Space (mathematics)
In mathematics, a space is a set (sometimes called a universe) with some added structure.
Mathematical spaces often form a hierarchy, i.e., one space may inherit all the characteristics of a parent space. For instance, all inner product spaces are also normed vector spaces, because the inner product induces a norm on the inner product space such that:
where the norm is indicated by enclosing in double vertical lines, and the inner product is indicated enclosing in by angle brackets.
Modern mathematics treats "space" quite differently compared to classical mathematics.
History
Before the golden age of geometry
In the ancient mathematics, "space" was a geometric abstraction of the three-dimensional space observed in the everyday life. The axiomatic method had been the main research tool since Euclid (about 300 BC). The method of coordinates (analytic geometry) was adopted by René Descartes in 1637.[1] At that time, geometric theorems were treated as an absolute objective truth knowable through intuition and reason, similar to objects of natural science;[2]:11 and axioms were treated as obvious implications of definitions.[2]:15
Two equivalence relations between geometric figures were used: congruence and similarity. Translations, rotations and reflections transform a figure into congruent figures; homotheties — into similar figures. For example, all circles are mutually similar, but ellipses are not similar to circles. A third equivalence relation, introduced by Gaspard Monge in 1795, occurs in projective geometry: not only ellipses, but also parabolas and hyperbolas, turn into circles under appropriate projective transformations; they all are projectively equivalent figures.
The relation between the two geometries, Euclidean and projective,[2]:133 shows that mathematical objects are not given to us with their structure.[2]:21 Rather, each mathematical theory describes its objects by some of their properties, precisely those that are put as axioms at the foundations of the theory.[2]:20
Distances and angles are never mentioned in the axioms of the projective geometry and therefore cannot appear in its theorems. The question "what is the sum of the three angles of a triangle" is meaningful in the Euclidean geometry but meaningless in the projective geometry.
A different situation appeared in the 19th century: in some geometries the sum of the three angles of a triangle is well-defined but different from the classical value (180 degrees). The non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry, introduced by Nikolai Lobachevsky in 1829 and János Bolyai in 1832 (and Carl Gauss in 1816, unpublished)[2]:133 stated that the sum depends on the triangle and is always less than 180 degrees. Eugenio Beltrami in 1868 and Felix Klein in 1871 obtained Euclidean "models" of the non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry, and thereby completely justified this theory.[2]:24[3]
This discovery forced the abandonment of the pretensions to the absolute truth of Euclidean geometry. It showed that axioms are not "obvious", nor "implications of definitions". Rather, they are hypotheses. To what extent do they correspond to an experimental reality? This important physical problem no longer has anything to do with mathematics. Even if a "geometry" does not correspond to an experimental reality, its theorems remain no less "mathematical truths".[2]:15
A Euclidean model of a non-Euclidean geometry is a clever choice of some objects existing in Euclidean space and some relations between these objects that satisfy all axioms (therefore, all theorems) of the non-Euclidean geometry. These Euclidean objects and relations "play" the non-Euclidean geometry like contemporary actors playing an ancient performance. Relations between the actors only mimic relations between the characters in the play. Likewise, the chosen relations between the chosen objects of the Euclidean model only mimic the non-Euclidean relations. It shows that relations between objects are essential in mathematics, while the nature of the objects is not.
The golden age and afterwards: dramatic change
According to Nicolas Bourbaki,[2]:131 the period between 1795 (Geometrie descriptive of Monge) and 1872 (the "Erlangen programme" of Klein) can be called the golden age of geometry. Analytic geometry made a great progress and succeeded in replacing theorems of classical geometry with computations via invariants of transformation groups.[2]:134,5 Since that time new theorems of classical geometry are of more interest to amateurs rather than to professional mathematicians.[2]:136
However, it does not mean that the heritage of the classical geometry was lost. According to Bourbaki,[2]:138 "passed over in its role as an autonomous and living science, classical geometry is thus transfigured into a universal language of contemporary mathematics".
According to the famous inaugural lecture given by Bernhard Riemann in 1854, every mathematical object parametrized by real numbers may be treated as a point of the -dimensional space of all such objects.[2]:140 Contemporary mathematicians follow this idea routinely and find it extremely suggestive to use the terminology of classical geometry nearly everywhere.[2]:138
In order to fully appreciate the generality of this approach one should note that mathematics is "a pure theory of forms, which has as its purpose, not the combination of quantities, or of their images, the numbers, but objects of thought" (Hermann Hankel, 1867).[2]:21 This is a controversial characterization of the purpose of mathematics, which is not necessarily committed to the existence of "objects of thought."
Function (mathematics)s are important mathematical objects. Usually they form infinite-dimensional function spaces, as noted already by Riemann[2]:141 and elaborated in the 20th century by functional analysis.
An object parametrized by n complex numbers may be treated as a point of a complex n-dimensional space. However, the same object is also parametrized by 2 n real numbers (if c is a complex number, then c = a + b i, where a and b are real), thus, a point of a real 2n-dimensional space. The complex dimension differs from the real dimension. This is only the tip of the iceberg. The "algebraic" concept of dimension applies to vector spaces. For topological spaces there are several dimension concepts including inductive dimension and Hausdorff dimension, which can be non-integer (especially for fractals). Some kinds of spaces (for instance, measure spaces) admit no concept of dimension at all.
The original space investigated by Euclid is now called three-dimensional Euclidean space. Its axiomatization, started by Euclid 23 centuries ago, was reformed with Hilbert's axioms, Tarski's axioms and Birkhoff's axioms. These axiom systems describe the space via primitive notions (such as "point", "between", "congruent") constrained by a number of axioms. Such a definition "from scratch" is now not often used, since it does not reveal the relation of this space to other spaces. The modern approach defines the three-dimensional Euclidean space more algebraically, via vector spaces and quadratic forms, namely, as an affine space whose difference space is a three-dimensional inner product space.
Also a three-dimensional projective space is now defined non-classically, as the space of all one-dimensional subspaces (that is, straight lines through the origin) of a four-dimensional vector space.
A space consists now of selected mathematical objects (for instance, functions on another space, or subspaces of another space, or just elements of a set) treated as points, and selected relationships between these points. It shows that spaces are just mathematical structures of convenience. One may expect that the structures called "spaces" are more geometric than others, but this is not always true. For example, a differentiable manifold (called also smooth manifold) is much more geometric than a measurable space, but no one calls it "differentiable space" (nor "smooth space").
Taxonomy of spaces
Three taxonomic ranks
Spaces are classified on three levels. Given that each mathematical theory describes its objects by some of their properties, the first question to ask is: which properties?
For example, the upper-level classification distinguishes between Euclidean and projective spaces, since the distance between two points is defined in Euclidean spaces but undefined in projective spaces. These are spaces of different types.
Another example. The question "what is the sum of the three angles of a triangle" makes sense in a Euclidean space but not in a projective space; these are spaces of different types. In a non-Euclidean space the question makes sense but is answered differently, which is not an upper-level distinction.
Also, the distinction between a Euclidean plane and a Euclidean 3-dimensional space is not an upper-level distinction; the question "what is the dimension" makes sense in both cases.
In terms of Bourbaki[4] the upper-level classification is related to "typical characterization" (or "typification"). However, it is not the same (since two equivalent structures may differ in typification).
On the second level of classification one takes into account answers to especially important questions (among the questions that make sense according to the first level). For example, this level distinguishes between Euclidean and non-Euclidean spaces; between finite-dimensional and infinite-dimensional spaces; between compact and non-compact spaces, etc.
In terms of Bourbaki[4] the second-level classification is the classification by "species". Unlike biological taxonomy, a space may belong to several species.
On the third level of classification, roughly speaking, one takes into account answers to all possible questions (that make sense according to the first level). For example, this level distinguishes between spaces of different dimension, but does not distinguish between a plane of a three-dimensional Euclidean space, treated as a two-dimensional Euclidean space, and the set of all pairs of real numbers, also treated as a two-dimensional Euclidean space. Likewise it does not distinguish between different Euclidean models of the same non-Euclidean space.
More formally, the third level classifies spaces up to isomorphism. An isomorphism between two spaces is defined as a one-to-one correspondence between the points of the first space and the points of the second space, that preserves all relations between the points, stipulated by the given "typification". Mutually isomorphic spaces are thought of as copies of a single space. If one of them belongs to a given species then they all do.
The notion of isomorphism sheds light on the upper-level classification. Given a one-to-one correspondence between two spaces of the same type, one may ask whether it is an isomorphism or not. This question makes no sense for two spaces of different type.
Isomorphisms to itself are called automorphisms. Automorphisms of a Euclidean space are motions and reflections. Euclidean space is homogeneous in the sense that every point can be transformed into every other point by some automorphism.
Two relations between spaces, and a property of spaces
Topological notions (continuity, convergence, open sets, closed sets etc.) are defined naturally in every Euclidean space. In other words, every Euclidean space is also a topological space. Every isomorphism between two Euclidean spaces is also an isomorphism between the corresponding topological spaces (called "homeomorphism"), but the converse is wrong: a homeomorphism may distort distances. In terms of Bourbaki,[4] "topological space" is an underlying structure of the "Euclidean space" structure. Similar ideas occur in category theory: the category of Euclidean spaces is a concrete category over the category of topological spaces; the forgetful (or "stripping") functor maps the former category to the latter category.
A three-dimensional Euclidean space is a special case of a Euclidean space. In terms of Bourbaki,[4] the species of three-dimensional Euclidean space is richer than the species of Euclidean space. Likewise, the species of compact topological space is richer than the species of topological space.
Euclidean axioms leave no freedom, they determine uniquely all geometric properties of the space. More exactly: all three-dimensional Euclidean spaces are mutually isomorphic. In this sense we have "the" three-dimensional Euclidean space. In terms of Bourbaki, the corresponding theory is univalent. In contrast, topological spaces are generally non-isomorphic, their theory is multivalent. A similar idea occurs in mathematical logic: a theory is called categorical if all its models of the same cardinality are mutually isomorphic. According to Bourbaki,[5] the study of multivalent theories is the most striking feature which distinguishes modern mathematics from classical mathematics.
Types of spaces
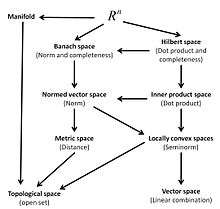
Linear and topological spaces
Two basic spaces are linear spaces (also called vector spaces) and topological spaces.
Linear spaces are of algebraic nature; there are real linear spaces (over the field of real numbers), complex linear spaces (over the field of complex numbers), and more generally, linear spaces over any field. Every complex linear space is also a real linear space (the latter underlies the former), since each real number is also a complex number.[details 1] Linear operations, given in a linear space by definition, lead to such notions as straight lines (and planes, and other linear subspaces); parallel lines; ellipses (and ellipsoids). However, orthogonal (perpendicular) lines cannot be defined, and circles cannot be singled out among ellipses. The dimension of a linear space is defined as the maximal number of linearly independent vectors or, equivalently, as the minimal number of vectors that span the space; it may be finite or infinite. Two linear spaces over the same field are isomorphic if and only if they are of the same dimension.
Topological spaces are of analytic nature. Open sets, given in a topological space by definition, lead to such notions as continuous functions, paths, maps; convergent sequences, limits; interior, boundary, exterior. However, uniform continuity, bounded sets, Cauchy sequences, differentiable functions (paths, maps) remain undefined. Isomorphisms between topological spaces are traditionally called homeomorphisms; these are one-to-one correspondences continuous in both directions. The open interval is homeomorphic to the whole real line but not homeomorphic to the closed interval , nor to a circle. The surface of a cube is homeomorphic to a sphere (the surface of a ball) but not homeomorphic to a torus. Euclidean spaces of different dimensions are not homeomorphic, which seems evident, but is not easy to prove. Dimension of a topological space is difficult to define; "inductive dimension" and "Lebesgue covering dimension" are used. Every subset of a topological space is itself a topological space (in contrast, only linear subsets of a linear space are linear spaces). Arbitrary topological spaces, investigated by general topology (called also point-set topology) are too diverse for a complete classification (up to homeomorphism). They are inhomogeneous (in general). Compact topological spaces are an important class of topological spaces ("species" of this "type"). Every continuous function is bounded on such space. The closed interval and the extended real line are compact; the open interval and the line are not. Geometric topology investigates manifolds (another "species" of this "type"); these are topological spaces locally homeomorphic to Euclidean spaces. Low-dimensional manifolds are completely classified (up to homeomorphism).
The two structures discussed above (linear and topological) are both underlying structures of the "linear topological space" structure. That is, a linear topological space is both a linear (real or complex) space and a (homogeneous, in fact) topological space. However, an arbitrary combination of these two structures is generally not a linear topological space; the two structures must conform, namely, the linear operations must be continuous.
Every finite-dimensional (real or complex) linear space is a linear topological space in the sense that it carries one and only one topology that makes it a linear topological space. The two structures, "finite-dimensional (real or complex) linear space" and "finite-dimensional linear topological space", are thus equivalent, that is, mutually underlying. Accordingly, every invertible linear transformation of a finite-dimensional linear topological space is a homeomorphism. In the infinite dimension, however, different topologies conform to a given linear structure, and invertible linear transformations are generally not homeomorphisms.
Affine and projective spaces
It is convenient to introduce affine and projective spaces by means of linear spaces, as follows. An -dimensional linear subspace of an -dimensional linear space, being itself an -dimensional linear space, is not homogeneous; it contains a special point, the origin. Shifting it by a vector external to it, one obtains an -dimensional affine space. It is homogeneous. In the words of John Baez, "an affine space is a vector space that's forgotten its origin". A straight line in the affine space is, by definition, its intersection with a two-dimensional linear subspace (plane through the origin) of the -dimensional linear space. Every linear space is also an affine space.
Every point of the affine space is its intersection with a one-dimensional linear subspace (line through the origin) of the -dimensional linear space. However, some one-dimensional subspaces are parallel to the affine space; in some sense, they intersect it at infinity. The set of all one-dimensional linear subspaces of an -dimensional linear space is, by definition, an -dimensional projective space. Choosing an -dimensional affine space as before one observes that the affine space is embedded as a proper subset into the projective space. However, the projective space itself is homogeneous. A straight line in the projective space, by definition, corresponds to a two-dimensional linear subspace of the -dimensional linear space.
Defined this way, affine and projective spaces are of algebraic nature; they can be real, complex, and more generally, over any field.
Every real (or complex) affine or projective space is also a topological space. An affine space is a non-compact manifold; a projective space is a compact manifold.
Metric and uniform spaces
Distances between points are defined in a metric space. Every metric space is also a topological space. Bounded sets and Cauchy sequences are defined in a metric space (but not just in a topological space). Isomorphisms between metric spaces are called isometries. A metric space is called complete if all Cauchy sequences converge. Every incomplete space is isometrically embedded into its completion. Every compact metric space is complete; the real line is non-compact but complete; the open interval is incomplete.
A topological space is called metrizable, if it underlies a metric space. All manifolds are metrizable.
Every Euclidean space is also a complete metric space. Moreover, all geometric notions immanent to a Euclidean space can be characterized in terms of its metric. For example, the straight segment connecting two given points and consists of all points such that the distance between and is equal to the sum of two distances, between and and between and .
Uniform spaces do not introduce distances, but still allow one to use uniform continuity, Cauchy sequences, completeness and completion. Every uniform space is also a topological space. Every linear topological space (metrizable or not) is also a uniform space. More generally, every commutative topological group is also a uniform space. A non-commutative topological group, however, carries two uniform structures, one left-invariant, the other right-invariant. Linear topological spaces are complete in finite dimension but generally incomplete in infinite dimension.
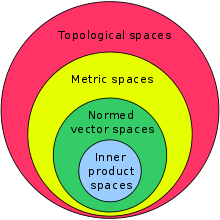
Normed, Banach, inner product, and Hilbert spaces
Vectors in a Euclidean space are a linear space, but each vector has also a length, in other words, norm, . A (real or complex) linear space endowed with a norm is a normed space. Every normed space is both a linear topological space and a metric space. A Banach space is a complete normed space. Many spaces of sequences or functions are infinite-dimensional Banach spaces.
The set of all vectors of norm less than one is called the unit ball of a normed space. It is a convex, centrally symmetric set, generally not an ellipsoid; for example, it may be a polygon (on the plane). The parallelogram law (called also parallelogram identity) generally fails in normed spaces, but holds for vectors in Euclidean spaces, which follows from the fact that the squared Euclidean norm of a vector is its inner product to itself.
An inner product space is a (real or complex) linear space endowed with a bilinear (or sesquilinear) form satisfying some conditions and called inner product. Every inner product space is also a normed space. A normed space underlies an inner product space if and only if it satisfies the parallelogram law, or equivalently, if its unit ball is an ellipsoid. Angles between vectors are defined in inner product spaces. A Hilbert space is defined as a complete inner product space. (Some authors insist that it must be complex, others admit also real Hilbert spaces.) Many spaces of sequences or functions are infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Hilbert spaces are very important for quantum theory.[6]
All -dimensional real inner product spaces are mutually isomorphic. One may say that the -dimensional Euclidean space is the -dimensional real inner product space that's forgotten its origin.
Smooth and Riemannian manifolds (spaces)
Smooth manifolds are not called "spaces", but could be. Smooth (differentiable) functions, paths, maps, given in a smooth manifold by definition, lead to tangent spaces. Every smooth manifold is a (topological) manifold. Smooth surfaces in a finite-dimensional linear space (like the surface of an ellipsoid, not a polytope) are smooth manifolds. Every smooth manifold can be embedded into a finite-dimensional linear space. A smooth path in a smooth manifold has (at every point) the tangent vector, belonging to the tangent space (attached to this point). Tangent spaces to an -dimensional smooth manifold are -dimensional linear spaces. A smooth function has (at every point) the differential, – a linear functional on the tangent space. Real (or complex) finite-dimensional linear, affine and projective spaces are also smooth manifolds.
A Riemannian manifold, or Riemann space, is a smooth manifold whose tangent spaces are endowed with inner product (satisfying some conditions). Euclidean spaces are also Riemann spaces. Smooth surfaces in Euclidean spaces are Riemann spaces. A hyperbolic non-Euclidean space is also a Riemann space. A curve in a Riemann space has the length. A Riemann space is both a smooth manifold and a metric space; the length of the shortest curve is the distance. The angle between two curves intersecting at a point is the angle between their tangent lines.
Waiving positivity of inner product on tangent spaces one gets pseudo-Riemann (especially, Lorentzian) spaces very important for general relativity.
Measurable, measure, and probability spaces
Waiving distances and angles while retaining volumes (of geometric bodies) one moves toward measure theory. Besides the volume, a measure generalizes area, length, mass (or charge) distribution, and also probability distribution, according to Andrey Kolmogorov's approach to probability theory.
A "geometric body" of classical mathematics is much more regular than just a set of points. The boundary of the body is of zero volume. Thus, the volume of the body is the volume of its interior, and the interior can be exhausted by an infinite sequence of cubes. In contrast, the boundary of an arbitrary set of points can be of non-zero volume (an example: the set of all rational points inside a given cube). Measure theory succeeded in extending the notion of volume (or another measure) to a vast class of sets, so-called measurable sets. Indeed, non-measurable sets almost never occur in applications, but anyway, the theory must restrict itself to measurable sets (and functions).
Measurable sets, given in a measurable space by definition, lead to measurable functions and maps. In order to turn a topological space into a measurable space one endows it with a σ-algebra. The σ-algebra of Borel sets is most popular, but not the only choice (Baire sets, universally measurable sets etc. are used sometimes). Alternatively, a σ-algebra can be generated by a given collection of sets (or functions) irrespective of any topology. Quite often, different topologies lead to the same σ-algebra (for example, the norm topology and the weak topology on a separable Hilbert space). Every subset of a measurable space is itself a measurable space.
Standard measurable spaces (called also standard Borel spaces) are especially useful. Every Borel set (in particular, every closed set and every open set) in a Euclidean space (and more generally, in a complete separable metric space) is a standard measurable space. All uncountable standard measurable spaces are mutually isomorphic.
A measure space is a measurable space endowed with a measure. A Euclidean space with Lebesgue measure is a measure space. Integration theory defines integrability and integrals of measurable functions on a measure space.
Sets of measure 0, called null sets, are negligible. Accordingly, a isomorphism is defined as isomorphism between subsets of full measure (that is, with negligible complement).
A probability space is a measure space such that the measure of the whole space is equal to 1. The product of any family (finite or not) of probability spaces is a probability space. In contrast, for measure spaces in general, only the product of finitely many spaces is defined. Accordingly, there are many infinite-dimensional probability measures (especially, Gaussian measures), but no infinite-dimensional Lebesgue measure.
Standard probability spaces are especially useful. Every probability measure on a standard measurable space leads to a standard probability space. The product of a sequence (finite or not) of standard probability spaces is a standard probability space. All non-atomic standard probability spaces are mutually isomorphic one of them is the interval with Lebesgue measure.
These spaces are less geometric. In particular, the idea of dimension, applicable (in one form or another) to all other spaces, does not apply to measurable, measure and probability spaces.
A topological space becomes also a measurable space when endowed with the Borel σ-algebra.[details 2] However, the topology is not uniquely determined by its Borel σ-algebra; and not every σ-algebra is the Borel σ-algebra of some topology.[details 3]
See also
- Mathematical structure
- Transport of structure
- Set (mathematics)
- Affine space
- Algebraic space
- Baire space
- Banach space
- Cantor space
- Cauchy space
- Conformal space
- Complex analytic space
- Hardy space
- Hausdorff space
- Inner product space
- Kolmogorov space
- Lp space
- Minkowski space
- Normed vector space
- Polish space
- Quadratic space
- Quotient space
- Sobolev space
- Symplectic space
Notes
- ↑ For example, the complex plane treated as a one-dimensional complex linear space may be downgraded to a two-dimensional real linear space. In contrast, the real line can be treated as a one-dimensional real linear space but not a complex linear space. See also Examples of vector spaces#Field extensions.
- ↑ The Borel σ-algebra is the most notable choice; some other choices: almost open sets; Baire sets; universally measurable sets.
- ↑ The space (equipped with its tensor product σ-algebra) has a measurable structure which is not generated by a topology. A slick proof can be found in this answer on MathOverflow.
Footnotes
- ↑ Itô 1993, page 987
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Bourbaki, Nicolas (1994), Elements of the history of mathematics, Masson (original), Springer (translation)
- ↑ Jeremy Gray (1989) Ideas of Space: Euclidean, Non-Euclidean and Relativistic, Part 2, Clarendon Press
- 1 2 3 4 Bourbaki 1968, Chapter IV
- ↑ Bourbaki 1968, page 385
- ↑ Cornelius Lanczos (1970) Space through the Ages: The Evolution of Geometrical Ideas from Pythagoras to Hilbert and Einstein, page 269, Academic Press
References
- Itô, Kiyosi, ed. (1993), Encyclopedic dictionary of mathematics (second ed.), Mathematical society of Japan (original), MIT press (translation).
- Gowers, Timothy; Barrow-Green, June; Leader, Imre, eds. (2008), The Princeton Companion to Mathematics, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-11880-2.
- Bourbaki, Nicolas, Elements of mathematics, Hermann (original), Addison-Wesley (translation).
- Bourbaki, Nicolas (1968), Elements of mathematics: Theory of sets, Hermann (original), Addison-Wesley (translation).
External links
- Matilde Marcolli (2009) The notion of space in mathematics, from Caltech.
This article incorporates material from the Citizendium article "Space (mathematics)", which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License but not under the GFDL.