Sinzig
| Sinzig | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Sinzig Castle | ||
| ||
 Sinzig | ||
Location of Sinzig within Ahrweiler district 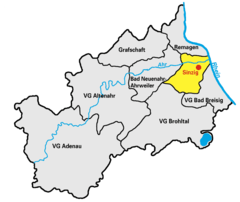
 | ||
| Coordinates: 50°32′43″N 7°15′07″E / 50.54528°N 7.25194°ECoordinates: 50°32′43″N 7°15′07″E / 50.54528°N 7.25194°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate | |
| District | Ahrweiler | |
| Government | ||
| • Stadtbürgermeister | Wolfgang Kroeger (CDU) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 41.02 km2 (15.84 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 17,330 | |
| • Density | 420/km2 (1,100/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 53489 | |
| Dialling codes | 02642, 02636 (Ortsteil Franken) | |
| Vehicle registration | AW | |
| Website | www.sinzig.de | |




Sinzig is a town in the district of Ahrweiler, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is situated on the river Rhine, about 5 km south-east of Remagen and 25 km south-east of Bonn, and it has approximately 20,000 inhabitants (2004).
History
Sinzig received its first official recognition in 762 A.D. On 10 July that year, King Pippin the Younger, the father of Charlemagne, presented a certificate of his decree in the Palace of Sinzig (Sentiaco Palacio), officially recognizing the town as "Sentiacum." Sinzig first received its rights as a town on 9 October 1267.
Because of the influence Emperor Frederick Barbarossa had on the town, it is nicknamed a "Barbarossa town".
Twice, the medieval town, which since 1300 has been protected by a massive wall, was almost entirely destroyed by fires, one in 1583 and another in 1758. Little of the wall now remains, as industrialization and urban development led to its nearly complete loss at the end of the 19th century. After World War II, Sinzig experienced a population explosion and soon evolved into an industrial town.
With the district reform of 1969, Bad-Bodendorf, Franken, Koisdorf, Löhndorf, and Westum became provinces of Sinzig. Today, Sinzig, together with the town of Remagen, have developed a modern consumer centre, with multiple schools and shopping centres.
Sightseeing
There is no point in the "Golden Mile" where the defining icon of Sinzig, the parish church of Saint Peter, cannot be seen. The late Roman Basilica is one of the most meaningful pieces of Roman architecture, reason enough for the church to be added to the United Nations' list of "World Culture Heritage" artifacts.
The Sinziger Schloss (Sinzig Castle) was built in the period of the Rhine Romantic. Between 1854 and 1858, a businessman, Gustav Bunge of Cologne, ordered the erection of a summer villa in Sinzig in the style of a neo-gothic palace. Surrounding the palace is a garden, constructed in the style of a Romantic park. The castle has now been turned into a museum.
Also worth seeing:
- Zehnthof
- remains of the Medieval town wall
- "Ahrmündung" Nature centre
Municipal subdivisions
- Sinzig
- Sinzig-Bad Bodendorf
- Sinzig-Westum
- Sinzig-Löhndorf (1997 Champion of the "Beautify our Town" Contest)
- Sinzig-Franken
- Sinzig-Koisdorf
Town song

- Heimattreue (Faith in the Homeland)
- Draußen im Lande ein Mädel ich fand,
- mit hellblondem Haar und feinzarter Hand
- und sie hat Augen so klar wie der Wein:
- sag Mädel die Heimat, sag bist du vom Rhein!
- sag Mädel die Heimat sag bist du vom Rhein!
- Refrain:
- Wo die Ahr zum Rhein hinfließt,
- heilend Wasser der Erd entsprießt,
- wo Mädchenaugen sind so blau,
- mitten in der goldnen Au.
- An dies Städtchen denk ich gern,
- bin ich denn auch noch so fern,
- an dich denk ich immer dar,
- Sinzig Rhein und Ahr.

- Ferne am Strande des weiten Meeres,
- steht eine Frau, schwer ist ihr ums Herz.
- Und sie singt leis` in die Wolken hinein:
- Grüßt mir die Heimat, mein Städtchen am Rhein!
- Grüßt mir die Heimat, mein Städtchen am Rhein!
- (Refrain)
- Schon Barbarossa hat Sinzig erkannt,
- als eines der schönsten Städtchen im Land.
- Und er befahl seinem Kaisertross:
- Wir rasten in Sinzig und wohnen im Schloss!
- Wir rasten in Sinzig und wohnen im Schloss!
- (Refrain)
References
- ↑ "Gemeinden in Deutschland mit Bevölkerung am 31. Dezember 2015" (PDF). Statistisches Bundesamt (in German). 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sinzig. |
- http://www.sinzig.de
- http://www.aktiplan-sinzig.de
- http://www.sinzig-loehndorf.de
- http://museum-sinzig.de
- http://www.sinziger-turmblaeser.de
- http://www.sinzig.org

