and in the last years the first Gulf War in 1990. In the year 2000, Saudi Arabia's government spent billions of dollars to expand the Saudi Forces including the Saudi Army.
Wars involving Saudi Army
- The Unification of Saudi Arabia (1902–1933).
- 1948 Arab–Israeli War more than 3,000 Saudi Troops participated in combat against Israel.
- 1967 RSLF deployed over 20,000 troops in Jordan.
- 1969 Al-Wadiah War. South Yemeni Forces invaded Al-Wadiah, a Saudi Town, but later were defeated by the Saudi Army.
- 1973 during the Yom Kippur War Saudi Arabia, along with other Persian Gulf nations, protested American intervention by raising oil prices and sent over 3,000 Saudi soldiers from the troops stationed in Jordan to fight on the Syrian frontline.
- Gulf War (1990–1991) Together with the allied forces, Saudi Armed Forces and SANG took a major part in the Battle of Khafji and the Liberation of Kuwait.
- 2007–2010 Houthi Insurgency. Yemeni Houthis attacked southern Saudi Arabia and were defeated later by the Saudi army.
- 2015 Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen at the request of the Yemeni president to drive away Houthi rebels allied with the deposed Ali Abdullah Saleh Yemeni Civil War (2015)
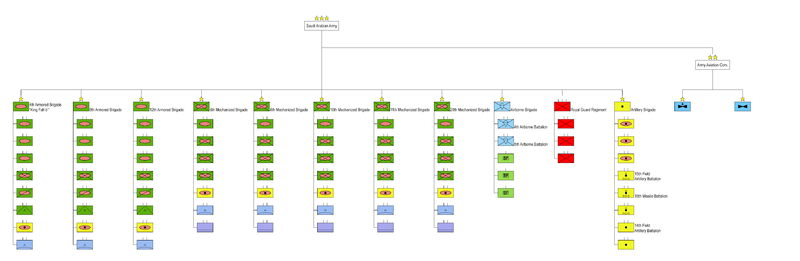
Structure

The combat strength of the Saudi Army consists of 3 armoured brigades, 5 mechanized infantry brigades, three light motorized rifle brigades, and one airborne brigade. It also has five independent artillery battalions and an aviation command. The Saudi Army deployed the 12th Armoured Brigade and 6th Mechanized Brigade at King Faisal Military City in the Tabuk area. It deployed the 4th Armoured Brigade, and 11th Mechanized Brigade at King Abdul Aziz Military City in the Khamis Mushayt area. It deployed the 20th Mechanized Brigade and 8th Mechanized Brigade at King Khalid Military City near Hafr al Batin. The 10th Mechanized Brigade is deployed at Sharawrah, which is near the border with Yemen and about 150 kilometers from Zamak.[5]
Despite the addition of a number of units and increased mobility achieved during the 1970s and 1980s, the army's personnel complement has expanded only moderately since a major buildup was launched in the late 1960s. The army has been chronically understrength, in the case of some units by an estimated 30 to 50 percent. These shortages have been aggravated by a relaxed policy that permitted considerable absenteeism and by a serious problem of retaining experienced technicians and noncommissioned officers (NCOs). The continued existence of a separate national guard also limited the pool of potential army recruits.[5]
Armor
- 4th (King Khaled) Armoured Brigade
- 6th (King Fah'd) Armoured Brigade
- 7th (Prince Sultan)Armoured Brigade
- 8th (King Fah'd)Armoured Brigade
- 10th (King Faisal)Armoured Brigade
A typical Saudi armoured brigade has an armoured reconnaissance company, three tank battalions with 42 tanks each, a mechanized infantry battalion with 54 AIFVs/APCs, and an artillery battalion with 18 self-propelled guns. It also has an army aviation company, an engineer company, a logistic battalion, a field workshop, and a medical company.[6]
Mechanized
- 11th Mechanized Brigade
- 12th Mechanized Brigade
- 13th Mechanized Brigade
- 14th Mechanized Brigade
- 20th Mechanized Brigade
A typical Saudi mechanized brigade has an armoured reconnaissance company, one tank battalion with 42 tanks, three mechanized infantry battalions with 54 AIFVs/APCs each, and an artillery battalion with 18 self-propelled guns. It also has an army aviation company, an engineer company, a logistic battalion, a field workshop, and a medical company. It has 24 anti-tank guided weapons launchers and four mortar sections with a total of eight 81 mm (3 in) mortars.[6]
Infantry
- 16th (king saud)Light motorized infantry brigade
- 17th ( Abu Bakr Assiddeeq)Light motorized infantry brigade
- 18th (King Abdullah)Light motorized infantry brigade
- 19th (ʿUmar ibn Al-Khattāb)Light motorized infantry brigade
Each infantry brigade consists of three motorized battalions, an artillery battalion, and a support battalion. Army brigades should not be confused with Saudi Arabian National Guard brigades.
Airborne
- The 1st Airborne Brigade
- 4th Airborne Battalion
- 5th Airborne Battalion
The Airborne Brigade is normally deployed near Tabuk. The Airborne Brigade has two parachute battalions and three Special Forces companies. Saudi Arabia is expanding its Special Forces and improving their equipment and training to help deal with the threat of terrorism. The Special Forces have been turned into independent fighting units to help deal with terrorists, and report directly to Prince Sultan.
Artillery Battalions
- five artillery battalions
The separate Royal Guard Regiment consists of four light infantry battalions.
Officers
| Officers | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lieutenant | First Lieutenant | Captain | Major | Lieutenant Colonel | Colonel | Brigadier General | Major General | Lieutenant General | General | ||
Enlisted Ranks
| Enlisted Ranks | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private | Private First Class | Corporal | Vice Sergeant | Sergeant | Sergeant First Class | Master Sergeant | |||||
Main equipment
Infantry weapons
Small arms
Grenade, rocket, anti-tank, and missile systems
| Model | Type | Quantity | Acquired | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M203 | Single shot grenade launcher | | |||
| FGM-148 Javelin | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| Swingfire | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| Vickers Vigilant | Anti-tank missile | 500 | | ||
| M47 Dragon | Anti-tank missile | 4,692 | | ||
| AGM-114 Hellfire | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,954 | | ||
| MILAN | Anti-tank guided missile | | |||
| HOT | Anti-tank guided missile | 3,500 | | ||
| HOT 2 | Anti-tank guided missile | 249 | | ||
| Bill 2 | SACLOS Anti-tank missile | 200 | | ||
| SS.11 | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,000 | | ||
| BGM-71 TOW | Anti-tank guided missile | 10,738 | | ||
| BGM-71C ITOW | Anti-tank guided missile | 2,538 | | ||
| BGM-71D TOW-2 | Anti-tank guided missile | 6,210 | | ||
| BGM-71E TOW-2A | Anti-tank guided missile | 5,131 | |
Mortars
| Model | Type | Quantity | Acquired | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M224 Mortar | Mortar | N/A | N/A | | |
| Brandt Mle CM60A1 | Mortar | N/A | N/A | | |
| MO-120-RT-61 120mm | Mortar | 200 | 200 | | |
| 2R2M 120MM | Mortar | 28 | 28 | | |
| M30 107 mm Mortar | Mortar | N/A | | ||
Vehicles
Tanks
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 Abrams | | | M1A2S | 442
+ 153 on order |
Saudi Arabia bought 373 M1A2 tanks,[7] with further 69 more M1A2S tanks ordered on 8 January 2013 and delivered by 31 July 2014.[8] Later Saudi Arabia decided to upgrade all of M1A2 variants to M1A2S configuration. 153 M1A2S on order since Aug 9, 2016[7] |
| M60 Patton | .jpg) | | M60A3 | 450[9] | 485 were acquired, currently in reserve. |
| AMX-30 |  | | AMX-30S | 145[9] | 250[10] were bought between 1973–1974. Now it serves as a reserve tank of frontier guards. Saudi Arabia has been retiring AMX-30 from the stock by selling it to numerous other countries. Many of the AMX-30's were put in store immediately upon arrival in Saudi Arabia and have seen almost no use. |
Infantry fighting vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 Bradley |  | | M2A2 | 400[9] | Principal IFV of the Saudi Army.[11] |
| AMX-10P |  | | 500[9] | 500[12] were bought from France in 1974; most are now stored as a reserve. | |
Armored personnel carriers
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M113 |  | | Many | 1,112 | 364 had been upgraded in Turkey.[11] |
| TPz Fuchs |  | | NBC reconnaissance Ambulance CP version | 175 | |
| Al-Masmak | | 2,750 | x[13][14] | ||
| Nexter Aravis | .jpg) | | 200 | [15] | |
| Panhard M3 |  | | 150 | ||
Utility vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMMWV |  | | various configurations | 15,000+ | |
| Oshkosh M-ATV |  |
United States | Many | 450 | Saudi Arabia began negotiations for an order for an undisclosed number of M-ATVs Saudi Arabia received an estimated 450 |
| URO VAMTAC |  | | 300 | [16] | |
| Didgori Medevac | Medical APC | 100 [17][18][19] | |||
| CUCV II[20] |  | | 2,000+ | ||
Artillery and missile systems
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M270 | _Vehicles_at_Camp_Bastion%2C_Afghanistan_MOD_45148148.jpg) | | MRL 270mm | 50 | ||
| Astros II MLRS | | | MRL 127mm | SS-30 | 72 | |
| PLZ-45 |  | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | 54[21] | ||
| M109 howitzer | | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | M109A5 M109A2 | 48 110 | |
| AMX-GCT | | | Self-propelled howitzer 155mm | 51 | ||
| M198 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | 42 | ||
| FH-70 | .jpg) | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | 40 | ||
| M114 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 155mm | M114A1 | 50 | All are stored in reserve. |
| M102 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 105mm | 140[11] | ||
| M101 howitzer |  | | Towed Howitzer 105mm | M101A1 | 100 | All are stored in reserve. |
Army aviation
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH-64 Apache |  | | Attack Helicopter | AH-64D | 94 | A further 29 AH-64D Longbow III requested for more than $1,200m. |
| Boeing AH-6 | United States | Armed Scout Helicopter | 0 | 36 on order for Saudi Arabian National Guard | ||
| Bell 406 |  | | Scout Helicopter | Bell 406CS | 13 | |
| Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk |  | | Transport Helicopter | UH-60L | 37 | A further 24 UH-60L requested for $350m. |
| Sikorsky S-70 |  | | Medevac Helicopter | S-70A1L | 8 | |
| Boeing CH-47 Chinook |  | | Cargo Helicopter | ? | ? | |
| Aeryon Scout[22] |  | | Miniature UAV | 10 | ||
| Saqr,2,3,4[23] | | Miniature UAV | ? | ? | ||
- (Anti-Air systems belong to Air Defense Force)
See also
- Military of Saudi Arabia
- Royal Saudi Air Force
- Royal Saudi Navy
- Royal Saudi Air Defense
- Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force
- Saudi Arabian National Guard
- Saudi Royal Guard Regiment
- King Khalid Military City
- Saudi Arabia
References
- 1 2 Wynbrandt, James (2004). A Brief History of Saudi Arabia (1st ed.). p. 353. Retrieved Oct 10, 2016.
- ↑ "Political Regimes in the Arab World: Society and the Exercise of Power". September 4, 2012.
- ↑ "Saudi King Salman cements hold on power". aljazeera.net. 30 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- ↑ Royal Saudi Land Forces.
- 1 2 Royal Saudi Land Forces
- 1 2 Accéder Google Francais
- 1 2 "The 2006 Saudi Shopping Spree: $2.9B to Upgrade M1 Abrams Tank Fleet". DefenseIndustryDaily.com. 4 January 2011. Archived from the original on October 25, 2006. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
- ↑ "Saudi Arabia Orders 69 More M1A2S Abrams Heavy Tanks". Deagel.com, 8 January 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "Royal Saudi Land Force Equipment". Global Security. Retrieved 2015-04-09.
- ↑ "American Alliance Policy in the Middle East". Retrieved 2015-04-09.
- 1 2 3 Military Balance 2005- page 135
- ↑
- ↑ "Al-Masmak Masmak Nyoka Mk2 MRAP Mine Resistant Armored Personnel Carrier technical data sheet - Army Recognition - Army Recognition". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ "Saudi Al-Masmak Achieves the Highest Protection Level Recorded for MRAP". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ "- " "". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ Administrator. "30 VAMTAC's to Saudi Arabia". Retrieved 25 December 2014.
- ↑ http://agenda.ge/news/51342/eng
- ↑ http://www.janes.com/article/57621/saudi-arabia-takes-delivery-of-georgian-armoured-medevac-vehicles
- ↑ http://civil.ge/eng/article.php?id=28938
- ↑ "Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicle: CUCV II". Olive-drab.com. Retrieved 2013-03-15.
- ↑ Chinese Guns Conquer Arabia
- ↑ "picture of Saudi Army with Aeryon Scout".
- ↑
External links
- RSLF official website
- CIA World Factbook
- Pakistani tanks deal
- 2006 Military spending of Saudi Forces
- latest French tanks deal












