Severny Island
| Native name: <span class="nickname" ">о́стров Се́верный | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Severny | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia |
| Coordinates | 75°30′N 60°00′E / 75.500°N 60.000°ECoordinates: 75°30′N 60°00′E / 75.500°N 60.000°E |
| Archipelago | Novaya Zemlya |
| Area | 48,904 km2 (18,882 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 30th |
| Administration | |
|
Russia | |
| Oblast | Arkhangelsk Oblast |
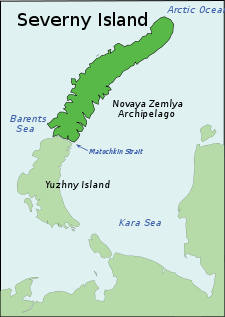
Severny Island (Russian: о́стров Се́верный, Northern Island) is the northern island of the Novaya Zemlya archipelago, lying approx 400 km north of the Russian mainland. It has an area of 48,904 square kilometres (18,882 sq mi), making it the 30th-largest island in the world.[1]
Geography
Severny Island is separated from Yuzhny Island (Southern) by the narrow Matochkin Strait. 40% of the island is covered by the Severny Island ice cap which is the largest glacier by area and by volume in Europe (if counted as part of it).[2] Severny Island is known for its numerous glaciers.[3] Cape Flissingsky is the easternmost point of Severny Island.
Ice cap and glaciers
Unlike Yuzhny Island, Severny has an inner ice cap with numerous glaciers, most of which have their terminus in the eastern or western shore of the island.[4]
 Terminus of Inostrantsev Glacier in the west coast. |
 View of Cape Zhelaniya |
History
Sukhoy Nos cape, located at the southern end of the island, was used for nuclear weapons testing between 1958 and 1961. The Tsar Bomba hydrogen bomb test destroyed all buildings in the village of Severny (both wooden and brick).[5] The village was located 55 kilometres (34 miles) from ground zero within the Sukhoy Nos test range. Tsar Bomba was the most powerful nuclear weapon detonated (October 30, 1961) and was the most powerful anthropogenic explosion in human history. It had a yield of 50 megatons of TNT although it was designed for a 100 megaton yield.[6] Severny is now the site of a Russian Army base and has a harbor.
There is a meteorological station at Cape Zhelaniya, Severny's northernmost cape.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Romanenko, F.; Shilovtseva, O. (1995). Russian-Soviet polar stations and their role in the Arctic Seas exploration..
- ↑ Zeeberg, J. J. "Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago". Russian Arctic: 82–84.
- ↑ Staalesen, Atle. "Børge Ousland heads for Novaya Zemlya". Barrents Observer. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- ↑ J. J. Zeeberg, Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic.
- ↑ "Big Ivan, The Tsar Bomba ("King of Bombs")". nuclearweaponarchive.org. Nuclear Weapon Archive. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ↑ Khalturin, Vitaly I.; Rautian, Tatyana G.; Richards, Paul G.; Leith, William S. (2005). "A Review of Nuclear Testing by the Soviet Union at Novaya Zemlya, 1955–1990" (PDF). Science and Global Security. 1 (13): 1–42. doi:10.1080/08929880590961862. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- ↑ Zeeberg, JaapJan; Floore, Pieter (2005). Into the Ice Sea: Barents' Wintering on Novaya Zemlya ; a Renaissance Voyage of Discovery. Netherlands: JaapJan Zeeberg and Rijksmuseum. ISBN 9789051707878. Retrieved 24 September 2016.