Solar hybrid power systems
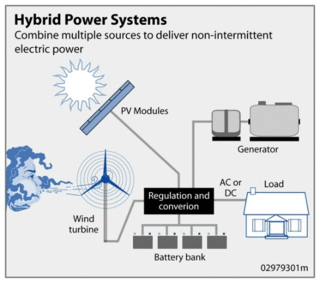
Solar hybrid power systems are hybrid power systems that combine solar power from a photovoltaic system with another power generating energy source.[1][2] A common type is a photovoltaic diesel hybrid system,[3][4] combining photovoltaics (PV) and diesel generators, or diesel gensets, as PV has hardly any marginal cost and is treated with priority on the grid. The diesel gensets are used to constantly fill in the gap between the present load and the actual generated power by the PV system.[2]
As solar energy is fluctuating, and the generation capacity of the diesel genesets is limited to a certain range, it is often a viable option to include battery storage in order to optimize solar's contribution to the overall generation of the hybrid system.[2][5]
The best business cases for diesel reduction with solar and wind energy can normally be found in remote locations because these sites are often not connected to the grid and transport of diesel over long distances is expensive.[1] Many of these applications can be found in the mining sector [6] and on islands [2][7][8]
In 2015, a case-study conducted in seven countries concluded that in all cases generating costs can be reduced by hybridising mini-grids and isolated grids. However, financing costs for diesel-powered electricity grids with solar photovoltaics are crucial and largely depend on the ownership structure of the power plant. While cost reductions for state-owned utilities can be significant, the study also identified short-term economic benefits to be insignificant or even negative for non-public utilities, such as independent power producers, given historical costs at the time of the study.[9][10]
Other solar hybrids include solar-wind systems. The combination of wind and solar has the advantage that the two sources complement each other because the peak operating times for each system occur at different times of the day and year. The power generation of such a hybrid system is more constant and fluctuates less than each of the two component subsystems.[11]
Gallery
-

Typical wind and solar hybrid system
-

Hybrid in Leh, India
-

Hybrid on Žirje, Croatia
-

Small wind and solar hybrid system
See also
References
- 1 2 Thomas Hillig (22 January 2015). "Renewables for the Mining Sector". decentralized-energy.com.
- 1 2 3 4 "Hybrid power plants (wind- or solar-diesel)". TH-Energy.net – A platform for renewables & mining. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- ↑ Thomas Hillig (24 February 2016). "Hybrid Power Plants". th-energy.net.
- ↑ Amanda Cain (22 January 2014). "What Is a Photovoltaic Diesel Hybrid System?". RenewableEnergyWorld.com.
- ↑ Kunal K. Shah, Aishwarya S. Mundada, Joshua M. Pearce. Performance of U.S. hybrid distributed energy systems: Solar photovoltaic, battery and combined heat and power. Energy Conversion and Management 105, pp. 71–80 (2015). DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.048
- ↑ http://www.th-energy.net/english/platform-renewable-energy-and-mining/database-solar-wind-power-plants/
- ↑ Thomas Hillig (January 2016). "Sun For More Than Fun". solarindustrymag.com.
- ↑ http://www.th-energy.net/english/platform-renewable-energy-on-islands/database-solar-wind-power-plants/
- ↑ "New study: Hybridising electricity grids with solar PV saves costs, especially benefits state-owned utilities". SolarServer.com. 31 May 2015.
- ↑ "Renewable Energy in Hybrid Mini-Grids and Isolated Grids: Economic Benefits and Business Cases". Frankfurt School – UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance. May 2015.
- ↑ "Hybrid Wind and Solar Electric Systems". energy.gov. DOE. 2 July 2012.
External links
- Wind, Solar, and Hybrid Plants used in the Mining Industry Project database "Renewables in Mining"
- Wind, Solar, and Hybrid Plants used on Islands Project database "Renewables on Islands"