Soviet integrated circuit designation

This article describes the nomenclature for integrated circuits manufactured in the Soviet Union. 25 years after the dissolution of the Soviet Union this designation is still used by a number of manufacturers in Russia, [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] Belarus, [34] [35] [36] Ukraine, [37] [38] [39] [40] Latvia, [41] [42] and Uzbekistan. [43] The designation uses the Cyrillic alphabet which sometimes leads to confusion where a Cyrillic letter has the same appearance as a Latin letter but is romanized as a different letter. Furthermore, for some Cyrillic letters the Romanization is ambiguous.
History
The nomenclature for integrated circuits has changed somewhat over the years as new standards were published:
- 1968 – NPO.034.000 (Russian: НПО.034.000) [44][45](pp19–23)
- 1973 – GOST 18682—73 (Russian: ГОСТ 18682—73) [45](pp19–23)
- 1980 – OST 11.073.915—80 (Russian: ОСТ 11.073.915—80) [46](pp10–16)[47]
- 2000 – OST 11.073.915—2000 (Russian: ОСТ 11.073.915—2000) [48]
- 2010 – GOST RV 5901-005—2010 (Russian: ГОСТ РВ 5901-005—2010) [49]
Throughout this article the standards are referred to by the year they came into force. Before 1968 each manufacturer used its own integrated circuit designation.[50][44]
In general, devices already in production when a new standard came out kept their old designation. However, in some case devices were renamed:
- When the 1980 standard was published, devices named after the 1968 standard and still in production were renamed, e.g. К1ЛБ553 to К155ЛА3.[44][51] As in this example, the renaming was often fairly straightforward: The two parts of the serial number were combined (1 and 55 to 155), the functional group remained unchanged or was converted as in the table below (ЛБ to ЛА), and the variant number remained unchanged (3). In some series the renaming was more complicated.[52] This change affected many series (e.g. 101, 116, 118, 122, 133, 140, 153, 155, 174, 237, 501).
- Before the introduction of a package designation in 1980 the suffix П (P) was used in some series to indicate a plastic package (as opposed to the then more common ceramic package). In 1983 the package designation was changed for the 531 series (e.g. К531ЛА19П to КР531ЛА19).[46](pp59–60) Other series were similarly renamed at some point (e.g. К501ХЛ1П to КР501ХЛ1).
- Before the definition of group В (V) in 1980 computing devices were all assigned subgroup ИК (IK), e.g. microprocessors (КР580ИК80А), peripheral devices (КР580ИК51А). With the introduction of group В the devices in the 580 series were renamed (to КР580ВМ80А and КР580ВВ51А, respectively) in 1986.
Structure of the designation
Structure (1968)

Structure (1973 / 1980)
.png)
Structure (2000)
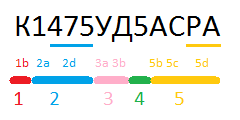
Elements:
- 1 – Prefix (zero to three letters)
- 1a – Export designation: The letter Э (E) here indicates an integrated circuit intended for export with a pin spacing of 2.54mm (1/10") or 1.27mm (1/20"). If this element is empty then the device has the Soviet (metric) spacing of 2.5mm or 1.25mm between pins.
- 1b – Application area: The letter К (K) here indicates an integrated circuit for commercial and consumer applications. If this element is empty then the device is intended for military or aero-space applications.
- 1c – Package designation (1980) (Note that the letters Э and К are not valid package designations. If this element is empty then the package is simply not specified in the designation, i.e. it could be any of the packages.)
- 2 – Series (three or four digits)
- 2a – Manufacturing technology (one digit):
- Monolithic integrated circuits: 1, 5, or 6
- Monolithic integrated circuits – bare chip without package: 7
- Hybrid integrated circuits: 2, 4, or 8
- Other integrated circuits (e.g. thin film): 3
- 2b – For four-digit series the second digit of the number of the series has significance as well:
- Series for household electronics: 0
- Series of analogue devices: 1
- Series of operational amplifiers: 4
- Series of digital devices: 5
- Series of memory devices: 6
- Series of microprocessor families: 8
- 2c – Number of the series (2 digits): The numbers of the series are assigned sequentially and have no further meaning. Devices in a series have some characteristic in common although it varies from one series to another which characteristic that is (e.g. logic family for logic gates, instruction set for microprocessors).
- 2d – Number of the series (2 or 3 digits): The 2000 standard does not assign a special meaning to the second digit of a 4-digit series.
- 2a – Manufacturing technology (one digit):
- 3 – Functional Group (two letters)
- 3a – Group
- 3b – Subgroup within the group: All groups have the subgroup П (P) for "others", that is for devices that fall into the group but not into any of the other defined subgroups.
- 4 – Variant within the functional subgroup (one to four digits): Usually the variant numbers are assigned sequentially for devices within the subgroup (e.g. ЛА1, ЛА2, ЛА3, etc.). In some series the variant number matches the last two or three digits of the designation of its Western counterpart (e.g. К500ЛК117 and MC10117).
- 5 – Suffix
- 5a – Version (one letter, А to Я except З and Й): This optional element indicates versions of an integrated circuit with different electrical or thermal characteristics (e.g. switching speed, voltage range, etc.). It can also indicate an improved version of a device (e.g. К580ИК80 vs. К580ИК80А). Before 1980 the suffix П (P) was sometimes used to indicate a version in a plastic package instead of a ceramic package (e.g. К145ИК2П, К531ЛА19П) or a round metal can (e.g. К144ИР1П).
- 5b – Version (one letter, А to М except З and Й)
- 5c – Package designation (2000) (one letter, Н to Я): If this element is empty then the package is simply not specified in the designation, i.e. it could be any of the packages. Note that the letter ranges for version and package designation do not overlap.
- 5d – Manufacturer designation (two letters)
Functional Groups
| Group | Description | Example[46][53][54] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian | English | 1968 | 1973 | 1980 | 2000 | Original | Equivalent |
| А | A | Pulse shapers and drivers | |||||
| АА | AA | — | Magnetic-core memory address current drivers | К170АА7 | SN75327 | ||
| АГ | AG | — | Square wave pulse shapers (including monostable multivibrators) | К555АГ4 | 74LS221 | ||
| АИ | AI | — | — | — | Time interval shaper (timer) | 1512АИ1У | |
| АН | AN | — | — | — | Voltage pulse shaper | ||
| АП | AP | — | Other pulse shapers (e.g. digital buffers including tri-state buffers, bubble memory drivers, CCD drivers) | 533АП5 | 54LS244 | ||
| АР | AR | — | Magnetic-core memory discharge current drivers | 146АР1 | |||
| АТ | AT | — | — | — | Current pulse shaper | ||
| АФ | AF | — | Pulse shapers for special waveforms | К174АФ5 | |||
| Б | B | Delay devices [lower-alpha 1] | Array of cells [lower-alpha 2] | ||||
| БА | BA | — | — | — | Array of analogue cells | Н1451БА1У-А502 | |
| БК | BK | — | — | — | Array of mixed signal cells | 1451БК2У | |
| БМ | BM | — | Passive delay device | — | |||
| БП | BP | — | Other delay device | Other array of cells (e.g. gate array plus processor) | К5512БП1Ф | ||
| БР | BR | — | Active delay device (e.g. bucket-brigade device) | — | КА528БР2 | ||
| БЦ | BTs, BC | — | — | — | Array of digital cells (gate array) | 5585БЦ1У | |
| В | V | Computing devices [lower-alpha 3] | |||||
| ВА | VA | — | — | Bus interface | КР580ВА86 | Intel 8286 | |
| ВБ | VB | — | — | Synchronization device (e.g. arbiter) | КР1810ВБ89 | Intel 8289 | |
| ВВ | VV | — | — | Input / output interface (e.g. serial or parallel interface) | КР580ВВ55А | Intel 8255 | |
| ВГ | VG | — | — | Controller (e.g. memory controller, video display controller) | КР1810ВГ88 | Intel 8288 | |
| ВЕ | VE | — | — | Single chip microcontroller | КМ1816ВЕ48 | Intel 8748 | |
| ВЖ | VZh | — | — | Specialized device (e.g. error correction circuit) | К1800ВЖ5 | Motorola MC10905 | |
| ВИ | VI | — | — | Timer device, real-time clock | КР580ВИ53 | Intel 8253 | |
| ВК | VK | — | — | Combined device (e.g. bus controller, GPIB controller) | КР580ВК28 | Intel 8228 | |
| ВМ | VM | — | — | Microprocessor [lower-alpha 4] | КР580ВМ80A | Intel 8080 | |
| ВН | VN | — | — | Programmable interrupt controller | КР580ВН59 | Intel 8259 | |
| ВП | VP | — | — | Other computing devices (e.g. gate array) | К1801ВП1 | ||
| ВР | VR | — | — | Extender for e.g. word size, number of ports, number of interrupt lines, available arithmetic operations (esp. a multiplier) | КМ1804ВР1 | AMD Am2902 | |
| ВС | VS | — | — | Microprocessor section, esp. bit-slice | КМ1804ВС1 | AMD Am2901 | |
| ВТ | VT | — | — | Memory controller | КР1804ВТ1 | AMD Am2964 | |
| ВУ | VU | — | — | Microcode control device | КР1804ВУ1 | AMD Am2909 | |
| ВФ | VF | — | — | Data transformation functions (calculation of e.g. CRC, Fourier transform) | 1815ВФ3 | ||
| ВХ | VKh, VX, VH | — | — | Devices for calculators | К145ВХ1 | ||
| ВЦ | VTs, VC | — | — | — | Digital signal processors [lower-alpha 4] | 1967ВЦ2Ф | ADSP-TS201 |
| ВЮ | VYu | — | — | — | Controller with analogue inputs and outputs | ||
| ВЯ | VYa | — | — | — | Digital signal processors with analogue inputs and outputs | 1879ВЯ1Я | |
| Г | G | Signal generators and oscillators | |||||
| ГГ | GG | — | Square wave generators (including astable multivibrators and blocking oscillators) | КР531ГГ1 | 74S124 | ||
| ГЛ | GL | — | Sawtooth wave generators (e.g. for CRT deflection circuits) | К174ГЛ1 | TDA1170 | ||
| ГМ | GM | — | Noise generators | ||||
| ГН | GN | — | — | — | Programmable signal generators | ||
| ГП | GP | — | Other signal generators | КМ1012ГП1 | MM5555 | ||
| ГС | GS | Sine wave generators (including harmonic oscillators) | К277ГС1 | ||||
| ГФ | GF | Signal generators for special waveforms (including generators for multiple waveforms) | К174ГФ2 | XR2206 | |||
| Д | D | Detectors and demodulators | |||||
| ДА | DA | Amplitude modulation detectors | К157ДА1 | ||||
| ДИ | DI | Pulse modulation detectors | |||||
| ДП | DP | Other detectors | К1230ДП46П | ||||
| ДС | DS | Frequency modulation detectors | К2ДС241 | ||||
| ДФ | DF | Phase modulation detectors | К1102ДФ1 | MC4044 | |||
| Е | E | Power supply devices | |||||
| ЕА | EA | — | — | — | Positive fixed voltage linear regulator | ||
| ЕВ | EV | — | Rectifiers | ||||
| ЕГ | EG | — | — | — | Negative adjustable voltage linear regulator | 1349ЕГ1У | LM137 |
| ЕД | ED | — | — | — | Dual-polarity symmetric fixed voltage linear regulator | ||
| ЕИ | EI | — | — | — | Negative fixed voltage linear regulator | 1343ЕИ5У | 7905 |
| ЕК | EK | — | — | Switched-mode power supply devices | К1156ЕК1АП | LM2596 | |
| ЕЛ | EL | — | — | — | Dual-polarity asymmetric fixed voltage linear regulator | ||
| ЕМ | EM | — | Electric power conversion devices (e.g. thyristor controller) | КР1182ЕМ2 | |||
| ЕН | EN | Linear voltage regulators | К142ЕН8А | 7808 | |||
| ЕП | EP | Other power supply devices (e.g. charge pump devices) | КР1168ЕП1 | ICL7660 | |||
| ЕР | ER | — | — | — | Positive adjustable voltage linear regulator | 1325ЕР1У | AMS1117 |
| ЕС | ES | — | — | Power supply systems (e.g. bandgap voltage reference) | 1369EC014 | AD780 | |
| ЕТ | ET | Constant current sources | УР1101ЕТ51 | TSM1051 | |||
| ЕУ | EU | — | — | Controller for switched-mode power supplies | КР1033ЕУ2 | TDA4605 | |
| Ж | Zh | Multi-functional devices [lower-alpha 5] | |||||
| ЖА | ZhA | Analog multi-functional devices | — | — | — | К2ЖА375 | |
| ЖЛ | ZhL | Digital multi-functional devices | — | — | — | К1ЖЛ551 | |
| И | I | Digital circuits | |||||
| ИА | IA | — | — | Arithmetic logic unit [lower-alpha 6] | 1815ИА1 | ||
| ИВ | IV | — | Encoder [lower-alpha 7] | 1564ИВ3 | 54HC147 | ||
| ИД | ID | Decoder | КР1564ИД4 | 74HC155 | |||
| ИЕ | IE | Counter | 1594ИЕ19 | 54ACT393 | |||
| ИК | IK | Combination of digital circuits [lower-alpha 3][lower-alpha 6] | К145ИК1807 | ||||
| ИЛ | IL | Half adder | К137ИЛ1 | ||||
| ИМ | IM | — | Full Adder [lower-alpha 8] | КР1594ИМ6 | 74ACT283 | ||
| ИН | IN | — | — | — | Interface receiver, transmitter, or transceiver | 5559ИН1Т | MAX232 |
| ИП | IP | Other digital circuits (e.g. parity bit checker, multiplier) [lower-alpha 6] | К155ИП3 | 74181 | |||
| ИР | IR | Register, shift register | К561ИР2 | 4015 | |||
| ИС | IS | Full Adder [lower-alpha 8] | — | — | — | ||
| ИФ | IF | — | — | — | Function expander (e.g. multiplier) | 1825ИФ1У | |
| ИШ | ISh | Encoder [lower-alpha 7] | — | — | — | К5ИШ011 | |
| К | K | Switches and Multiplexers | |||||
| КД | KD | Diode-based switch | — | — | — | ||
| КН | KN | — | Analogue switches and Multiplexers for voltages [lower-alpha 9] | КР590КН1 | |||
| КП | KP | Other switches and Multiplexers (especially digital; also optocouplers) | К561КП1 | 4052 | |||
| КТ | KT | Transistor-based switch | Analogue switches and Multiplexers for currents [lower-alpha 9] | К561КТ3 | 4066 | ||
| Л | L | Logic gates | |||||
| ЛА | LA | — | — | NAND gates [lower-alpha 10] | К155ЛА3 | 7400 | |
| ЛБ | LB | NAND gates and NOR gates [lower-alpha 10] | 134ЛБ1 | ||||
| ЛД | LD | — | Expander [lower-alpha 11] | 133ЛД1 | 5460 | ||
| ЛЕ | LE | — | — | NOR gates [lower-alpha 10] | 530ЛЕ1 | 54S02 | |
| ЛИ | LI | AND gates | КР531ЛИ3 | 74S11 | |||
| ЛК | LK | AND-OR-NOT/AND-OR gates [lower-alpha 12] | 199ЛК3 | ||||
| ЛЛ | LL | OR gates | 533ЛЛ1 | 54LS32 | |||
| ЛМ | LM | — | — | OR-NOT/OR gates | К500ЛМ101 | Motorola MC10101 | |
| ЛН | LN | NOT gates | К555ЛН1 | 74LS04 | |||
| ЛП | LP | Expander [lower-alpha 11] | Other gates (e.g. XOR gates, majority function gates) [lower-alpha 13] | 1531ЛП5 | 54F86 | ||
| ЛР | LR | AND-OR-NOT gates | КР1531ЛР11 | 74F51 | |||
| ЛС | LS | AND-OR gates [lower-alpha 12] | К561ЛС2 | 4019 | |||
| ЛЭ | LE | Other gates [lower-alpha 13] | — | — | — | К1ЛЭ941 | |
| М | M | Modulators | |||||
| МА | MA | Amplitude modulators (e.g. ring modulator) | КР140МА1 | ||||
| МИ | MI | Pulse modulators | К854МИ1 | ||||
| МП | MP | Other modulators | |||||
| МС | MS | Frequency modulators | |||||
| МФ | MF | Phase modulators | К1327МФ1У | ||||
| Н | N | Arrays of electronic components | |||||
| НД | ND | Diode array | К142НД3 | ||||
| НЕ | NE | Capacitor array | 2НЕ601 | ||||
| НК | NK | Array with a combination of components | К217НК1 | ||||
| НП | NP | — | Array of other components | ||||
| НР | NR | — | Resistor array [lower-alpha 14] | К318НР1 | |||
| НС | NS | Resistor array [lower-alpha 14] | — | — | — | 3НС011А | |
| НТ | NT | Transistor array | КР198НТ9 | ||||
| НФ | NF | — | — | Array with a specific function (e.g. resistor ladder) | 317НФ1 | ||
| П | P | Signal converters | |||||
| ПА | PA | — | Digital-to-analogue converter [lower-alpha 15] | КР572ПА7 | AD7541 | ||
| ПВ | PV | — | Analogue-to-digital converter [lower-alpha 16] | Н572ПВ3А | AD7574 | ||
| ПД | PD | Digital-to-analogue converter [lower-alpha 15] | Pulse duration converter | К1102ПД1 | |||
| ПЕ | PE | — | — | Analogue frequency multiplier | |||
| ПК | PK | Analogue-to-digital converter [lower-alpha 16] | — | Analogue frequency divider | К1055ПК1Т1 | ||
| ПЛ | PL | — | — | Frequency synthesizer | КР1508ПЛ1 | NJ88C30 | |
| ПМ | PM | Signal shape converter | Power converter | КР1446ПМ1 | |||
| ПН | PN | Voltage converter | Voltage or current converter | К252ПН1 | |||
| ПП | PP | Other converter (including photovoltaic optocouplers) | КР572ПП2 | ICL7104 | |||
| ПР | PR | — | Code converter | К155ПР7 | 74185 | ||
| ПС | PS | Frequency converter (includig frequency mixers, analog multipliers) | К174ПС4 | ||||
| ПУ | PU | Signal level converter (including impedance matching, logic voltage level shifters) | К561ПУ4 | 4050 | |||
| ПФ | PF | Phase converter | — | — | 5862ПФ1Н4 | ||
| ПЦ | PTs, PC | — | — | Digital frequency divider | К555ПЦ1 | 74LS292 | |
| Р | R | Memory devices [lower-alpha 17] | |||||
| РА | RA | — | — | Associative memory | К589РА04 | Intel 3104 | |
| РВ | RV | — | Matrix of ROM elements (e.g. Diode matrix) | К539РВ1А | |||
| РГ | RG | — | — | — | FIFO [lower-alpha 18] | 1642РГ1РБМ | IDT7205L |
| РД | RD | — | — | — | DRAM [lower-alpha 19] | 1654РД2 | MT48LC4M16A2P |
| РЕ | RE | — | ROM (including PROM) [lower-alpha 20] | Mask ROM [lower-alpha 20] | К155РЕ21 | 74187 | |
| РК | RK | — | — | — | Multi-ported RAM (e.g. dual-ported RAM) [lower-alpha 18] | 1642РК1УБМ | IDT7005 |
| РМ | RM | — | Matrix of RAM elements | К188РМ1 | |||
| РН | RN | — | — | — | NVRAM | ||
| РП | RP | — | Other memory devices (e.g. dual-ported RAM) [lower-alpha 18] | Other memory devices | К1800РП6 | Motorola MC10806 | |
| РР | RR | — | — | EEPROM [lower-alpha 20] | EEPROM or Flash memory with a parallel interface [lower-alpha 21] | КМ1609РР1 | 2816 |
| РС | RS | — | — | — | EEPROM or Flash memory with a serial interface [lower-alpha 21] | 1644PC1ATБM | 24FC65 |
| РТ | RT | — | — | PROM [lower-alpha 20] | 530РТ1 | 54S287 | |
| РУ | RU | — | RAM (DRAM or SRAM) | SRAM [lower-alpha 19] | КР537РУ16А | 6264 | |
| РФ | RF | — | — | EPROM [lower-alpha 20] | К573РФ8А | 27256 | |
| РЦ | RTs, RC | — | — | Bubble memory | К1602РЦ2А | ||
| С | S | Comparators | |||||
| СА | SA | Amplitude (signal level) comparator [lower-alpha 22] | Voltage comparator | К1401СА1 | LM339 | ||
| СВ | SV | Timing comparator | К2СВ381 | ||||
| СК | SK | — | — | Amplitude (signal level) comparator (including sample-and-hold circuits)[lower-alpha 22] | КР1100СК3 | LF398 | |
| СП | SP | — | Other comparator (especially digital comparator) | Other comparator | К555СП1 | 74LS85 | |
| СС | SS | Frequency comparator | К284СС2А | ||||
| СФ | SF | Phase comparator | — | — | |||
| СЦ | STs | — | — | — | Digital comparator | ||
| Т | T | Triggers / Flip-Flops | |||||
| ТВ | TV | — | JK flip-flops | 1533ТВ6 | 54ALS107 | ||
| ТД | TD | Dynamic flip-flops | |||||
| ТК | TK | Combination of triggers / flip-flops | КР501ТК1 | ||||
| ТЛ | TL | — | Schmitt triggers [lower-alpha 23] | КР1533ТЛ2 | 74ALS14 | ||
| ТМ | TM | — | D flip-flops | 1554ТМ2 | 54AC74 | ||
| ТП | TP | — | Other triggers / flip-flops | ||||
| ТР | TR | RS flip-flops | КР1554ТР2 | 74AC279 | |||
| ТС | TS | T flip-flops [lower-alpha 24] | — | — | — | К2ТС241 | |
| ТТ | TT | — | T flip-flops [lower-alpha 24] | ||||
| ТШ | TSh | Schmitt triggers [lower-alpha 23] | — | — | — | К1ТШ221В | |
| У | U | Amplifiers | |||||
| УБ | UB | Video amplifier | — | — | — | К1УБ181Б | |
| УВ | UV | — | Radio frequency (high frequency) amplifier | 171УВ2 | μA733 | ||
| УГ | UG | — | — | — | Low-noise amplifier | ||
| УД | UD | — | Operational amplifier or Differential amplifier [lower-alpha 25] | Operational amplifier | КР140УД7 | μA741 | |
| УЕ | UE | — | Unity gain buffer (e.g. emitter follower) [lower-alpha 26] | КР1436УЕ1 | |||
| УИ | UI | Pulse amplifier | КР1054УИ1 | TBA2800 | |||
| УК | UK | — | — | Wideband amplifier (e.g. video amplifier) | К174УК1 | TCA660 | |
| УЛ | UL | — | Read amplifier (e.g. for magnetic core memory, magnetic tape, magnetic disks) | КР1075УЛ1 | TA7784P | ||
| УМ | UM | — | Indicator amplifier | 564УМ1 | 4054 | ||
| УН | UN | — | Audio frequency (low frequency) amplifier | КР1438УН2 | LM386 | ||
| УП | UP | — | Other amplifier (e.g. log amplifier, limiter, gyrator) | 174УП2 | TL441CN | ||
| УР | UR | — | Intermediate-Frequency (IF) amplifier | К174УР12 | TDA4420 | ||
| УС | US | Sine wave amplifier | — | Differential amplifier [lower-alpha 25] | К157УС1 | ||
| УТ | UT | DC amplifier | КР119УТ1 | ||||
| УЭ | UE | Unity gain buffer (e.g. emitter follower) [lower-alpha 26] | — | — | — | К2УЭ182 | |
| Ф | F | Filters | |||||
| ФА | FA | — | — | — | Adaptive filter | ||
| ФБ | FB | — | — | — | Band-pass filter [lower-alpha 27] | ||
| ФВ | FV | High-pass filter | 528ФВ1 | ||||
| ФЕ | FE | — | Band-pass filter [lower-alpha 27] | — | 811ФЕ1 | ||
| ФМ | FM | — | — | — | Programmable filter | ||
| ФН | FN | Low-pass filter | И1146ФН1 | ||||
| ФП | FP | Band-pass filter [lower-alpha 27] | Other filter | КР1146ФП1 | MK5912 | ||
| ФР | FR | — | Band-stop filter [lower-alpha 28] | ||||
| ФС | FS | Band-stop filter [lower-alpha 28] | — | — | — | ||
| ФУ | FU | — | — | — | Universal filter | 1478ФУ1Т | MAX274 |
| Х | Kh, X, H | Multi-functional devices [lower-alpha 5] | |||||
| ХА | KhA, XA, HA | — | Analog multi-functional devices | КР1568ХА3 | TDA4555 | ||
| ХБ | KhB, XB, HB | — | — | — | Multifunctional device for radio, television, tape recorders, displays | К1879ХБ1Я | |
| ХВ | KhV, XV, HV | — | — | — | Multi-functional device for automotive electronics | К1323ХВ1Р | L497B |
| ХД | KhD, XD, HD | — | — | — | Multi-functional device for telecommunications | 1892ХД1Я | |
| ХИ | KhI, XI, HI | — | — | — | Array of analogue cells | ||
| ХК | KhK, XK, HK | — | Mixed signal multi-functional devices | КР1051ХК1 | TDA8432 | ||
| ХЛ | KhL, XL, HL | — | Digital multi-functional devices | КР1568ХЛ2 | TDA3048 | ||
| ХМ | KhM, XM, HM | — | — | Array of digital cells (gate array) [lower-alpha 2] | — | 1515ХМ1 | |
| ХН | KhN, XN, HN | — | — | Array of analogue cells [lower-alpha 2] | — | Н1451ХН3-А502 | |
| ХП | KhP, XP, HP | — | Other multi-functional devices (e.g. programmable logic devices) | Other multi-functional devices | КР1556ХП4 | PAL16R4 | |
| ХР | KhR, XR, HR | — | — | — | Multi-functional circuit for household devices | К1331ХР1П | |
| ХС | KhS, XS, HS | — | — | — | Programmable logic devices | 5577ХС2Т | Actel RH1020 |
| ХТ | KhT, XT, HT | — | — | Array of mixed signal cells [lower-alpha 2] | — | 5515ХТ1У | |
| ХХ | KhKh, XX, HH | — | — | — | Multi-functional devices for power electronics | 1474ХХ3Т | HCPL316J |
| Ц | Ts, C | Charge-coupled device image sensors | |||||
| ЦЛ | TsL, CL | — | — | One-dimensional (linear) image sensor | 1200ЦЛ3 | CCD131 | |
| ЦМ | TsM, CM | — | — | Two-dimensional image sensor | К1200ЦМ1 | CCD211 | |
| ЦП | TsP, CP | — | — | Other image sensor | |||
| Ч | Ch | Transducers / Sensors | |||||
| ЧВ | ChV | — | — | — | Humidity sensor | ||
| ЧГ | ChG | — | — | — | Gas sensor | ||
| ЧД | ChD | — | — | — | Pressure sensor | К1245ЧД1Н3 | |
| ЧИ | ChI | — | — | — | Ionizing radiation sensor | ||
| ЧМ | ChM | — | — | — | Mechanical displacement sensor | ||
| ЧП | ChP | — | — | — | Other sensor | ||
| ЧТ | ChT | — | — | — | Temperature sensor | 1019ЧТ4У | LM135 |
| ЧЭ | ChE | — | — | — | Electromagnetic field sensor | ||
| Э | E | Delay devices [lower-alpha 1] | |||||
| ЭМ | EM | — | — | — | Passive delay device | ||
| ЭП | EP | — | — | — | Other delay device | ||
| ЭР | ER | — | — | — | Active delay device (e.g. bucket-brigade device) | ||
| Я | Ya | Memory devices [lower-alpha 17] | |||||
| ЯП | YaP | Memory element (RAM or ROM) | — | — | — | K5ЯП011 | |
| ЯМ | YaM | Matrix of memory elements (RAM or ROM) | — | — | — | К1ЯМ411 | |
- 1 2 In 2000 group Б was moved to Э. Unfortunately, this makes some transcriptions ambiguous since both Е and Э are transcribed as E.
- 1 2 3 4 In 2000 all arrays of cells were moved from group Х to group Б. Subgroup ХМ became БЦ, ХН became БА, and ХТ became БК.
- 1 2 Before the definition of group В (V) in 1980 computing devices were all assigned subgroup ИК (IK), e.g. microprocessors (КР580ИК80А), peripheral devices (КР580ИК51А). With the introduction of group В the devices in the 580 series were renamed (to КР580ВМ80А and КР580ВВ51А, respectively) in 1986.
- 1 2 Initially digital signal processors were assigned subgroup ВМ (VM, e.g. 1867ВМ2). In 2000 the new subgroup ВЦ (VTs) was added (e.g. 1867ВЦ2АТ).
- 1 2 In 1973 group Ж was replaced with group Х.
- 1 2 3 Before the introduction of subgroup ИА in 1980, many ALU devices had already been assigned subgroups ИК (e.g. КР531ИК2) or ИП (e.g. К155ИП3, 564ИП3, КР1530ИП14).
- 1 2 In 1973 encoders were moved from subgroup ИШ to subgroup ИВ.
- 1 2 In 1973 full adders were moved from subgroup ИС to subgroup ИМ.
- 1 2 The distinction between voltage switches (КН) and current switches (КТ) is somewhat unclear. There are analogue switches and multiplexers in both subgroups.
- 1 2 3 With the introduction of subgroups ЛА and ЛЕ in 1980 most devices from subgroup ЛБ were re-labelled (e.g. К1ЛБ553 to К155ЛА3). It appears that subgroup ЛБ was kept in the standard for devices from subgroup ЛБ that fit neither in ЛА nor in ЛЕ (e.g. 134ЛБ2 with 2 NAND gates and 1 NOT gate).
- 1 2 In 1973 expander circuits were moved from subgroup ЛП to subgroup ЛД.
- 1 2 All known ECL devices in subgroup ЛК are listed as OR-AND-NOT instead of AND-OR-NOT.[46](p90)[53] The equivalent Motorola devices (e.g. Motorola MC10117 for К500ЛК117) are also listed as OR-AND-NOT. Similarly, ECL devices in subgroup ЛС are listed as OR-AND instead of AND-OR (e.g. К500ЛС118, equivalent to Motorola MC10118).
- 1 2 In 1973 the catch-all subgroup ЛЭ was moved to ЛП.
- 1 2 In 1973 resistor arrays were moved from subgroup НС to subgroup НР.
- 1 2 In 1973 D/A converters were moved from subgroup ПД to subgroup ПА.
- 1 2 In 1973 A/D converters were moved from subgroup ПК to subgroup ПВ.
- 1 2 In 1973 group Я was replaced with group Р.
- 1 2 3 Initially FIFO and multi-port devices were included in subgroup РП. In 2000 they were assigned the separate subgroups РГ and РК, respectively.
- 1 2 In 2000 subgroup РУ was split into РУ and РД, with РУ from then on limited to SRAM.
- 1 2 3 4 5 In 1980 subgroup РЕ was split into РЕ, РР, РТ, and РФ, with РЕ from then on limited to mask ROM.
- 1 2 Initially subgroup РР was used for all EEPROM and Flash devices, regardless of the interface. In 2000 subgroup РС was introduced for devices with a serial interface and subgroup РР was limited to devices with a parallel interface.
- 1 2 In 1980 amplitude comparators were moved from subgroup СА to subgroup СК.
- 1 2 In 1973 Schmitt triggers were moved from subgroup ТШ to subgroup ТЛ.
- 1 2 In 1973 T flip-flops were moved from subgroup ТС to subgroup ТТ.
- 1 2 In 1980 differential amplifier were moved out of subgroup УД into their own subgroup УС.
- 1 2 In 1973 unity gain buffers were moved from subgroup УЭ to subgroup УЕ.
- 1 2 3 In 1973 band-pass filters were moved from subgroup ФП to subgroup ФЕ, and then in 2000 to subgroup ФБ.
- 1 2 In 1973 band-stop filters were moved from subgroup ФС to subgroup ФР.
Packages
Package designation (1973)
The package of an integrated circuit was generally not indicated in the 1973 designation, with two exceptions:
- Bare chips without a package received a series number in the 7xx range, e.g. K712RV2-1 (К712РВ2-1).
- The suffix П (P) was sometimes used to indicate a version in a plastic package instead of a ceramic package (e.g. К145ИК2П, К531ЛА19П) or a round metal can (e.g. К144ИР1П).
Package designation (1980)
| Package | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Russian | English | |
| А | A | Plastic Flatpack |
| Б | B | Bare chip without package |
| Е | E | Metall-polymer dual in-line package (DIP) |
| И | I | Glass-ceramic Flatpack |
| Л | L | Pin grid array (PGA) or ball grid array (BGA) |
| М | M | Metall-ceramic dual in-line package (DIP) |
| Н | N | Ceramic leadless chip carrier |
| Р | R | Plastic dual in-line package (DIP) |
| С | S | Glass-ceramic dual in-line package (DIP) |
| Ф | F | Small outline package |
Package designation (2000)
| Package | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Russian | English | |
| Н | N | Bare chip without package |
| П | P | Single in-line package (SIP), Zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) |
| Р | R | Dual in-line package (DIP) |
| С | S | Round metal can package |
| Т | T | Flatpack, Small outline package (SOP), Quad Flat Package (QFP) |
| У | U | Chip carrier |
| Ф | F | Pin grid array (PGA) |
| Я | Ya | Ball grid array (BGA) |
Manufacturer designation
A manufacturer designation was introduced only with the 2000 standard. The table below is incomplete, many manufacturers still do not use their assigned designation. Manufacturer logos[55] are more common.
| Designation | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|
| Russian | English | |
| АМ | AM | Angstrem, Zelenograd, Russia[1] |
| АР | AR | AS Alfa, Riga, Latvia[42] |
| БМ | BM | OAO "Integral", Minsk, Belarus[34] |
| ВК | VK | AO "Voshod", Kaluga, Russia[28] |
| ИМ | IM | "Transistor" branch of OAO "Integral", Minsk, Belarus[35] |
| МК | MK | ZAO "OKB MEL", Kaluga, Russia[29] |
| ММ | MM | OAO "NIIME and Mikron", Moscow, Russia[56] |
| НИ | NI | MVC, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia[27] |
| НН | NN | AO "NZPP", Novosibirsk, Russia[19] |
| НТ | NT | AO "NIIPP", Tomsk, Russia[21] |
| РА | RA | RD Alfa, Riga, Latvia[41] |
| СП | SP | ZAO Svetlana Semiconductors, Saint Petersburg, Russia[17] |
| ЭВ | EV | OAO "VZPP-S", Voronesh, Russia[6] |
| ЭП | EP | OAO "Exiton", Moscow, Russia[10] |
Romanization
The Romanization of Russian is standardized, only there are at least 11 standards to choose from. Fortunately, the Soviet integrated circuit designation uses a subset of the Cyrillic alphabet where rather few letters are ambiguous:
- Ж: Ž, Zh
- Х: X, H, Ch, Kh
- Ц: C, Cz, Ts, Tc
- Ч: Č, Ch
The more common romanizations in bold are given as alternatives in the above tables.
Е and Э are both romanized as E.
It should be noted that the French romanization of Russian and the German romanization of Russian differ in some letters from the one used in English. For instance, the Russian КР580ВМ80A becomes KR580VM80A in English and French but KR580WM80A in German literature.
See also
- List of Soviet microprocessors
- Commons:Gallery of Soviet integrated circuits
- 7400 series – Second sources in Europe and the Eastern Bloc
- List of 7400 series integrated circuits
- Pro Electron – Integrated circuits
References
- 1 2 "Продукты" [Products] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- ↑ "Микроэлектронные компоненты" [Microelectronic components] (in Russian). NTC Module. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
- ↑ "Микропроцессоры и СБИС" [Microprocessors and VLSI] (in Russian). Moscow: MCST. Retrieved 11 April 2016.
- ↑ "Микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Elvees Multicore. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
- ↑ "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "NIIET". Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- 1 2 "Каталог изделий" [Product catalog] (PDF) (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "VZPP-S". Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "ОСВОЕННЫЕ МИКРОСХЕМЫ" [Integrated circuits in production] (in Russian). Voronesh: OAO "SKTB ES". Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ↑ "Номенклатура" [Nomenclature] (PDF) (in Russian). Zelenograd: PKK Milandr. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ↑ "АО "НИИТАП"" [AO "NIITAP"] (in Russian). Zelenograd: AO "NIITAP". Retrieved 28 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Moscow: OAO "Exiton". Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Moscow: OAO NPO "Fizika". Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ↑ "Электронные компоненты" [Electronic components] (in Russian). Moscow: AO "Optron". Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Moscow: PAO NPP "Sapfir". Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Moscow: OAO NPP "Pulsar". Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ↑ "Микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Moscow: NPK "TTs". Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ "БИС и СБИС" [LSI and VLSI] (in Russian). Moscow: AO NIIMA "Progress". Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Каталог продукции" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: ZAO Svetlana Semiconductors. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "Оптроны и твердотельные реле" [Optocouplers and solid state relays] (in Russian). Oryol: OAO "Proton". Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- 1 2 "ПРОДУКЦИЯ" [Products] (in Russian). Novosibirsk: AO NZPP. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "ПРОДУКЦИЯ" [Products] (in Russian). Novosibirsk: AO "NPP Vostok". Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Каталог продукции" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Tomsk: AO "NIIPP". Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Интегральные микросхемы для техники специального назначения" [Integrated circuits for special-purpose machinery] (in Russian). Saransk: AO "Orbita". Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- ↑ "КАТАЛОГ ИЗДЕЛИЙ" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Bryansk: ZAO Kremny Marketing. Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- ↑ "Каталог" [Catalog] (in Russian). Bryansk: ZAO "NTTs SIT". Retrieved 27 June 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Nalchik: OAO "NZPP-KBR" (former "Elkor"). Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Novgorod: OAO "OKB-Planeta". Retrieved 5 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Nishny Novgorod: MVC. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Kaluga: AO "Voshod". Retrieved 8 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Kaluga: ZAO "OKB MEL". Retrieved 12 June 2016.
- ↑ "Новые разработки" [New developments] (in Russian). Ulyanovsk: AO "NPP Iskra". Retrieved 8 June 2016.
- ↑ "Тонкопленочные наборы резисторов, ГИС ЦАП и АЦП ВТ на их основе" [Thin film resistors sets, hybrid integrated DAC and ADC based on them] (in Russian). Penza: OAO "NIIEMP". Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- ↑ "Микросхемы серии 301" [Integrated circuit series 301] (in Russian). Kotovsk: OAO "Almaz". Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- ↑ "Микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Tomilino: OAO NPP "Eltom". Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Minsk: OAO "Integral". Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Minsk: "Transistor" branch of OAO "Integral". Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Minsk: OOO "NTTs DELS". Retrieved 28 June 2016.
- ↑ "ПРОДУКЦИЯ И ЦЕНЫ" [Products and prices] (in Russian). Kiev: DP "Kvazar-IS". Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products] (in Russian). Kiev: OOO "NPO Kristall". Retrieved 15 June 2016.
- ↑ "Каталог товаров" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Ivano-Frankivsk: TOV TD "Elektronni komponenti" (former "Rodon" and "Logika"). Retrieved 15 June 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция предприятия" [The company's products] (in Russian). Kherson: DP "Dnepr Semiconductors". Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- 1 2 "Каталог товаров" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Riga: RD Alfa. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Аннотация продукции АО "Альфа"" [Abstract of products from AS Alfa] (in Russian). Riga: AS Alfa RPAR. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ↑ "Каталог продукции" [Product catalog] (in Russian). Tashkent: OAO "Foton". Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- 1 2 3 "102ая и 116ая серии" [Series 102 and 116] (in Russian). Музей электронных раритетов. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- 1 2 Москатов, Евгений Анатольевич. "Справочник по полупроводниковым приборам" [Handbook of semiconductor devices] (PDF) (in Russian). Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Ниссельсон, Л.И. (1989). Цифровые и аналоговые интегральные микросхемы [Digital and analog integrated circuits] (in Russian). Радио и связь. ISBN 5256002597.
- ↑ "Система условных обозначений отечественных интегральных микросхем" [Nomenclature of domestic integrated circuits] (in Russian). СМИ Сайт-ПАЯЛЬНИК 'cxem.net'. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ "Система условных обозначений отечественных интегральных микросхем" [Nomenclature of domestic integrated circuits] (in Russian). Retrieved 7 May 2016.
- ↑ "ГОСТ РВ 5901-005—2010" [GOST RV 5901-005—2010] (in Russian). Moscow: Russian State Library. 14 June 2012. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ↑ "Обозначения первых микросхем" [Designations of the first integrated circuits] (in Russian). Музей электронных раритетов. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ↑ "О новых обозначениях". Радио (in Russian). March 1981. p. 61. Retrieved 3 June 2016.
- ↑ "156ая серия" [156 series] (in Russian). Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- 1 2 Козак, Виктор Романович (24 May 2014). "Номенклатура и аналоги отечественных микросхем" [Nomenclature and equivalents of domestic integrated circuits] (in Russian). Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ "Активные элементы" [Active components] (in Russian). Музей электронных раритетов. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ Vishnevsky, Igor (20 March 2008). "Logos of soviet manufacturers". Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ "Продукция ОАО «НИИМЭ и Микрон»" [Products of OAO "NIIME and Mikron"] (in Russian). Radiant. Retrieved 28 November 2016.