São José dos Campos
| São José dos Campos | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
| The Municipality of São José dos Campos | |||
|
View of the city | |||
| |||
|
Nickname(s): Capital of the Valley and The Airplane Capital | |||
|
Motto: "Aura terraque generosa" (Latin) "Generous are the winds of my land" | |||
 Location in the state of São Paulo and Brazil | |||
| Coordinates: 23°11′11″S 45°52′43″W / 23.18639°S 45.87861°WCoordinates: 23°11′11″S 45°52′43″W / 23.18639°S 45.87861°W | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Region | Southeast | ||
| State |
| ||
| Metropolitan Region | Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Carlinhos Almeida (PT) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Municipality | 1,099.77 km2 (424.62 sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 298.99 km2 (115.44 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 600 m (1,970 ft) | ||
| Population (2013) | |||
| • Municipality | 688.597[1] | ||
| Time zone | UTC-3 (UTC-3) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-2 (UTC-2) | ||
| Postal Code | 12200-000 | ||
| Area code(s) | +55 12 | ||
| Website | São José dos Campos, São Paulo | ||
São José dos Campos (Portuguese pronunciation: [sɐ̃w̃ ʒuˈzɛ dus ˈkɐ̃pus], meaning Saint Joseph of the Fields) is a major city and the seat of the municipality of the same name in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. One of the leading industrial and research centers in Latin America,[2] the city is located in the Paraíba Valley, between the two most active production and consumption regions in the country, São Paulo (80 km (50 mi) from the city) and Rio de Janeiro (320 km (200 mi)). It is the main city of the Metropolitan Region of Vale do Paraíba e Litoral Norte.[3] A native of São José dos Campos is called a joseense (Portuguese pronunciation: [ʒozɛˈẽsi]).
Geographic information
Area
- total area: 1,099.60 km2 (424.56 sq mi)
- urban area: 353.9 km2 (136.6 sq mi) (32.18%)
- rural: 745.7 km2 (287.9 sq mi) (67.82%)
Source: City administration website (in Portuguese) [4]
Borders
- Northern Border: Camanducaia, Sapucaí Mirim in Minas Gerais
- Southern Border: Jacareí, Jambeiro in São Paulo State
- Eastern Border: Monteiro Lobato, Caçapava in São Paulo State
- Western border: Igaratá, Joanópolis, Piracaia in São Paulo State
Cityscape
The municipality comprises three districts: São José dos Campos — the city itself, (also the seat), Eugênio de Melo and São Francisco Xavier. The last one is known for its natural sites and ecotourism.
The district of São José dos Campos is also subdivided into 2 subdistricts (São José dos Campos and Santana do Paraíba).
However, for administrative purposes, the city is composed of 7 urban regions: Center, North, South, West, East, Southeast and São Francisco Xavier.
Topography
Highlands predominate in the northern region of the municipality with altitudes ranging from 660 to 975 m (2,165 to 3,199 ft). The northern border of the municipality lies over the Serra da Mantiqueira Mountains (Mantiqueira Range), with some peaks reaching over 2000 meters (6500 ft.). The highest point in the municipality is known as 'Pico do Selado' at an altitude of 2082 meters.
In the urban area, there are rolling plateaus and hills. The lowest elevation in the city (and also in the municipality) is found in the Paraíba do Sul river, at an elevation of 550 m.
The municipality is bounded at the south by the 'Serra do Jambeiro' mountains, with an elevation of about 900m.
- Municipality: Elevations 550 to 2,082 m (1,804 to 6,831 ft)
- City: Elevations 550 to 690 m (1,800 to 2,260 ft).
The municipality holds the 11,559 hectares (28,560 acres) São Francisco Xavier Environmental Protection Area, established in 2002.[5] It contains part of the 292,000 hectares (720,000 acres) Mananciais do Rio Paraíba do Sul Environmental Protection Area, created in 1982 to protect the sources of the Paraiba do Sul river.[6]
Climate
| São José dos Campos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The climate of the city can be, perhaps, best described as a mix between the subtropical climate of southern parts of the country, the tropical climate of most of the country and the subtropical highland climate (in Portuguese: clima tropical de altitude) of neighbouring mountainous regions.
Technically, the city has a humid subtropical climate with significant less precipitation during winters (transitioning between Cfa and Cwa climatic types in the Köppen classification[7]). Winters are very mild, with average temperature in the coldest month of 17 °C. Summers are not excessively hot, with average temperature of the hotttest month of 24 °C. With global warming it is very likely that the city's climate will transition to a true tropical climate (type 'Aw' in the Köppen climate classification) in the near future.
Frosts are very rare, happening on average once per decade. There's no record of snow precipitation in the city.
The peaks at the northern border of the municipality (some over 2000 m high) due to altitude have a colder Cwb/Cfb climates, with very occasional snowfalls (about once per decade).[8]
History
The origins of São José dos Campos lie at the end of the 16th Century when Jesuits founded a cattle farm, Aldeia do Rio Comprido. The farm was created through a concession of settlements around 1590 to the Society of Jesus. The farm was located on the banks of the Rio Comprido, natural division between São José and the city of Jacareí today.
| Historical populations | |
|---|---|
| Census year | Population |
| 1940 | 36,279 |
| 1950 | 44,804 |
| 1960 | 77,533 |
| 1970 | 148,332 |
| 1980 | 287,513 |
| 1991 | 442,370 |
| 2000 | 539,313 |
| 2002 est. | 559,710 |
| 2004 est. | 589,050 |
| 2005 est. | 600,089 |
| 2006 est. | 610,965 |
| 2011 (IBGE) | 636,876 |
The farm status was an artifice to hide a religious outpost, one of the several Jesuit Reductions in Brazil, known for their resistance to enslavement, from the Portuguese expedition leaders and indigenous people hunters, known as the Bandeirantes.
On September 10, 1611, the local was officially recognized and the farmers precluded from utilizing the Natives as slaves. However, a turmeric conflict between farmers and the religious led to the expulsion of the Jesuits in 1640 from the region and the consequent dispersion of the mission.
Nevertheless, the Jesuits returned and reestablished a new settlement, where the current city center is spotted. It was about 15 km (9.3 mi) northeast of the previous mission, on a higher plain with a privileged view above a geological depression, which guaranteed security against invasions and floods. Again, despite being a new mission, it was officially treated as a cattle farm.
The initial urbanization plan is attributed to the Jesuit priest Manoel de Leão, whose main occupation was really to be an administrator of the community.
In 1692, documents named the village as Residência do Paraíba do Sul; in 1696 as Residência de São José.
At the beginning of the gold mining economic cycle in Brazil, the settlement goes through serious difficulties due to the exit of labor to the mines.
After the definitive expulsion of Jesuits from the Portuguese Empire in 1759, all the religious order's assets, such as farms, colleges and villages were taken under the Portuguese Crown's custody. The governor, D. Luis Antonio Botelho Mourão, had as a priority to turn these new assets into productive units and increase tax collection. For that, Boutelho Mourão successfully requested authorization from the Viceroy to create civil parishes, known as freguesias, and to change the fiscal status of villages to the category of Vila (town).
Then, on July 27, 1767, São José reached the official status of town, with a hall and a pillory, passing over the status of civil parish; and the name Vila de São José do Paraíba was formalized. But for many years it maintained the same rural characteristics. The main difficulty was the fact that the Estrada Real (Royal Road) passed by its limits, far from the village.
Cotton and coffee
In the middle of the 19th century, the village of São José do Paraíba had demonstrated some signs of economic growth through the development of agriculture. Cotton production evolved rapidly in the region, exported to the English textile industry. The production reached a peak in 1864.
In the same year, on April 22, the town became the seat of a municipality, acquiring finally, in 1871, the current name of São José dos Campos, followed by the creation of a judiciary district in 1872. Almost simultaneously, there was development of coffee crops in Paraíba Valley, which started to take off in 1870.
In 1886, after the opening of the Estrada de Ferro Central do Brasil railway (1877), the coffee production peaked. Then started to decay, running steady until the 1930s.
Hydro-mineral retreat and industrialization
Former sanatoria (date of opening/beds):
- Sanatório Vicentina Aranha (1924/130)
- Sanatório Vila Samaritana (1928/70)
- Sanatório Rui Dória (1934/68)
- Sanatório Maria Imaculada (1935/na)
- Sanatório Ezra (1936/120)
- Sanatório Ademar de Barros (1936/na)
- Sanatório Antoninho da Rocha Marmo (1952/na)
- Sanatório São José (1957/110)
The call for the municipality of São José dos Campos for the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis by sanatoriums became noticed at the beginning of last century, due to its supposedly favorable climate conditions. The city became to be known as the Sanatorium City. The country's then-largest hospital, the Vicentina Aranha Sanitarium, was opened in town in 1924, and in 1935 the municipality was officially recognized as a health retreat.
With the advent of antibiotics in the 1940s, tuberculosis begins to be treated anywhere, thus ending the healthcare advantage carried out by São José, whereas the establishment of industries was about just to start.
The industrialization process of the municipality takes hold from the installation of the Technological Institute of Aeronautics in 1950 and also with the opening of the Dutra Highway (BR-116), thus making possible a faster connection between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo and cutting into the urban area of São José dos Campos. Altogether, these factors allowed the municipality to make strides towards fulfilling its scientific and technological potential.
Government
São José dos Campos has a "strong mayoral" system in which the mayor is vested with extensive executive powers, as it is in all municipalities in Brazil. The mayor is elected to a four-year term by universal voting. The City Council is elected every four years with the mayor. The current mayor is Carlinhos Almeida, from the political party PT and was elected in 2012.
The state administrative region of São José dos Campos
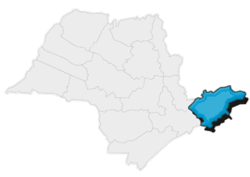
The State of São Paulo is divided politically and administratively into 15 regions. São José dos Campos is the seat and the name of the 3rd Administrative Region, which includes the North Coast of São Paulo state and the Paraíba Valley.
The region comprises 39 municipalities with sharp contrasts. São José dos Campos is a densely populated city, with approximately 2,100 inhabitants/square kilometers in urban area, whereas the quiet municipality of São José do Barreiro has only seven inhabitants/square kilometer. There are both highly industrialized cities and the others in the region are focused on agriculture and tourism. São José dos Campos is well known as the Capital do Vale which means that São José dos Campos is the most important city of the Paraíba Valley.
It is one of the state's most dynamic areas, the fourth one in terms of population density, and covers 11.3% of the state's territory. The main municipalities are São José dos Campos, Taubaté, Jacareí, Guaratingueta, Caraguatatuba, Campos do Jordão, São Sebastião, Lorena, Pindamonhangaba, Ubatuba and Caçapava.
- Population of the region: 2,243,687 (est. 2006/IBGE)
- Population Density: 288.56 inhabitants per square kilometer
List of mayors
- João Cursino (1908/1910, 1913/1916, 1919/1930)
- Rui Dória (1931)
- Francisco José Longo (1938/1941)
- Elmano Ferreira Veloso (1949/1950, 1953/1956, 1958/1961, 1966/1970)
- Jorge Zarur (1947 and 1950)
- José Marcondes Pereira (1962/1966)
- Sérgio Sobral de Oliveira (1970/1975)
- Ednardo José de Paula Santos (1975/1978)
- Joaquim Vicente Ferreira Bevilacqua (1978/1982, 1989/1990)
- Hélio Augusto (1986)
- Ângela Guadagnin (1993/1996)
- Emanuel Fernandes (1997/2000, 2001/2004)
Shopping areas
All the major hypermarkets, supermarket chains and discount and department stores are in city. The largest malls are:
- CenterVale Shopping;
- Shopping Colinas;
- Vale Sul Shopping;
- Shopping Faro;
- Shopping Centro.
Besides those malls, the most important commercial centers include:
- The Old Downtown area including:
- Rua Sete de Setembro - Calçadão - a popular street shopping area.
- Rua XV de Novembro - located in Praça Afonso Pena, the town square. This street was the main street in São José dos Campos in the 1950s and 1960s. On the weekends, handcraft exhibitions are held there and in other squares.
- Other streets: Rua Rubião Júnior, Rua Vilaça, Rua Siqueira Campos and Rua Sebastião Hummel.
- the Municipal Market (popular groceries, stores);
And newer areas such as:
- Avenida Francisco José Longo and Avenida Nelson D´Ávila (hotels and maintenance services);
- Avenida Nove de Julho (fashionable boutiques and restaurants)
- Rua Luis Jacinto (nightclubs and restaurants);
- Rua São João (with a small mall with exquisite boutiques called Shopping Esplanada, as well as restaurants and schools);
- Avenida Adhemar de Barros, where there are schools and the Santos-Dumont Park.
The Vila Ema district has sites for nightlife including bars and restaurants.
Sites
Several fairs and expositions are done at the two pavilions located in the city.
A list of notable sites:
- Augusto Ruschi Biological Reserve
- Burle Marx Municipal Park with the Olivo Gomes residence
- CTA and MAB (Brazilian Aerospace Memorial)
- Espaço Mário Covas (former City Council seat)
- INPE - (National Institute for Space Research)
- Sanatorium Vicentina Aranha
- Santos Dumont Park (total area: 46.347 m²)
Notable residents
- Aline Nakashima
- Casemiro
- Cassiano Ricardo
- Geovanna Tominaga
- Fabíola Molina
- Ozires Silva
- Rudolf Komorek
- Roque Júnior
Sister city
A Japanese garden is open for visits within the Santos-Dumont Park, celebrating the sister cities.
Entertainment, leisure and sports
Although São José is an industrial center, the city still preserves green areas and quiet town districts. Around 62% of the area from the municipality is characterized as an environmental preservation area. On the oustskirts of the urban area, Augusto Ruschi Ecology Reserve has many local plant species. The natural reserve has 2,500,000 m2 (27,000,000 sq ft), being a government protect area for the local flora. São Francisco Xavier is a community the offers many of those attributes as well.
Furthermore, there is easy access to the mountain cities (Campos do Jordão, Santo Antônio do Pinhal) and to the beaches of the Northern Coast of São Paulo.
The city has three parks and several sports and country clubs. Tenis Clube and Associação Esportiva São José have hosted the 35th Banana Bowl International Tennis Federation Juniors Circuit in 2005 and 2006.
A soccer stadium, called Estádio Martins Pereira, is the home ground of São José Esporte Clube, a professional soccer team.
Notable teams from the city:
| Club | Sport | Arena | Foundation of the Club | Logo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Associação Esportiva São José | Basketball | Ginásio Linneu de Moura | 1913 | |
| Associação Esportiva São José | Swimming | Ginásio Linneu de Moura | 1913 | |
| São José Esporte Clube | Football | Estádio Martins Pereira | 1933 | |
| Tenis Clube São José | Basketball | Ginásio Municipal José Edvar Simões | 1948 | |
| Tenis Clube São José | Volleyball | Ginásio Esportivo Manoel Bosco Ribeiro | 1948 | |
| São José Rugby Clube | Rugby union | Estádio Martins Pereira | 1987 | |
| Clube Atlético Joseense | Football | Estádio Martins Pereira / Estádio ADC Parahyba | 1998 | |
| Scott-Marcondes Cesar-São José dos Campos | Cycling | n/a | 1993 | N/a |
| São José/Vale Sul Futsal | Indoor Soccer/Futsal | Tenis Clube São José | na | n/a |
| FC Primeira Camisa | Football | Estádio ADC Parahyba | 2007 |
There are 19 movie theaters and 2 theaters including one inside the Univap - University of Vale do Paraíba.
Education and research centers
The Brazilian National Institute for Space Research (INPE) has its headquarters in São José dos Campos. It coordinates intensive research and development in areas such as Earth observation, space sciences and space technologies. Also the Brazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology (CTA) has its facilities in the city. There are 53 secondary schools, 54 primary schools and 109 preschools.
Universities and colleges
- Faculdade INPG - INPG college campus in S.J dos Campos; Nationally ranked MBA School by Magazine Você S/A, Edition Nov/2010.
- IBTA - Instituto Brasileiro de Tecnologias Avançadas
- Unip - Universidade Paulista
- Unifesp - Federal University of São Paulo
- Univap - University of Vale do Paraíba
- Faap - Fundação Armando Alvares Penteado
- Unesp -Universidade do Estado de São Paulo
- Fatec -Faculdade de Tecnologia de São José dos Campos
- ITA - Aeronautics Technological Institute
- Instituto de Filosofia Santa Terezinha
- Faculdades de Ciências Aplicadas
- EEI - Escola de Engenharia Industrial de São José dos Campos
- Inea - National Advanced Instruction Institute
- FGV - Fundação Getulio Vargas - Conveniado Conexão Desenvolvimento Empresarial
Research centers
- INPE - The Brazilian National Institute for Space Research
- Brazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology (CTA) with its four institutes: Aeronautics and Space Institute (IAE), Institute for Advanced Studies (IEAv), Industrial Foment and Coordination Institute (IFI) and ITA
Technical schools
- ETEP - Escola Técnica Everardo Passos
- CETEX - Expoente Technical Center
Infrastructure
Transportation and Communication

The city has two bus stations, having lines to cities in all regions of the country and international routes to Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay and Chile.
São José dos Campos boasts an extensive bus system. Operated by three companies (Expresso Maringa, Julio Simões and Viação Capital do Vale), these lines serve nearly all areas in the city with 319 buses. São José dos Campos also has an alternative system with minivans to supplement the regular buses.
The city uses a ring road system, that interconnects it to important national and state highways:
- BR-116 (federal highway), which crosses the urban area of São José. It runs in a north-south direction in the country, near but not on Brazil's coastline. The section that connects Rio de Janeiro to São Paulo is known as Presidente Dutra. It is widely used inside the urban area of São José dos Campos for commuting purposes;
- SP-070 (state highway) also known as Rodovia Carvalho Pinto which connects São Paulo to Taubaté;
- SP-065 Connects São Jose dos Campos to Campinas
- SP-099 (state highway) also known as Rodovia dos Tamoios which connects São José to the coastal lowlands of the city of Caraguatatuba;
- SP-050 (state highway) - the old road which connects São José dos Campos to Campos do Jordão and the southern region of Minas Gerais.
The city is also served by a railway (the former Central do Brasil), administered by MRS Logística, which today only carries freight.
The ports of São Sebastião and Santos can be reached by the highways SP-099, SP-155, and BR-101. The transportation of cargo to the domestic and foreign markets is made through both ports.
The São José dos Campos Airport (IATA: SJK, ICAO: SBSJ) has a heavy passenger flow, mainly business trips during weekdays, and it is an important connection between São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. With a 3,000 m (9,800 ft) runaway, the airport also serves people who come to visit the tourist city of Campos de Jordão. The airlines Azul Brazilian Airlines and TRIP Linhas Aéreas fly from São José dos Campos to several destinations and presently are the only commercial airlines operating on São José dos Campos.
It is also used for the transportation of cargo from the several industries located in the so-called Cone Leste Paulista ("São Paulo's East Cone"). Infraero and the Federal Revenue Agency are also introducing a new concept called airport-industry, that will offer fiscal incentives and fast importation and exportation procedures. The municipality has also a Customs Station for the Hinterland (dry port), controlled by the Federal Revenue Agency.
São José dos Campos receives natural gas from two gas pipelines, and large companies such as General Motors, Kodak, Monsanto and Embraer are among the main users. The city is the third largest in the country referring to the distribution net of natural gas for residential use.
It has also a large network of fiber optics, with broadband services covering 75% of the city. There is 1 telephone for each 3 inhabitants and a vast service network of cellular telephones.
Economy
| Economic statistics | ||
|---|---|---|
| GDP | BRL 17.6 billion (2004) | |
| Value added | BRL 14,795 million (2005) | |
| GDP per capita | BRL 29,950 (2004) | |
| Labour force | 267,332 (2003) (from 45% to 50% of pop.) | |
| Labour force by occupation | industry (19.4%), commerce (17.3%), services (50.9%), construction (2.2%), public sector (9.6%), other (0.5%) (2003) | |
| Main industries | aerospace, defense, automotive, chemical, pharmaceutical, telecommunications, components, consumer durables, oil and petrochemical | |
| Foreign commerce | ||
| Exports | BRL 4,947 million (2005) | |
| Imports | BRL 2,619 million (2005) | |
| Public finances | ||
| Municipal Budget | BRL 868 million (2005) | |
| Announced investments | $0.436 billion (2004) | |
| Social statistics | ||
| Human Development Index (UNDP) | 0.849 - high (2000) versus Brazilian HDI of 0.800 - high (2005) | |
| Literacy rate | 96.3% (2003) | |
Agriculture
The municipality cultivates different crops: rice, tomato, potatoes, orange and many vegetables; cattle are raised for beef and milk supply. There are also farms for production of eggs and chicken.
Industry

In contrast to the rural town in 1950s, today São José is an important manufacturing center and holds a large array of industries. Over 1,251 industries are in the municipality and nearby 47,000 inhabitants work for industries. The three main industries are automotive, oil/petrochemical and aerospace. There are significant pharmaceutical, consumer durables, chemical, and telecommunication companies in the city.
It is also known as the "Brazilian aeronautics capital" because it is home of CTA and one of the biggest aircraft manufacturers in the world, Embraer.
International Trade
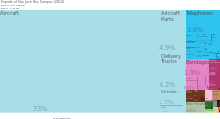
In 2014 São José dos Campos ranked as the 5th largest exporter, by value, of all Brazilian municipalities exporting $4.6B (USD) worth of materials.[11] In that year, between aircraft and aircraft parts categories, São José Dos Campos exported $3.57B (USD) or 81.9% of the total exports of the municipality.[12][13]
Service industry
Since the 1990s, the local economy has been evolving in a different direction. The manufacturing economy has been downsized or replaced by tertiary and quaternary sectors of industries.
For instance, the Entrepreneurial District of Chacaras Reunidas concentrates companies of micro, small and medium size, which are mainly the result of downsizing from old large local industries. Yet even though most of these are industries, these companies provide service as well.
Two technological parks and five (one in project) business incubators have been created within universities or industrial facilities.
There are incubators with technological start-up companies installed at Univap and at Henrique Lage Refinery of Petrobrás. The CTA houses other incubator, Incubaero, specialized in the aeronautical field.
Univap features a technological park with capacity for around 40 small to medium-sized innovating companies in the areas of materials, electronics and telecommunications, information technology, aerospace, energy, environment control, biotechnology, bioinformatics, chemical engineering, and software among others. A new technological park, managed by the municipality and the state government of São Paulo, will house two new think tanks: the Institute for Technological Research (IPT) and the ItecBio (Instituto de Tecnologias Biomédicas).
As a result of its geographical location, the city became an important distribution center, having several logistics providers. Activities like purchasing, transport, planning and warehousing have employed many people recently.
Commerce and real estate ventures have developed in the last years, reflecting the changes in the economy. For instance, the largest shopping mall in the region was an old manufacturing facility. Serving the region's population of approximately one million, the city is the regional hub for shopping and services for the Vale do Paraíba, the northern coast of São Paulo and southern Minas Gerais.
References
- ↑ "Estimativa Populacional 2015" (PDF). Pesquisa Demográfica por Amostra de Domicílios 201 (in Portuguese). Codeplan. 2015. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
- ↑ Inter-American Development Bank, Professor (2001). "Innovation Systems in Latin America". Competitiveness: The Business of Growth--Economic and Social Progress in Latin America, 2001 Report. Inter-American Development Bank. p. 229. ISBN 1886938962. Retrieved 2015-05-04.
- ↑ Assembleia Legislativa do Estado de São Paulo, Lei Complementar Nº 1.166
- ↑ http://www.sjc.sp.gov.br/sao_jose/dados_da_cidade.aspx
- ↑ Área de Proteção Ambiental São Francisco Xavier (in Portuguese), SAP: Sistema Ambiental Paulista, retrieved 2016-10-01
- ↑ Unidade de Conservação: Área de Proteção Ambiental Bacia Hidrográfica do Paraíba do Sul (in Portuguese), MMA: Ministério do Meio Ambiente, retrieved 2016-10-01
- ↑ "Climatic classification in São Paulo State" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Instituto Agronômico de Campinas. Retrieved September 11, 2016.
- ↑ http://www.monteverdemg.com.br/vm-clima.htm
- ↑ "A lista de cidades-irmãs". Estadão.com.br. October 13, 2007. Retrieved 18 March 2009.
- ↑ "S. José tem cidade-irmã no Japão desde 1973". Vale Paraibano. June 18, 2003. Retrieved 18 March 2009.
- ↑ DataViva. "2014 Brazilian Trade by Municipality", DataViva, Retrieved on June 24, 2015.
- ↑ DataViva. "International Trade Data for São José dos Campos in 2014", DataViva, Retrieved on June 24, 2015.
- ↑ DataViva. "Exports of São José dos Campos (2014)", DataViva, Retrieved June 24, 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to São José dos Campos. |
-
 São José dos Campos travel guide from Wikivoyage
São José dos Campos travel guide from Wikivoyage - (Portuguese) Official website




