Sprut anti-tank gun
| 2A45 Sprut-A | |
|---|---|
|
Sprut anti-tank gun | |
| Type | Anti-tank gun |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union/Russia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1989–present |
| Used by | See operators |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Petrov Design Bureau |
| Designed | late 1980s |
| Manufacturer | Artillery Plant Number 9 |
| Produced | 1989–present |
| Variants | See models |
| Specifications | |
| Weight |
Transport: 6,500 kg (14,300 lb) Self-propelled: 6,800 kg (15,000 lb) Firing: 6,575 kg (14,495 lb) |
| Length |
Transport: 7.12 m (23 ft 4 in) Self-propelled: 6.79 m (22 ft 3 in) |
| Barrel length |
Bore: 51 calibres Bore axis: 0.925 m (3 ft 0.4 in) |
| Width | 2.66 m (8 ft 9 in) |
| Height |
Transport: 2.09 m (6 ft 10 in) Self-propelled: 2.35 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | 7 |
|
| |
| Caliber | 125 mm (4.9 in) |
| Recoil | hydropneumatic |
| Carriage | tripod |
| Elevation | -6° to 25° |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 6-8 rpm |
| Effective firing range |
2,000 m (2,200 yd) (APFSDS) 5,000 m (5,500 yd) (9M119 Svir ATGM) 12,200 m (13,300 yd) (HE) |
|
| |
Operational range | 50 km (55,000 yd) (in APU mode) |
| Speed | 14 km/h (8.7 mph) (in APU mode) |
2A45 and 2A45M are the respective GRAU designations of the Sprut-A and Sprut-B (Russian for Octopus or Kraken[1]) Soviet smoothbore 125 mm anti-tank gun.
Development
The 2A45M was created in the late 1980s by the Petrov Design Bureau at Artillery Plant Number 9 (OKB-9), which was also responsible for the 122 mm howitzer 2A18 (D-30).
Description (Sprut-B)
A feature of the Sprut-B is its integrated engine, which can propel the gun on relatively flat surfaces (up to 15 degrees slope) and at 14 km/h on roads. This gives the gun a measure of mobility on the battlefield. It takes two minutes to go from firing position to travelling position and 90 seconds to go from travelling position to firing position. Such guns are known in Russian as "self-moving" (самодвижущиеся) as opposed to self-propelled (самоходные), and outside of battle it is towed by an MT-LB.
The gun features a crew of seven. An OP4M-48A direct fire sight is used the day, while a 1PN53-1 night vision sight is used at night. For indirect fire, 2Ts33 iron sights are used, along with a PG-1m panoramic sight. The gun can reliably engage targets two metres high at a distance of 2000 metres.[2]
The barrel features a thermal sleeve to prevent temperature changes affecting the accuracy. The gun uses the same semi-fixed ammunition as the T-64, T-72, T-80 and T-90 tanks.
With the addition of the 9S53 laser fire-control system, the gun can fire laser guided projectiles such as the 9M119 Svir or 9K120 Refleks.
Ammunition
The gun uses the same ammunition as the D-81 series of guns used on the T-64, T-72, T-80 and T-90 tanks.
Models
- Sprut-A 2A45 Pure towed gun.
- Sprut-B 2A45M Self-propelled towed gun.
- Sprut-SD 2S25 A self-propelled gun mounted on the BMD-3 chassis with a turret mounting the stabilised 2A75 125 mm smoothbore gun [3]
Operators
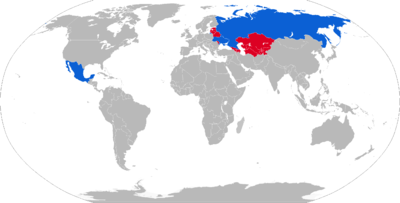
Current operators
Former operators
-
 Soviet Union passed construction license to successor states
Soviet Union passed construction license to successor states -
 Belarus
Belarus
See also
- 125 mm smoothbore ammunition
- 2A46 - Soviet/Russian tank-mounted 125mm cannon
- List of Soviet tanks
References
- Hull, A.W., Markov, D.R., Zaloga, S.J. (1999). Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices 1945 to Present. Darlington Productions. ISBN 1-892848-01-5.
- Military Parade
- Enemy Forces
- 2A45M on manufacturer site
- Jane's Armour and Artillery 2002-2003
