Scottish Labour Party
Scottish Labour Party Pàrtaidh Làbarach na h-Alba Scots Labour Pairty | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Leader | Kezia Dugdale MSP |
| Deputy Leader | Alex Rowley MSP |
| General Secretary | Brian Roy |
| Founded | 1900 [1][2] |
| Headquarters |
290 Bath Street Glasgow G2 4RE |
| Student wing | Scottish Labour Students |
| Youth wing | Scottish Young Labour |
| Membership | 18,824 [3][Note 1] |
| Ideology |
British unionism Social democracy[6] Pro-Europeanism[7] |
| Political position | Centre-left |
| European affiliation | Party of European Socialists |
| International affiliation |
Progressive Alliance, Socialist International (Observer) |
| European Parliament group | Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats |
| Colours | Red |
| Scottish seats in the House of Commons |
1 / 59 |
| Scottish seats in the European Parliament |
2 / 6 |
| Scottish Parliament |
23 / 129 |
| Local government in Scotland |
396 / 1,223 |
| Website | |
|
www | |
The Scottish Labour Party (Scottish Gaelic: Pàrtaidh Làbarach na h-Alba, Scots: Scots Labour Pairty;[8] branded Scottish Labour) is the brand name of the British Labour Party branch in Scotland.
Labour hold 23 of 129 seats in the Scottish Parliament and two of six Scottish seats in the European Parliament. Labour won the largest share of the vote in Scotland at every UK general election from 1964 until 2015, when they lost heavily to the Scottish National Party,[9] every European Parliament general election from 1979 until defeated by the SNP in 2009, and in the first two elections to the Scottish Parliament in 1999 and 2003. After these, Scottish Labour entered a coalition with the Scottish Liberal Democrats, forming a majority Scottish Executive. In the 2007 Scottish Parliament election, Scottish Labour became the second largest party, with a lower share of the vote and one fewer seat than the Scottish National Party (SNP), who subsequently formed a minority government. It remained the second largest party after the 2011 Scottish Parliament election, with the SNP forming the first majority government since devolution in 1999. In a landslide defeat at the 2015 UK general election, it was reduced to a single Member of Parliament, losing 40 of its 41 seats to the SNP, the first time the party had not won the largest number of seats in Scotland since 1959.[10] In the 2016 Scottish Parliament election, Scottish Labour lost 13 of its 37 seats, becoming the third largest party for the first time after being surpassed by the Scottish Conservative Party.
Organisation
The Scottish Labour Party is registered as an Accounting Unit (AU) of the Labour Party with the Electoral Commission and is therefore not a registered political party under the terms of the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000.
Kezia Dugdale is the directly elected Leader of the Scottish Labour Party, as outlined in the Party's constitution.
Scottish Executive Committee
The Scottish Labour Party is administered by the Scottish Executive Committee (SEC), which is responsible to the Labour Party's National Executive Committee (NEC).
The Scottish Executive Committee is made up of representatives of party members, elected members and party affiliates, for example, trade unions and socialist societies.
Party Officers:
- Chair: Jamie Glackin
- Vice Chair: Jacqueline Martin
- Treasurer: Cathy Peattie
Leader of the Labour Group in the Scottish Parliament
- Donald Dewar (7 May 1999 – 11 October 2000)
- Henry McLeish (27 October 2000 – 8 November 2001)
- Jack McConnell (22 November 2001 – 15 August 2007)
- Wendy Alexander (14 September 2007 – 28 June 2008)
- Iain Gray (13 September 2008 – 17 December 2011)
Leader of the Scottish Labour Party
- Johann Lamont (17 December 2011 – 24 October 2014)
- Anas Sarwar (acting: 24 October 2014 – 13 December 2014)
- Jim Murphy (13 December 2014 – 13 June 2015)
- Iain Gray (acting: 13 June 2015 – 15 August 2015)
- Kezia Dugdale (15 August 2015 – present)
Deputy Leader of the Scottish Labour Party
- Anas Sarwar (17 December 2011 – 13 December 2014)
- Kezia Dugdale (13 December 2014 – 13 June 2015)
- Vacant (13 June 2015 – 15 August 2015)
- Alex Rowley (15 August 2015 – present)
Leader of the Labour Party in the Scottish Parliament
- Donald Dewar (7 May 1999 – 11 October 2000)
- Henry McLeish (27 October 2000 – 8 November 2001)
- Jack McConnell (22 November 2001 – 15 August 2007)
- Cathy Jamieson (15 August 2007 – 14 September 2007) (Acting)
- Wendy Alexander (14 September 2007 – 28 June 2008)
- Cathy Jamieson (28 June 2008 – 13 September 2008) (Acting)
- Iain Gray (13 September 2008 – 17 December 2011)
- Johann Lamont (17 December 2011 – 24 October 2014)
- Jackie Baillie (24 October 2014 – 13 December 2014) (Acting)
- Kezia Dugdale (13 December 2014 – 13 June 2015 (As Deputy Party Leader, in the Parliament)
- Iain Gray (13 June 2015 – 15 August 2015) (Acting)
- Kezia Dugdale (15 August 2015 – present)
General Secretary of the Scottish Labour Party
As with Welsh Labour, the Scottish Labour Party has its own general secretary which is the administrative head of the party, responsible for the day-to-day running of the organisation, and reports to the UK General Secretary of the Labour Party.
The current Scottish general secretary is Brian Roy. His predecessor was Ian Price, who succeeded Colin Smyth in 2013.[11]
Headquarters
The Scottish Labour headquarters is currently at Bath Street, Glasgow. It was formerly co-located with the offices of Unite the Union at John Smith House, 145 West Regent Street.
Conference
The party holds an annual conference during February/March each year.
Membership
Labour Party full members (excluding affiliates and supporters)
In 2008, Scottish Labour Party membership was reported as 17,000, down from a peak of approximately 30,000 in the run-up to the 1997 general election.[12] The figures included in the Annual Report presented to the Scottish Party Conference in 2008, also recorded that more than half of all Constituency Labour parties (CLPs) had less than 300 members, with 14 having less than 200 members.[13]
In September 2010, the party issued 13,135 ballot papers to party members during the Labour Party (UK) leadership election. These did not necessarily equate to 13,135 individual members – due to the party's electoral structure, members can qualify for multiple votes.[14] The party has declined to reveal its membership figures since 2008, and did not publish the number of votes cast in the leadership elections of 2011 or 2014, only percentages.[15]
In November 2014 the party's membership was claimed by an unnamed source reported in the Sunday Herald to be 13,500.[16] Other recent reports in the media have quoted figures of "as low as 8,000" (the Evening Times) [17] and "less than 10,000" (New Statesman).[18] In December 2014 the newly elected leader Jim Murphy claimed that the figure was "about 20,000" on the TV programme Scotland Tonight.[19]
According to the accounts it submitted to the Electoral Commission the party had an income from membership of £115,636 in 2013, the most recent year for which figures have been published.
In late September 2015, following a membership boost resulting from the 2015 Labour leadership election, a total of 29,899 people were associated with the party; 18,824 members, 7,790 people affiliated through trade unions and other groups, and 3,285 registered supporters.[3]
History
The Labour Party campaigned for the creation of a devolved Scottish Parliament as part of its wider policy of a devolved United Kingdom. In the late 1980s and 1990s it and its representatives participated in the Scottish Constitutional Convention with the Scottish Liberal Democrats, Scottish Green Party, trades unions and churches, and also campaigned for a "Yes-Yes" vote in the 1997 referendum.
1999–2007 Lib–Lab pact & coalition
In the first elections to the Scottish Parliament on 6 May 1999, the Scottish Labour Party, led by Donald Dewar, won 56 seats out of 129, well ahead of their main opponents, the SNP under Alex Salmond, with 35 seats. Lacking a majority in Parliament, the party formed a coalition government with the Scottish Liberal Democrats, with Dewar agreeing to their demand for the abolition of up-front tuition fees for university students as the price for a coalition deal. Consequently, on 13 May, Dewar was nominated as First Minister, and was officially appointed by the Queen on 17 May at a ceremony in Holyrood Palace. He later travelled to the Court of Session to be sworn in by the Lord President, and received the Great Seal of Scotland.
In April 2000, Dewar was admitted to hospital for tests on his heart, following a previous test in which a minor irregularity had been discovered. The following month, he had surgery to repair a leaking heart valve, and was forced to take a three-month break from Parliament, with Deputy First Minister Jim Wallace taking over as Acting First Minister. On 10 October 2000, Dewar sustained a fall. He seemed fine at first but later that day suffered a massive cerebral haemorrhage which was possibly triggered by the anticoagulant medication he was taking after the heart surgery. Donald Dewar died the following day in Edinburgh's Western General Hospital.
On 27 October 2000, a fortnight after Dewar's death, Henry McLeish was elected as Leader of Scottish Labour, defeating rival Jack McConnell. McLeish resigned the following year amid a scandal involving the renting of his constituency office and allegations of financial wrongdoings. McLeish felt his resignation would allow the Scottish Labour Party a clean break to prepare for the 2003 Parliamentary elections.
After McLeish's resignation, Jack McConnell quickly emerged as the only candidate, and was elected First Minister by the Parliament on 22 November 2001.
2007 Scottish Parliament elections and aftermath
In the run-up to the 2007 Scottish Parliament general election, McConnell was criticised by many inside and outside of the Labour party for his role in the party's poor start to the campaign, with Labour solidly behind the Scottish National Party (SNP) in many opinion polls. On 10 April, McConnell unveiled Scottish Labour's election manifesto, which included plans to scrap (?) bills for pensioners and reform Council Tax. The manifesto also proposed a large increase in public spending on education, which would allow for the school leaving age to be increased to 18 and reduce average class sizes to 19 pupils.
McConnell's ruling Labour Party was defeated by the SNP, both in terms of the popular vote and number of seats. The SNP won 47 seats in the new parliament, whilst the Labour Party won 46, thus securing them a one-seat majority over Labour, but still well short of a majority of the parliament. On 15 August 2007, McConnell announced his intention to resign as Scottish Labour leader.
On 17 August 2007, Wendy Alexander formally launched her campaign for the leadership of the Labour Party in Holyrood. As the only candidate, Alexander was installed as leader of the Labour group in the Scottish Parliament on 14 September 2007. That same year, a funding scandal developed after it emerged that she had accepted an illegal donation from Paul Green, a property magnate, a matter that was investigated by the Electoral Commission. Further newspaper reports on 30 November indicated Alexander was aware of the identity of the donor, after having sent a personal letter of gratitude to Mr Green (at his home in the tax haven of Jersey) concerning the donation. Accepting a donation from someone who is not registered on the UK electoral roll is illegal under electoral law, and is subject to criminal prosecution. However, the Electoral Commission concluded in February 2008 that Alexander had taken 'significant steps' to comply with funding regulations and decided not to refer the matter to the Procurator Fiscal. In a separate development, a few days earlier in February 2008, the standards watchdog for Scotland reported Wendy Alexander to the Procurator Fiscal for failing to publicly declare campaign donations.
During a TV interview on 4 May 2008, Wendy Alexander performed a major U-turn on previous Scottish Labour Party's policy by seeming to endorse a referendum on Scottish independence, despite previously refusing to support any referendum on the grounds that she did not support independence. During a further TV interview on 6 May 2008 she reiterated this commitment to a referendum and claimed that she had the full backing of current British Prime Minister Gordon Brown. The following day, Gordon Brown denied this was Labour policy and that Wendy Alexander had been misrepresented during Prime Minister's Questions in Westminster. Despite this lack of backing, Wendy Alexander once again reiterated her commitment to a referendum during First Minister's Questions in the Scottish Parliament.
On 28 June 2008, Wendy Alexander announced her resignation as Leader of the Scottish Labour Party as a result of the pressure on her following the donation scandal. Cathy Jamieson subsequently became interim leader of the Scottish Labour Party.
2008 Glasgow East by-election
In late June 2008, David Marshall, MP for the Glasgow East (Glasgow Shettleston) constituency since 1979, resigned on health grounds. The resignation was sudden, however the seat was the 3rd safest Labour seat in the country and at the Westminster general election in 2005, Labour had a 13,057 majority over second placed SNP. In the resultant by-election on 24 July 2008, SNP candidate, serving Glasgow City Council member John Mason managed a spectacular 22.5% swing in the nationalists' favour to win the seat.
2008 Scottish Labour leadership elections
On 1 August 2008, the contest for the new Leader of the Scottish Labour Party began. The contenders were Iain Gray, MSP for East Lothian, a former Enterprise Minister in the previous Labour Executive, Andy Kerr, MSP for East Kilbride and former Health Secretary in the previous administration, and Cathy Jamieson MSP, who had been deputy leader under Jack McConnell and caretaker leader since Wendy Alexander resigned following the illegal donation scandal.
On 13 September 2008, Iain Gray was elected leader and promised a "fresh start" for Labour in Scotland.
2008 Glenrothes by-election
On 13 August 2008, Labour Member of Parliament (MP) for Glenrothes in Fife, John MacDougall died, triggering a by-election in a constituency that neighboured both the constituency of Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Gordon Brown, and the constituency of Dunfermline and West Fife that had been won by the Liberal Democrats in a by-election in 2006. In the event, Labour held the parliamentary seat, increasing their vote by 3.2%. Lindsay Roy became Labour MP for the constituency, on 7 November 2008, defeating the SNP's candidate, Peter Grant, current council leader in Fife, in what was viewed by many as a surprise. Grant had been widely fancied to take the seat and after their stunning success in Glasgow East the SNP were disappointed. The voting was: Lindsay Roy, Labour, 19,946; Peter Grant, SNP 13,209. The Conservative Party which came 3rd with 1,381 votes, the Liberal Democrats with 947 votes and four other candidates lost their deposits.[20]
2010 UK general election
On 6 May 2010, contrary to polls preceding the election, Labour consolidated their vote in Scotland, losing no seats (despite losing 91 seats across the rest of Britain) and recovering Glasgow East from the SNP. This resulted in incumbent Scottish secretary Jim Murphy stating that the result provided an impetus for Scottish Labour to attempt to become "the biggest party in Holyrood" in the 2011 Scottish Parliament elections.[21]
2011 Scottish Parliament election
The Scottish Labour Party lost seven seats compared to the notional 2007 result although its share of the constituency vote declined by less than 1%. Party leader Iain Gray, who held on to his own seat by only 150 votes, announced that he would be resigning with effect from later in the year.
2011 Inverclyde by-election
The seat of Inverclyde was held by David Cairns until his death on 9 May 2011. The resulting by-election held on 30 June, was won comfortably with a 5,838 majority by Scottish Labour candidate Iain McKenzie despite several high-profile campaign visits by SNP First Minister, Alex Salmond and the SNP coming within 511 votes of winning the nearest equivalent seat in the Holyrood elections a matter of weeks previously. Coupled with the 2010 UK General Election results, this suggests that Scottish Labour's disappointing performance in the 2011 Scottish Parliament Election does not necessarily translate into support for its political opponents in other elections.
2011 Murphy/Boyack Review
Following the 2011 Scottish election, Ed Miliband commissioned a review of the future structure and operation of the Labour Party in Scotland, co-chaired by Jim Murphy MP and Sarah Boyack MSP.
2011 Scottish Labour leadership elections
On 17 December 2011, Johann Lamont MSP was elected as leader and Anas Sarwar MP elected as her deputy.
2012–2014 independence referendum campaign
The announcement of the upcoming referendum on Scottish independence in the aftermath of the Scottish National Party's victory at the Scottish Parliament elections in 2011 led to the Scottish Labour Party joining with the Conservatives and the Liberal Democrats in the pro-union Better Together campaign against Scottish independence.
In July 2012, a member of Scottish Labour started Labour for Independence, a rebel group of Labour supporters who back Yes Scotland in the campaign for Scottish independence.[22] The group has since evolved into a fully-fledged political organisation, but has been dismissed by the Scottish Labour leadership as lacking "real support" from within the party.[23]
In December 2012, Scottish Labour announced that they would be running their own campaign alongside Better Together to "continue articulating [their] vision for a better Scotland in education and in health".[24] This would be comparable to the "Conservative Friends of the Union" campaign started by the Conservative Party, and would likely not be recognised as an official campaign organisation by the Electoral Commission. This was eventually revealed to be the "2014 Truth Team", described by the party as "dedicated to cutting through the noise and delivering [...] facts on independence".[25]
In May 2013, Scottish Labour continued its own pro-UK campaign with the launch of United with Labour with the support of former Prime Minister Gordon Brown.[26]
2013 Falkirk Labour Party investigation
In 2013, Labour and Police Scotland launched separate investigations into claims that officials within the Unite union had signed up members to Labour to get their preferred candidate adopted to represent the party in the Falkirk constituency; they were later cleared of any wrongdoing.[27] Subsequent claims were made that key evidence thought to have been retracted, had not been withdrawn, prompting several Falkirk councillors to urge the UK Labour Party leader, Ed Miliband to publish details of the party's internal inquiry or hold a fresh investigation.[27] Speaking on 4 November edition of Good Morning Scotland, Scottish Labour leader Johann Lamont said there was a case for a fresh inquiry, but that Labour does not publish details of its internal investigations.[27][28] Later the same day, Labour said that it would not be reopening the investigation.[29] Miliband subsequently said that a new investigation was unnecessary.[30]
2014 Scottish Labour leadership elections
On 25 October 2014, Johann Lamont MSP resigned as leader; Anas Sarwar MP became acting leader and resigned as deputy leader. Sarah Boyack confirmed that she would be standing as a candidate for party leader. She was joined by Neil Findlay and Jim Murphy, who declared the following day. Katy Clark and Kezia Dugdale stood for the vacant deputy leader post.[31]
On 13 December 2014, it was announced Jim Murphy had been elected as leader of the party, winning 55.77% of the vote. Kezia Dugdale was elected as deputy leader, winning 62.9% of the vote.[32]
In his victory speech, Murphy said that his election marked a "fresh start" for Scottish Labour: "Scotland is changing and so too is Scottish Labour. I'm ambitious for our party because I'm ambitious for our country".[33][34] He also said that he planned to defeat the SNP in 2016, and that he would use the increased powers being devolved to Holyrood to end poverty and inequality. In her speech, Dugdale said that the party's "focus has to be on the future – a Scottish Labour party that's fighting fit and fighting for our future".[33]
2015 UK general election
Following his election as leader in December 2014, Murphy claimed he was confident the party would hold all 41 of their seats, and would gain the marginal East Dunbartonshire from the Liberal Democrats.[35] However, the party suffered a landslide defeat in the general election in May 2015, losing 40 of their 41 seats to the SNP. Many senior party figures were unseated, including Murphy himself (East Renfrewshire), Shadow Foreign Secretary Douglas Alexander (Paisley and Renfrewshire South) and Shadow Scotland Secretary Margaret Curran (Glasgow East). Ian Murray (Edinburgh South) was the only MP re-elected. It was the first time since 1959 that the party hadn't won the most seats in Scotland at a general election.
2015 Scottish Labour leadership elections
On 16 May 2015 Jim Murphy resigned as leader effective 13 June 2015; under normal circumstances, Deputy Leader Kezia Dugdale would become acting leader, but former Leader Iain Gray was appointed Acting Leader whilst a leadership and a deputy leadership election are being simultaneously held on account of Dugdale resigning as Deputy Leader to stand for Leader. Dugdale was later elected Leader on 15 August 2015.
2016 Scottish Parliament election
The Labour party lost a third of its seats, dropping from 37 to 24.
Labour got its lowest percentage of the vote in Scotland in 100 years with 23%, its vote share dropped by 9.2% in the constituencies and 7.2% in the regional lists compared with 2011, which pushed the party into 3rd place, a position it last occupied in Scotland in 1910.
Ken Macintosh resigned his Labour party membership when he was elected the new Presiding Officer.
2016 UK Labour leadership crisis
- 26 June 2016: Ian Murray resigned as Scottish Secretary from the Shadow Cabinet as part of a mass walkout from the frontbench, saying Corbyn is the not right person to lead the Labour party
- 27 June 2016: Corbyn loses a vote of no confidence by 172 votes to 40 among Labour MPs
- 28 June 2016: Kezia Dugdale called on Corbyn to consider his position after losing the confidence of the vast majority of his MPs and mass resignations from the frontbench[36]
- 29 June 2016: 80 Scottish Labour members, including MSP Elaine Smith, condemn Ian Murray for "putting factional party politics over getting the best outcome for the people of Scotland".[37]
- 29 June 2016: More than 200 Scottish Labour members (including former MPs, MSPs, MEPs, senior councillors and party officials) signed a letter calling for Corbyn to resign[38] Signatories include Lord Foulkes, Margaret Curran, former party chairman Jamie Glackin, MEP Catherine Stihler, MSP Daniel Johnson and the former head of Glasgow city council Gordon Matheson[39]
- 30 June 2016: 13 Labour MSPs (Jackie Baillie, Claire Baker, Claudia Beamish, Neil Bibby, Mary Fee, Iain Gray, Mark Griffin, Daniel Johnson, James Kelly, Johann Lamont, Lewis Macdonald, Anas Sarwar, Colin Smyth) signed a letter calling for Corbyn to resign.[40][41]
- 30 June 2016: 3 Labour MSPs Alex Rowley, Neil Findlay and Richard Leonard signed a letter calling on Labour MPs opposed to Corbyn to respect his mandate.
- 1 July 2016: Corbyn appoints English Labour MP for Blaydon, Dave Anderson, as the party's new Shadow Secretary of State for Northern Ireland and Scotland
- 18 July 2016: Kezia Dugdale appoints Ian Murray as Scottish Labour's Westminster Spokesperson
2016 UK Labour leadership election
According to the LabourList blog, Labour was dealt a blow by GMB Scotland, which decided they would not carry out a ballot of its members on the leadership contest of the UK Labour Party because of the perception of the party’s "increasing irrelevance in Scotland".[42]
In a statement, GMB Scotland said "In Scotland, Labour’s decline over the last decade has been stark. Opinion polls now consistently show declining support among the Scottish electorate, both in Holyrood or Westminster and the party now sits in third place behind the Tories after the recent Scottish Parliament elections. Therefore, GMB Scotland sees no merit in a ballot of our entire Scottish membership on the question of the UK Labour leadership when the party’s resonance is so minimal. Instead, our party members in GMB Scotland will make up their own minds through their own private vote and we will make members aware about how they can participate and who is eligible.”[43]
A GMB Scotland spokesperson told CommonSpace that "the leadership drama was an English phenomenon, and that the stark decline in Scottish Labour’s fortunes meant that the contest wasn’t a matter for their Scottish members. Obviously the debate in the Labour party is much more acute in England. There's been a stark decline for Labour in Scotland - that doesn't need to be debated. Scottish Labour is in third place behind the Conservatives. We have our main business to get on with. It isn't practical or useful for us to send out an open ended question to our 55,000 members across the country."[44]
2016 UK NEC election controversy
The pro-Corbyn Momentum campaign organisation attacked leading Blairite and ex-Scottish Leader Jim Murphy as "disgraceful" for allegedly helping to block Scottish Labour activist Rhea Wolfson from running for Labour's ruling body National Executive Committee when she failed to win the nomination of her local Constituency Labour Party of Eastwood in Renfewshire, meaning she could no longer run. Rhea Wolfson was running with the backing of Momentum to replace Ken Livingstone on the party's NEC following his suspension from the NEC over anti-Semitism allegations.[45]
In an angry statement, Wolfson blamed an opposing faction of the party and Jim Murphy in particular for blocking her. She said: "Last night Eastwood CLP, where my family home is, met to nominate candidates for the NEC. It was proposed that, given I am currently a member of the CLP, there would be a straight vote for or against my nomination. I made my case and answered questions from the room. I was then asked to leave the room while they discussed my nomination further. Once I had left, the ex-leader of Scottish Labour, Jim Murphy, appealed to the CLP to not nominate me. He argued that it would not be appropriate to nominate me due to my endorsement by Momentum, which he claimed has a problem with anti-Semitism. The constituency has a large Jewish population. The CLP then voted to not endorse me, before re-inviting me back into the room. Needless to say, this is hugely disappointing. It is disappointing because I am the only Jewish candidate in this election, because the wide range of organisations endorsing me includes the Jewish Labour Movement, and because I have a long record of challenging anti-Semitism and have in fact faced it on a daily basis since my candidacy was announced. But above all, it is disappointing because I know there are many members who want to vote for me, who could now have lost that opportunity. I am considering my options going forward."[46]
Nick Hopkins, chair of the Eastwood CLP, said to Huffington Post: "Wolfson's links with Momentum were partly to blame for their decision. We don’t usually nominate to the NEC, so we decided to give special consideration to Rhea’s nomination as a member of our constituency. The first concern was about factionalism generally and not endorsing a faction. The second concern was around Momentum in particular and its role within the party at the moment. The third thing was the party felt it wants to get to know Rhea better as an individual. She presented her thoughts very well, people were impressed by her. But I think at the end they just decided not to go with her nomination – or any nomination. We certainly weren’t going to nominate anyone else in that context.”[47]
Elected representatives (current)
House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
| Member of Parliament | Constituency | First elected | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ian Murray | Edinburgh South | 2010 | Former Shadow Secretary of State for Scotland |
Shadow Cabinet
- Kezia Dugdale - Leader of the Scottish Labour Party and Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Finance and the Constitution
- Alex Rowley - Deputy Leader and Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Community, Social Security and Equalities
- Iain Gray - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Education, Skills and Science
- Anas Sarwar - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Health
- Lewis Macdonald - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Culture, Sport and External Affairs
- Claudia Beamish - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Environment, Climate Change and Land Reform
- Rhoda Grant - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for the Rural Economy and Connectivity
- Claire Baker - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Justice
- Jackie Baillie - Shadow Cabinet Secretary for Economy, Jobs and Fair Work
- James Kelly - Parliamentary Business Manager and Shadow Minister without Portfolio
Junior Shadow Ministers
- Mark Griffin & *Pauline McNeill - Shadow Community Ministers
- Monica Lennon - Shadow Inequality Minister (Health and Education role)
- Daniel Johnson - Shadow Education Minister
- David Stewart - Shadow Environment Minister
- Neil Bibby - Shadow Transport and Town Centres Minister
- Richard Leonard - Shadow Economy Minister
- Mary Fee - Shadow Justice Minister
- Mark Griffin & Colin Smyth - Shadow Whips
Members of the Scottish Parliament
Electoral performance
European Parliament Elections
| Year | Share of votes | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| 1979 | 33.0% | 2 / 8 |
| 1984 | 40.7% | 5 / 8 |
| 1989 | 41.9% | 7 / 8 |
| 1994 | 42.5% | 6 / 8 |
| 1999 | 28.7% | 3 / 8 |
| 2004 | 26.4% | 2 / 7 |
| 2009 | 20.8% | 2 / 6 |
| 2014 | 25.9% | 2 / 6 |
UK General Elections
.svg.png)
| Year | Share of votes | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| 1910 (January) | 5.1% | 2 / 70 |
| 1910 (December) | 3.6% | 3 / 70 |
| 1918 | 22.9% | 6 / 71 |
| 1922 | 32.2% | 29 / 71 |
| 1923 | 35.9% | 34 / 71 |
| 1924 | 41.1% | 26 / 71 |
| 1929 | 42.3% | 36 / 71 |
| 1931 | 32.6% | 7 / 71 |
| 1935 | 36.8% | 20 / 71 |
| 1945 | 47.9% | 37 / 71 |
| 1950 | 46.2% | 37 / 71 |
| 1951 | 47.9% | 35 / 71 |
| 1955 | 46.7% | 34 / 71 |
| 1959 | 46.7% | 38 / 71 |
| 1964 | 48.7% | 43 / 71 |
| 1966 | 49.8% | 46 / 71 |
| 1970 | 44.5% | 44 / 71 |
| 1974 (Feb) | 36.6% | 40 / 71 |
| 1974 (Oct) | 36.3% | 41 / 71 |
| 1979 | 41.6% | 44 / 71 |
| 1983 | 35.1% | 41 / 72 |
| 1987 | 42.4% | 50 / 72 |
| 1992 | 39.0% | 49 / 72 |
| 1997 | 45.6% | 56 / 72 |
| 2001 | 43.3% | 56 / 72 |
| 2005 | 39.5% | 41 / 59 |
| 2010 | 42.0% | 41 / 59 |
| 2015 | 24.3% | 1 / 59 |
Scottish Parliament Elections
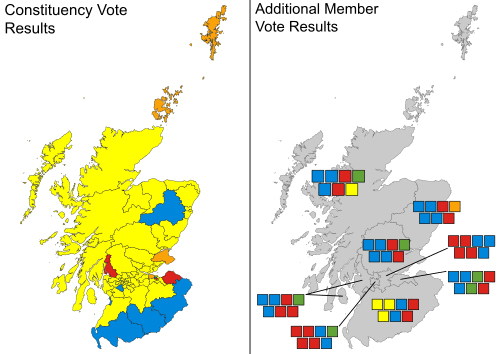
| Year | Share of votes (constituency) | Share of votes (list) | Seats | Position | Outcome | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 38.8% | 33.6% | 56 / 129 |
1st | Coalition Government | First election to the re-constituted Scottish Parliament. Formed a coalition with the Liberal Democrats. |
| 2003 | 34.6% | 29.3% | 50 / 129 |
1st | Coalition Government | |
| 2007 | 32.2% | 29.2% | 46 / 129 |
2nd | Opposition | Became the official opposition to the minority SNP government. |
| 2011 | 31.7% | 26.3% | 37 / 129 |
2nd | Opposition | |
| 2016 | 22.6% | 19.1% | 24 / 129 |
3rd | Opposition | Became the third largest party for the first time since 1918. Surpassed by the Scottish Conservative Party. |
Further reading
- Scottish Labour Leaders 1918–1939: A Biographical Dictionary, William Know, Mainstream Publishing, 1984.
- Dictionary of Labour Biography, Greg Rosen, 2001, Politicos Publishing, ISBN 1-902301-18-8
- The Scottish Labour Party, Gerry Hassan, 2003, Edinburgh University Press, ISBN 0-7486-1784-1
- Donald Dewar, Scotland's First Minister, Wendy Alexander, Mainstream Publishing, 2005.
- Old Labour to New, Greg Rosen, 2005, Politicos Publishing.
- John Smith – A Life, Mark Stuart, Politicos Publishing, 2005.
- Strange Death of Labour in Scotland, Gerry Hassan, Eric Shaw, Edinburgh University Press, ISBN 0748640029, 2012.
References
- ↑ "History of the Scottish Labour Party". www.scottishlabour.org.uk/. Scottish Labour Party. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "History of the Labour Party". www.labour.org.uk. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- 1 2 Whitaker, Andrew (27 September 2015). "Interview: Kezia Dugdale on reform of Scots Labour". The Scotsman.
- ↑ Oliver Wright (10 September 2015). "Labour leadership contest: After 88 days of campaigning, how did Labour's candidates do?". The Independent. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
the electorate is divided into three groups: 292,000 members, 148,000 union “affiliates” and 112,000 registered supporters who each paid £3 to take part
- ↑ Dan Bloom (25 August 2015). "All four Labour leadership candidates rule out legal fight - despite voter count plummeting by 60,000". Daily Mirror. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
total of those who can vote now stands at 550,816 ... The total still eligible to vote are now 292,505 full paid-up members, 147,134 supporters affiliated through the unions and 110,827 who've paid a £3 fee.
- ↑ Wolfram Nordsieck. "Parties and Elections in Europe: The database about parliamentary elections and political parties in Europe".
- ↑ Kezia Dugdale launches Scottish Labour’s bid to remain in EU.
Herald Scotland. Published 14 May 2016. Retrieved 15 June 2016. - ↑ Scots Glossary – All words. Mudcat.org. Retrieved on 29 October 2013.
- ↑ The 2005 General Election in Scotland, by David Denver, Scottish Affairs, No. 53, Autumn 2005; accessed 7 January 2009
- ↑ http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/1959_general_election.htm
- ↑ "Scottish Labour recruits Ian Price as general secretary", BBC News website, 2 February 2013
- ↑ "Panic within Labour as membership falls", The Scotsman, 5 March 2006
- ↑ "Labour foot soldiers fall away", BBC NEWS, 29 March 2008
- ↑ Macdonell, Hamish (29 September 2010). "The Scottish Labour Party and its mysterious expanding membership". Caledonian Mercury. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ↑ "Johann Lamont named new Scottish Labour leader", 17 December 2011
- ↑ "Revealed: just how many members does Labour really have in Scotland?". Sunday Herald. 9 November 2014. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- ↑ "Other parties should copy Sturgeon's US-style rallies". Evening Times. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Leader: The end of the "two-party" party". www.newstatesman.com. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Start as you mean to go on". 2014-12-16. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ Glenrothes result in full BBC News 7 November 2008
- ↑ "Election 2010: Jim Murphy's joy as Scotland says no to David Cameron". The Daily Record. Retrieved 18 December 2011.
- ↑ "Yes Scotland wins support from Labour rebel group". 30 July 2012. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
- ↑ "Scottish independence: Labour dismisses rebellion". 30 July 2012. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
- ↑ "Referendum campaign next year". Herald Scotland.
- ↑ "Anas Sarwar MP launches the 2014 Truth Team". 22 April 2013. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- ↑ "Scottish independence: Former PM Gordon Brown wants a 'union for social justice'". BBC News. 13 May 2013. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Alistair Darling calls for new Falkirk vote-rigging inquiry". BBC News. BBC. 4 November 2013. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ↑ Mason, Rowena (4 November 2013). "Falkirk vote-rigging inquiry may be reopened, says Scottish Labour leader". The Guardian. Guardian Media Group. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ↑ "Labour: 'No plans' to reopen Falkirk vote-rigging inquiry". BBC News. BBC. 4 November 2013. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ↑ Barnes, Eddie (6 November 2013). "Ed Miliband: No need for new Falkirk inquiry". The Scotsman. Johnston Press. Retrieved 14 November 2013.
- ↑ "Blow for Murphy as his own union backs Findlay as leader". Herald Scotland. 9 November 2014. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- ↑ "MP Jim Murphy named Scottish Labour leader". BBC News. 13 December 2014.
- 1 2 "MP Jim Murphy named Scottish Labour leader". BBC News. BBC. 13 December 2014. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- ↑ Johnston, Chris; Brooks, Libby (13 December 2014). "Jim Murphy is announced as leader of Scottish Labour party". The Guardian. Guardian Media Group. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- ↑ Brooks, Libby (2014-12-13). "Scottish Labour's new leader: we won't lose a single seat to the SNP". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Scottish Labour leadership split over Jeremy Corbyn". www.scotsman.com. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Scottish Labour figures urge Jeremy Corbyn to 'step aside'". BBC News. 2016-06-29. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Scottish Labour members call for Corbyn to go". 2016-06-29. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Over 200 Scottish Labour members call for Jeremy Corbyn resignation". Herald Scotland. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Majority of Labour MSPs say Corbyn should stand down". STV News. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Time for Corbyn to consider his position, say Labour MSPs | LabourList". 2016-07-01. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Unison and GMB set to consult members before fresh round of leadership endorsements | LabourList". 2016-08-02. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "GMB - GMB Scotland & Labour Leadership". www.gmb.org.uk. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "GMB Scotland will not ballot members on Labour leadership due to party "decline"". Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Momentum blast Jim Murphy after left-winger blocked from Labour ruling body". www.politicshome.com. 2016-06-01. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Blairite's 'dirty tricks' kick Wolfson out of NEC race". www.morningstaronline.co.uk. People's Printing Press Society. 2 June 2016. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ "Corbyn Supporter Blocked From NEC Election". 2016-06-01. Retrieved 2016-09-15.
- ↑ In addition, the party has 7,790 affiliated supporters (members of trade unions and socialist societies who opted to affiliate) and 3,285 registered supporters, making a total of about 30,000 members and supporters.[4][5]
External links
- The Scottish Labour Party official website
- Scottish Young Labour official website