Skeletal system of the horse
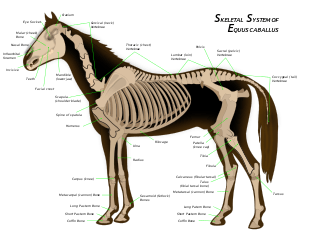
The skeletal system of the horse has three major functions in the body. It protects vital organs, provides framework, and supports soft parts of the body. Horses typically have 205 bones. The pelvic limb typically contains 19 bones, while the thoracic limb contains 20 bones.
Functions of bones
Bones serve three major functions in the skeletal system; they act as levers, they store minerals, and they are the site of red blood cell formation. Bones can be classified into five categories
- Long Bones: aid in locomotion, store minerals, and act as levers. They are found mainly in the limbs.
- Short Bones: Absorb concussion. Found in joints such as the knee, hock, and fetlock.
- Flat Bones: Enclose body cavities containing organs. The ribs are examples of flat bones.
- Irregular Bones: Protect the central nervous system. The vertebral column consists of irregular bones.
- Sesamoids: Bones embedded within a tendon. The horse's proximal digital sesamoids are simply called the "sesamoid bones" by horsemen, his distal digital sesamoid is referred to as the navicular bone.
Ligaments and tendons hold the skeletal system together. Ligaments hold bones to bones and tendons hold bones to muscles. Synovial membranes are found in joint capsules, where they contain synovial fluid, which lubricates joints. Bones are covered by a tough membrane called periosteum, which covers the entire bone excluding areas of articulation.
Ligaments
Ligaments attach bone to bone, and are vital in stabilizing joints as well as supporting structures. They are made up of fibrous material that is generally quite strong. Due to their relatively poor blood supply, ligament injuries generally take a long time to heal.
Ligaments of the upper body include:
- Nuchal and supraspinous ligaments: the nuchal ligament attaches to the dorsal surface of the cervical vertebrae. Its dorsal section extends from the occipital protuberance of the skull (the poll) to the withers, then narrows to become the supraspinous ligament. It also connects the 2-7th cervical vertebrae to the 1-3rd thoracic vertebrae. Its main purpose is to support the head and allow it to be moved upward or downward.
- Intercapital ligaments: lie between the first through eleventh ribs. Help to prevent thoracic disk herniation.
Ligaments of the legs include:
- Suspensory ligament: runs from the back of the cannon bone (between the two spint bones), then splits into two branches and attaches to the sesamoid bones at the bottom of the fetlock. Branches continue downward and attach to the extensor tendons. The main purpose of the suspensory is to support the fetlock joint, preventing it from overextending. Injury to this ligament is an important cause of lameness in performance horses. The suspensory is a modified muscle, the equine equivalent of the interosseous muscle, which contains both tendon fibers and residual muscle fibers.[1]
- Interosseous ligaments: connect the cannon bone to each splint bone. Injury to this ligament produces the condition known as "splints".
- Proximal and distal check ligaments: The proximal check ligament originates from the radius and attaches to the superficial digital flexor tendon. The distal check originates from the palmar carpal ligament and attaches to the deep digital flexor tendon, approximately 2/3-way down the metacarpus.
- Plantar ligament: in the hind leg, runs down the lateral side of the tarsus, attaches to the fibular, 4th tarsal, and 3rd metatarsal bones. Injury leads to a condition known as "curb."
- Inter-sesamoidean ligaments: supporting ligaments, run between the two sesamoid bones.
- Distal sesamoidean ligaments: run from the sesamoid bones to the two pastern bones. Important in the stay apparatus.
- Impar ligament: runs between the navicular bone and the 3rd phalanx.
- Annular ligament: goes around the back of the fetlock, surrounding the flexor tendons and their tendon sheath, attaching to the sesamoid bones. It helps to support the fetlock, and provides an enclosed "pulley" for the flexor tendons to run through.
- Sacrosciatic ligament: Originates from the sacrum and coccygeal vertebrae, inserts into the pelvis.
Axial skeleton

The axial skeleton contains the skull, vertebral column, sternum, and ribs. The sternum consists of multiple sternebrae, which fuse to form one bone, attached to the 8 "true" pairs of ribs, out of a total of 18.
The vertebral column usually contains 54 bones: 7 cervical vertebrae, including the atlas (C1) and axis (C2) which support and help move the skull, 18 (or rarely, 19) thoracic,[2] 5-6 lumbar, 5 sacral (which fuse together to form the sacrum), and 15-25 caudal[2] vertebrae with an average of 18. Differences in number may occur, particularly in certain breeds. For example, some, though not all, Arabians, may have 5 lumbar vertebrae, opposed to the usual 6, 17 thoracic vertebrae (and ribs) instead of 18, and 16 or 17 caudal vertebrae instead of 18. The withers of the horse are made up by the dorsal spinal processes of the thoracic vertebrae numbers 5 to 9.[3]
The skull consists of 34 bones and contains four cavities: the cranial cavity, the orbital cavity, oral, and the nasal cavity. The cranial cavity encloses and protects the brain and it supports several sense organs. The orbital cavitity surrounds and protects the eye. The oral cavity is a passage way into the respiratory and digestive systems. The nasal cavity leads into the respiratory system, and includes extensive paranasal sinuses. The nasal cavity contains turbinate bones that protect the mucous membrane that lines the cavity from warm inspired air. The skull consists of fourteen major bones
- Incisive bone (premaxillary): part of the upper jaw; where the incisors attach
- Nasal bone: covers the nasal cavity
- Maxillary bone: a large bone that contains the roots of the molars
- Mandible: lower portion of the jaw; largest bone in the skull
- Lacrimal bone: contains the nasolacrimal duct, which carries fluid from the surface of the eye, to the nose
- Frontal bone: creates the forehead of the horse
- Parietal bone: extends from the forehead to the back of the skull
- Occipital bone: forms the joint between the skull and the first vertebrae of the neck (the atlas)
- Temporal bone: contains the eternal acoustic meatus, which transmits sound from the ear to the cochlea (eardrum)
- Zygomatic bone: attaches to the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch (cheek bone)
- Palatine bone: forms the back of the hard palate
- Sphenoid: formed by fusion of the foetal basisphenoid and presphenoid bones, at the base of the skull. Can become fractured in horses that rear over backwards.
- Vomer: forms the top of the inside of the nasal cavity
- Pterygoid: small bone attached to the sphenoid that extends downward
Appendicular skeleton

The appendicular skeleton contains the fore and hindlimbs. The hindlimb attaches to the vertebral column via the pelvis, while the forelimb does not directly attach to the spine (as a horse does not have a collar bone), and is instead suspended in place by muscles and tendons. This allows great mobility in the front limb, and is partially responsible for the horse's ability to fold his legs up when jumping. Although the hindlimb supports only about 40% of the weight of the animal, it creates most of the forward movement of the horse, and is stabilized through attachments to the spine.
Important bones and joints of the forelimb
- Scapula (shoulder blade): flat bone with a large area of cartilage that partially forms the withers. The shoulder length and angle is very important to horsemen when evaluating conformation.
- Humerus: lies between the scapula and the radius, making an angle of about 55 degrees down and back. (Misspelled in the picture as "Humercus")
- Radius: extends from the elbow, where it articulates with the humerus, and travels downward to the carpus. It forms the "forearm" of the horse along with the ulna.
- Ulna: caudal to the radius, it is usually partially fused to that bone in an adult horse.
- Shoulder joint (scapulohumeral joint): usually has an angle of 120-130 degrees when the horse is standing, which can extended to 145 degrees, and flexed to 80 degrees (such as when the horse is jumping and obstacle).
- Elbow joint (humeroradial joint): hinge joint that can flex 55-60 degrees.
- Carpus (knee): consists of 7-8 bones placed in 2 rows to form 3 joints. The 1st carpal bone is present only 50% of the time. Which on humans is the wrist.
Important bones and joints of the hindlimb
- Pelvis: made up of the os coxae, the largest of the flat bones in a horse. It is made up of the ilium, the ischium, and the pubis. At the junction of these three bones is a cavity called the acetabulum, which acts as the socket of the hip joint. The pelvic cavity is larger in diameter in the mare than in the stallion, providing more room for the foal during birth.
- Femur: the largest long bone in a horse. Proximally it forms a ball-and-socket joint with the pelvis to form the hip joint, and distally it meets the tibia and patella at the stifle joint. It serves as an attachment point for the deep and middle glueteal muscles, and the accessory and round ligaments.
- Patella
- Tibia: runs from stifle to hock. The proximal end provides attachment for the patellar ligaments, meniscal ligaments, cruciate ligamnents, and collateral lligaments of the stifle. The distal end provides attachment for the collateral ligaments of the hock.
- Fibula: completely fused to the tibia in most horses.
- Hip joint : Ball-and-socket joint made up of the acetabulum of the pelvis and the femur. It is very stable.
- Stifle joint (femoropatellar joint): actually composed of three joint compartments: the femoropatellar joint, the medial femorotibial joint, and the lateral femorotibial joint, which are stabilized by a network of ligaments. The stifle has an articular angle of about 150 degrees.
- Tarsus (hock): consists of 6 bones (of which one is made up of the fused 1st and 2nd tarsal bones) aligned in 3 rows. The largest bone in the hock, the calcaneus or fibular tarsal bone, corresponds to the human heel, and creates the tuber calcis (point of hock). It is to this point that the tendon of the gastrocnemius, portions of the biceps femoris, and portions of the superficial digital flexor attach.
Bones of the lower limb
Bones of the lower limb, present in both the front and hind legs, include the cannon bone (3rd metacarpal/3rd metatarsal), splint bones (2nd and 4th metacarpal/metatarsal), proximal sesamoid bones, long pastern (proximal or 1st phalanx), short pastern (middle or 2nd phalanx), coffin bone (distal or 3rd phalanx), and navicular bone (distal sesamoid). There are usually slight differences in these bones when comparing the front and the hind. The 3rd metatarsal is about 1/6 longer than the 3rd metacarpal. Similarly, the 2nd and 4th metatarsals are longer in length when compared to their front-end counterpart. In the hindlimb, the 1st phalanx is shorter and the 2nd phalanx is longer than in the frontlimb. In addition, the 2nd and 3rd phalanx are narrower in the hind limb. The angle created by these three bones in the hindleg is steeper by about 5 degrees, therefore making the pastern angle steeper behind than in front.
Skeletal system disorders
- Arthritis (horse)
- Degenerative joint disease (DJD), such as bone spavin, ringbone, omarthritis
- Inflammatory joint disease such as Carpitis (sprained knee), osselets
- Bucked shins
- Curb
- Degenerative suspensory ligament desmitis (DSLD), and sprains of the suspensory ligament
- Fractures
- Locked kneecap (delayed patellar release or intermittent upward fixation of the patella)
- Navicular disease
- Osteochondrosis (horse)
- Sesamoiditis
- Splints
Joint disease in horses
Performance horses, like human athletes, place a high amount of stress on their bones and joints. This is especially true if the horse jumps, gallops, or performs sudden turns or changes of pace, as can be seen in racehorses, show jumpers, eventers, polo ponies, reiners, and western performance horses. A high percentage of performance horses develop arthritis, especially if they are worked intensely when young or are worked on poor footing.
Treatment of early joint disease often involves a combination of management and nutraceuticals. Intramuscular, intravenous, and intra-articular medications may be added as the disease progresses. Advanced therapies, such as Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Protein (IRAP) and stem cell treatments, are available for acute cases.
References
- ↑ The suspensory ligament
- 1 2 King, Christine, BVSc, MACVSc, and Mansmann, Richard, VMD, PhD. "Equine Lameness." Equine Research, Inc. 1997.
- ↑ Riegal, Ronald J. DVM, and Susan E. Hakola RN. Illustrated Atlas of Clinical Equine Anatomy and Common Disorders of the Horse Vol. II. Equistar Publication, Limited. Marysville, OH. Copyright 2000.
- Forney, Barbara C, MS, VMD.Equine Medications, Revised Edition. Blood Horse Publications. Lexington, KY. Copyright 2007.