Schnabel car

.jpg)

A Schnabel car is a specialized type of railroad freight car. It is designed to carry heavy and oversized loads in such a way that the load makes up part of the car. The load is suspended between the two ends of the cars by lifting arms; the lifting arms are connected to an assembly of pivots and frames that distribute the weight of the load and the lifting arm over a large number of wheels.
When a Schnabel car is empty, the two lifting arms are connected and the car can usually operate at normal freight train speeds. Some Schnabel cars include hydraulic equipment that will either lift or horizontally shift the load while in transit (at very low speeds) to clear obstructions along the car's route. As of 2012, there were 31 Schnabel cars operating in Europe, 30 in North America, 25 in Asia, and one in Australia.[1]
The largest Schnabel car in public railroads operation, reporting number WECX 801, was completed in 2012 by Kasgro Railcar for Westinghouse Nuclear and is used in North America primarily to transport reactor containment vessels.[1] It has 36 axles (18 for each half). Each half contains nine trucks which are connected by a complex system of span bolsters. Its tare (unloaded) weight is 399.6 short tons (362.5 t; 356.8 long tons) and has a load limit of 1,017.9 short tons (923.4 t; 908.8 long tons) for a maximum gross weight of 1,417.5 short tons (1,285.9 t; 1,265.6 long tons). WECX 801 has the ability to shift its load 44 inches (110 cm) vertically and up to 40 inches (100 cm) laterally on either side of the car's center line.[2] When empty, this car measures 231 ft (70 m) long; for comparison, a conventional boxcar currently operating on North American railroads has a single two-axle truck at each end of the car, measures 50 to 89 feet (15.24 to 27.13 m) long and has a capacity of 70 to 105 short tons (64 to 95 t; 63 to 94 long tons). The train's speed is limited to 25 mph (40 km/h) when WECX 801 is empty, but only 15 mph (24 km/h) when loaded and requires a crew of six operators in addition to the train's crew.[1]
The word Schnabel is from German Tragschnabelwagen, meaning "carrying-beak-wagon", because of the usually tapered shape of the lifting arms, resembling a bird's beak.
Patent history
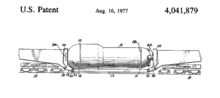
The Schnabel design is covered under US patent #US 4041879 A, filed December 1, 1975, issued to Charles R. Cockrell, with Combustion Engineering, Inc. as assignee. [3]
References
- 1 2 3 "Kasgro builds "World's Largest Railroad Car"". Railwayage.com. June 14, 2012. Retrieved February 9, 2016.
- ↑ "WECX 801". southern.railfan.net. Retrieved February 9, 2016.
- ↑ "Schnabel-type car, US 4041879 A". Google Patent Search.
- Daspit, Tom (2005). "CEBX 800". Retrieved May 6, 2005. (additional technical details on CEBX 800)
- GATX Corporation (2005). "Car types". Archived from the original on May 7, 2005. Retrieved May 6, 2005. (boxcar comparison figures)
- Passi, Peter (May 5, 2005). "Railroad Giant". Duluth News Tribune. Archived from the original on May 6, 2005. Retrieved May 6, 2005. (details on CEBX 800)
- Railway Industrial Clearance Association (2000). "Glossary of terms used in railroad high and wide clearances". Archived from the original on June 13, 2005. Retrieved May 6, 2005. (basic definition of a Schnabel car)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Schnabel cars. |
- Schnabel cars – photos and technical information on Schnabel cars used worldwide.
- Heavy Rail Transport Basics archived version