River Shannon
| River Shannon (Abhainn na Sionainne) | |
| River | |
 River Shannon from Drumsna bridge, County Leitrim | |
| Country | Ireland |
|---|---|
| Counties | Cavan, Leitrim, Roscommon, Longford, Offaly, Westmeath, Galway, Clare, Tipperary, Limerick, Kerry |
| Source | Shannon Pot |
| - location | Dowra, Cuilcagh Mountain, County Cavan |
| - elevation | 100 m (328 ft) |
| - coordinates | 54°14′06″N 7°55′12″W / 54.235°N 7.92°W |
| Mouth | Shannon Estuary |
| - location | Limerick |
| - coordinates | 52°39′25″N 8°39′36″W / 52.657°N 8.66°WCoordinates: 52°39′25″N 8°39′36″W / 52.657°N 8.66°W |
| Length | 360.5 km (224 mi) |
| Basin | 6,060 sq mi (15,695 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 208.1 m3/s (7,349 cu ft/s) |
The River Shannon (Irish: Abha na Sionainne / an tSionainn / an tSionna) is the longest river in Ireland at 360.5 km (224 miles).[1] It drains the Shannon River Basin which has an area of 16,865 km2 (6,512 sq mi),[2] one fifth of the area of Ireland.
The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster). County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception. The river represents a major physical barrier between east and west, with fewer than thirty crossing-points between Limerick city in the south and the village of Dowra in the north.
The river is named after Sionna, a Celtic goddess.[3]
The Shannon has been an important waterway since antiquity, having first been mapped by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy. The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the Atlantic Ocean through the 102.1 km (63.4 mi) long Shannon Estuary.[4] Limerick city stands at the point where the river water meets the sea water of the estuary. The Shannon is tidal east of Limerick as far as the base of the Ardnacrusha dam.[5]
Geography
By tradition the Shannon is said to rise in the Shannon Pot, a small pool on the slopes of Cuilcagh Mountain in County Cavan, from where the young river appears as a small trout stream. Surveys have defined a 12.8 km2 (4.9 sq mi) immediate pot catchment area covering the slopes of Cuilcagh. This area includes Garvah Lough, Cavan, 2.2 km (1.4 mi) to the northeast, drained by Pollnaowen.[n 1] Further sinks that source the pot include Pollboy and, through Shannon Cave, Pollahune in Cavan and Polltullyard and Tullynakeeragh in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland. The highest point in the catchment is a spring at Tiltinbane on the western end of the Cuilcagh mountain ridge.[6]
From the Shannon Pot, the river subsumes a number of tributaries before replenishing Lough Allen at its head.[7] The river runs through or between 11 of Ireland's counties, subsuming the tributary rivers Boyle, Inny, Suck, Mulkear and Brosna, among others, before reaching the Shannon Estuary at Limerick.
Many different values have been given for the length of the Shannon. A traditional value is 390 km (240 mi).[8] An official Irish source gives a total length of 360.5 km (224.0 mi) (being 258.1 km [160.4 mi] fresh and 102.1 km [63.4 mi] tidal).[4] Most Irish guides now give 344 km (214 mi).[9][10][11] Some academic sources give 280 km (170 mi),[12] although most will refuse to give a number. The reason is that there is no particular end to a river that empties into an estuary. The 344 km length relates to the distance between Shannon Pot and a line between Kerry Head and Loop Head, the furthest reaches of the land. (It also assumes the current shipping route via Ardnacrusha, which takes 7 km (4.3 mi) off the distance.) The 280 km distance finishes where the Shannon estuary joins the estuary of the River Fergus, close to Shannon Airport. Longer distances emerged before the use of modern surveying instruments.
At a total length of 360.5 km (224 miles), this means it is the longest river in Ireland.[11] That the Shannon is the longest river in the wider British Isles was evidently known in the 12th century, although a map of the time showed this river as flowing out of the south of Ireland.[13]
The River Shannon is a traditional freshwater river for about 45% of its total length. Excluding the 102 km (63 1⁄2 mi) tidal estuary from its total length of 360 km (224 mi), if one also excludes the lakes (L. Derg 39 km (24 mi), L. Ree 29 km (18 mi), L. Allen 11 km (7 mi)[14] plus L. Boderg, L. Bofin, L. Forbes, L. Corry) from the Shannon's freshwater flow of 258 km (160 1⁄2 mi), the Shannon, as a freshwater river, is only about 161 km (100 mi) long.
There are some tributaries within the Shannon River Basin which have headwaters that are further in length (from source to mouth) than the Shannon Pot source, such as the Owenmore River in County Cavan[15] and the Boyle River with its source in Mayo.[16]
Apart from being Ireland's longest river, the Shannon is also, by far, Ireland's largest river by flow. It has a long term average flow rate of 208.1 m3/s (7,350 cu ft/s) (at Limerick). This is double the flow rate of Ireland's second largest river, the River Corrib (104.8 m3/s [3,700 cu ft/s].[17] If the discharges from all of the rivers and streams into the Shannon Estuary (including the rivers Feale 34.6 m3/s [1,220 cu ft/s], Maigue 15.6 m3/s [550 cu ft/s], Fergus 25.7 m3/s [910 cu ft/s], and Deel 7.4 m3/s [260 cu ft/s])[18][19] are added to the discharge at Limerick, the total discharge of the River Shannon at its mouth at Loop Head reaches 300 m3/s (11,000 cu ft/s). Indeed, the Shannon is a major river by the time it leaves Lough Ree with an average flow rate (at Athlone weir) of 98 m3/s (3,500 cu ft/s),[20] larger than any of the other Irish river's total flow (apart from the River Corrib at Galway).
The Shannon Callows, areas of lowland along the river, are classified as a Special Area of Conservation.
Settlements along the river (going upriver) include Kilrush, Tarbert, Shannon Town, Limerick, Castleconnell, Killaloe, Ballina, Portumna, Banagher, Athlone, Lanesborough, Carrick-on-Shannon, Leitrim village and Dowra.
History and folklore

The river began flowing along its present course after the end of the last glacial period.
According to Irish mythology, the river was named after a woman named Sionann (older spelling: Sínann or Sínand), the granddaughter of Lir. She went to Connla's Well to find wisdom, despite being warned not to approach it. In some sources she, like Fionn mac Cumhaill, caught and ate the Salmon of Wisdom who swam there, becoming the wisest being on Earth. However, the well then burst forth, drowning Sionann and carrying her out to sea.[21] A similar tale is told of Boann and the River Boyne. It is believed that Sionann was the goddess of the river. Patricia Monaghan notes that "The drowning of a goddess in a river is common in Irish mythology and typically represents the dissolving of her divine power into the water, which then gives life to the land".[22]
The Shannon reputedly hosts a river monster named Cata, first appearing in the medieval Book of Lismore. In this manuscript we are told that Senán, patron saint of County Clare, defeated the monster at Inis Cathaigh.[23] Cata is described as a large monster with a horse's mane, gleaming eyes, thick feet, nails of iron and a whale's tail.[24]
Vikings settled in the region in 10th century and used the river to raid the rich monasteries deep inland. In 937 the Limerick Vikings clashed with those of Dublin on Lough Ree and were defeated.
In the 17th century, the Shannon was of major strategic importance in military campaigns in Ireland, as it formed a physical boundary between the east and west of the country. In the Irish Confederate Wars of 1641-53, the Irish retreated behind the Shannon in 1650 and held out for two further years against English Parliamentarian forces. In preparing a land settlement, or plantation after his conquest of Ireland Oliver Cromwell reputedly said the remaining Irish landowners would go to "Hell or Connacht", referring to their choice of forced migration west across the river Shannon, or death, thus freeing up the eastern landholdings for the incoming English settlers.
In the Williamite War in Ireland (1689–91), the Jacobites also retreated behind the Shannon after their defeat at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690. Athlone and Limerick, cities commanding bridges over the river, saw bloody sieges. (See Sieges of Limerick and Siege of Athlone).
As late as 1916, the leaders of the Easter Rising planned to have their forces in the west "hold the line of the Shannon". However, in the event, the rebels were neither well enough armed nor equipped to attempt such an ambitious policy.
The Shannon river is closely bound up with Ireland's social, cultural, military, economic and political history.
Navigation
.jpg)
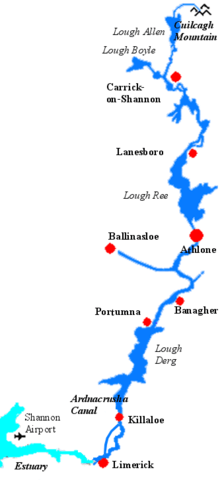

Though the Shannon has always been important for navigation in Ireland, there is a fall of only 18 m (59 ft) in the first 250 km (160 mi). Consequently, it has always been shallow with 0.5 m (1 ft 8 in) depths in various places. The first serious attempt to improve things came in 1755 when the Commissioners of Inland Navigation ordered Thomas Omer, a new, possibly Dutch immigrant from England, to commence work.[25] He tackled four places between Lough Derg and Lough Ree where natural navigation was obstructed, by installing lateral canals and either pound locks or flash locks. He then continued north of Lough Ree and made a number of similar improvements, most notably by creating the first Jamestown Canal which cut out a loop of the river between Jamestown and Drumsna as well lateral canals at Roosky and Lanesborough.
The lower Shannon between Killaloe and Limerick was a different story. Here the river falls by 30 m (98 ft) in only 20 km (12 mi). William Ockenden, also from England, was placed in charge of this in 1757 and spent £12,000 over the next four years without fully completing the task. In 1771 parliament handed over responsibility to the Limerick Navigation Company with a grant of £6,000 to add to their subscriptions of £10,000. A lateral canal 8 km (5 mi) long with six locks was started but the company needed more to complete it. In 1791, William Chapman was brought in to advise and discovered a sorry state of affairs. All the locks had been built to different dimensions and he spent the next three years rebuilding most of them. The navigation was finally opened in 1799, when over 1,000 long tons (1,000 tonnes) of corn came down to Limerick, as well as slates and turf. But even then, there were no tow paths in the river sections and there were still shoals in the summer months, no harbour facilities at Limerick and boats were limited to 15–20 long tons (15–20 tonnes) load, often less.
With the approaching opening of the Grand Canal, the Grand Canal Company obtained permission from the Directors General and asked John Brownrigg to do a survey which found that much of Omer's work had deteriorated badly, so they started repairs. After protracted negotiations on costs and conditions, the work was completed by 1810 so that boats drawing 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in) could pass from Athlone to Killaloe. Improvements on the lower levels were also undertaken, being completed by 1814.
When the Royal Canal was completed in 1817 there was pressure to improve the navigation above Lough Ree. The Jamestown Canal was repaired, harbours built and John Killaly designed a canal alongside the river from Battlebridge to Lough Allen which was opened in 1820.
In the latter part of the 1820s, trade increased dramatically with the arrival of paddle-wheeled steamers on the river which carried passengers and goods. By 1831 14,600 passengers and 36,000 long tons (37,000 tonnes) of freight were being carried. This put new pressure on the navigation and a commission was set up resulting in the Shannon Navigation Act of 1835 appointing five Commissioners for the improvement of navigation and drainage who took possession of the whole navigation. Over the next 15 years many improvements were made but in 1849 a railway was opened from Dublin to Limerick and the number of passengers fell dramatically. Freight, which had risen to over 100,000 long tons (100,000 tonnes) per year, was also halved.
But the work the commissioners carried out failed to solve the problems of flooding and there were disastrous floods in the early 1860s. Given the flat nature of most of the riverbank this was not easily addressed and nothing much was done till the twentieth century.
One of the first projects of the Irish Free State in the 1920s was the Shannon hydroelectric scheme which established the Ardnacrusha power station on the lower Shannon above Limerick. The old Killaloe to Limerick canal with its five locks was abandoned and the head race constructed from Lough Derg also served for navigation. A double lock was provided at the dam.
In the 1950s traffic began to fall and low fixed bridges would have replaced opening bridges but for the actions of the Inland Waterways Association of Ireland which persuaded the Tánaiste to encourage passenger launches, which kept the bridges high enough for navigation. Since then the leisure trade has steadily increased, becoming a great success story.
Canals

There are also many canals connecting with the River Shannon. The Royal Canal and the Grand Canal connect the Shannon to Dublin and the Irish Sea. It is linked to the River Erne and Lough Erne by the Shannon–Erne Waterway. Ballinasloe is linked to the Shannon via the River Suck and canal, while Boyle is connected via the Boyle canal, the river Boyle and Lough Key. There is also the Ardnacrusha canal connected with the Ardnacrusha dam south of Lough Derg. Near Limerick, a short canal connects Plassey with the Abbey River, allowing boats to bypass the Curraghower Falls, a major obstacle to navigation. Lecarrow village in County Roscommon is connected to Lough Ree via the Lecarrow canal. Jamestown Canal and the Albert Lock form a link between the River Shannon, from south of Jamestown, to Lough Nanoge to the south of Drumsna.
Economics

Despite being 360.5 km (224.0 mi) long, it rises only 76 m (249 ft) above sea level, so the river is easily navigable, with only a few locks along its length. There is a hydroelectric generation plant at Ardnacrusha belonging to the ESB.
Shipping in Shannon estuary was developed extensively during the 1980s, with over IR£2 billion (€2.5 billion) investment. A tanker terminal at Foynes and an oil jetty at Shannon Airport were built. In 1982 a large scale alumina extraction plant was built at Aughinish. 60,000 tonne cargo vessels now carry raw bauxite from West African mines to the plant, where it is refined to alumina. This is then exported to Canada where it is further refined to aluminium. 1985 saw the opening of a 915 MW coal-fired electricity plant at Moneypoint, fed by regular visits by 150,000 tonne bulk carriers.
Shannon eel management programme
A trap and transport scheme is in force on the Shannon as part of an eel management programme following the discovery of a reduced eel population. This scheme ensures safe passage for young eels between Lough Derg and the Shannon estuary.[26][27]
Fishing
Though the Shannon estuary fishing industry is now depleted, at one time it provided employment for hundreds of men along its length. At Limerick, fishermen based on Clancy's Strand used the Gandelow to catch Salmon.[28] In the 1920s the construction of a dam at Ardnacrusha severely impacted salmon breeding and that, and the introduction of quotas, had by the 1950s caused salmon fishing to cease.[29] However, recreational fishing still goes on. Further down the Shannon Estuary at Kilrush the Currach was used to catch herring as well as drift netting for salmon.
Water Extraction
Dublin City Council published a plan in 2011 to supply up to 350 million litres of water a day from Lough Derg to Dublin city and region. In 2016 the Parteen Basin to the south of lough was chosen as the proposed site of extraction. Water would be pumped to a break pressure tank Knockanacree near Cloughjordan in County Tipperary and gravity fed from there to Dublin. [30][31] [32] [33]
See also
- Shannon River Basin
- Shannon Airport
- Shannon Town
- Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
- Shannon Callows
- Rivers of Ireland
- List of loughs in Ireland
Notes
- ↑ Note Poll nm1: hole, pit, sink, leak, aperture (The Pocket Oxford Irish Dictionary - Irish-English)
References
- ↑ "Primary Seniors - Mountains, Rivers & Lakes". Ordnance Survey Ireland. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- ↑ Biology and Management of European Eel (Anguilla anguilla, L) in the Shannon Estuary, Ireland
- ↑ Mícheál O Súilleabháin. "Listening to difference: Ireland in a world of music". In Harry Bohan and Gerard Kennedy. Global aspirations and the reality of change.
- 1 2 "Facts". Ordnance Survey Ireland. Retrieved 2014-09-09.
- ↑ "Going through Ardnacrusha" (PDF). Inland Waterways News. IWAI (Summer 2001 - Volume 28 Number 2).
- ↑ Philip Elmer et al. Springs and Bottled Waters of the World Springer ISBN 3-540-61841-4
- ↑ The Shannon Guide
- ↑ Shannon. Encyclopedia Britannica. 1911.
- ↑ Delaney, Ruth (1996). Shell Guide to the River Shannon.
- ↑ "Cruising on the Shannon". Fodor.
- 1 2 "Nature & Scenery". Discover Ireland. Archived from the original on 2013-05-20.
- ↑ "Source of the River Shannon, Ireland". Environmental Geology. Springer. 27 (2): 110–112. Jan 31, 2005. doi:10.1007/BF01061681.
- ↑ Studia Hibernica. No.4. 1964 http://www.jstor.org/pss/20495797. (subscription required (help)). Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Ask about Ireland
- ↑ P. W. Joyce (1900). "Cavan". Atlas and Cyclopedia of Ireland. Murphy & McCarthy.
- ↑ Notes on River Basins: Page 64
- ↑ South Eastern River Basin Management: Page 38
- ↑ Long-term effects of hydropower installations and associated river regulation on River Shannon eel populations: mitigation and management
- ↑ SFPC Maintenance Dredging Application: Table 3-7
- ↑ Shannon Catchment-based Flood Risk Assessment and Management (CFRAM) Study P. 6
- ↑ Monaghan, Patricia. The Encyclopedia of Celtic Mythology and Folklore. Infobase Publishing, 2004. p.420
- ↑ Monaghan, p.27
- ↑ A Folklore Survey of County Clare: Supernatural Animals. Clarelibrary.ie. Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ↑ Cata The Monster of Shannon Waves : A true Story by Shane Mac Olon
- ↑ Ruth Delaney (2004). Ireland's Inland Waterways. Appletree Press.
- ↑ http://www.dcenr.gov.ie/nr/rdonlyres/3a6f7001-9bed-4fad-8e00-fbe2f7aea042/0/shirbd191208.pdf
- ↑ http://www.esb.ie/main/sustainability/eel-trap-and-transport.jsp
- ↑ McInerney, Jim (2005) "The Gandelow: a Shannon Estuary Fishing Boat" A.K. Ilen Company Ltd, ISBN 0-9547915-1-7
- ↑ Clare Traditional Boat and Currach Project 2008, http://www.clarelibrary.ie/eolas/coclare/heritage/pdfs/clare_traditional_boat_and_currach_project_2008.pdf
- ↑ http://www.watersupplyproject.ie/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/appendix_g_break_pressure_tank.pdf
- ↑ http://www.rte.ie/news/2008/0731/106457-water/
- ↑ http://www.limerickleader.ie/news/business/196725/Shannon-water-extraction-a-concern-for.html
- ↑ http://www.oireachtas.ie/parliament/media/committees/environmenttransportcultureandthegaeltacht/8november/River-Shannon-Protection-Alliance-Position-Paper.pdf
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to River Shannon. |
- Information, maps etc. on The Shannon Navigation (from Inland Waterways Association of Ireland)
- "River Shannon". Encyclopædia Britannica.